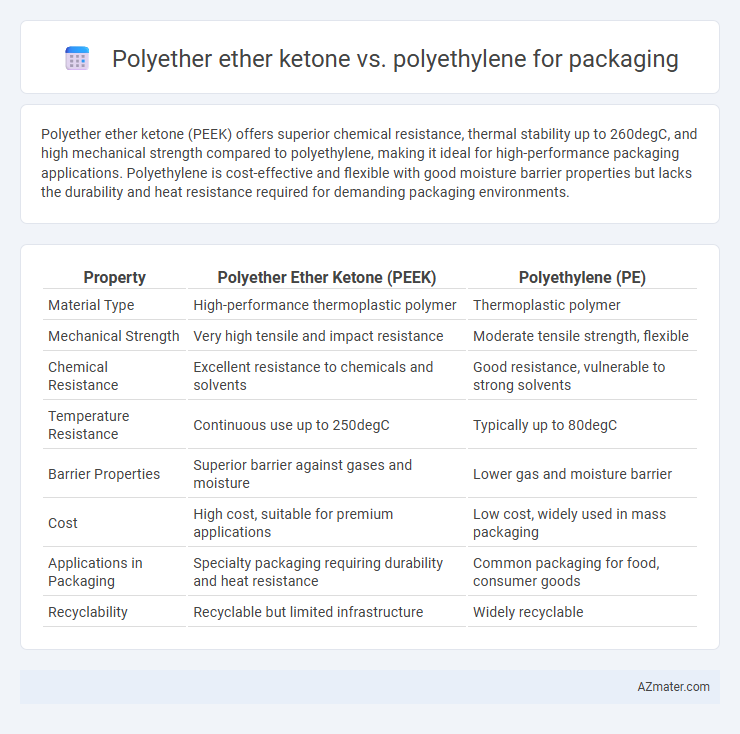
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) offers superior chemical resistance, thermal stability up to 260degC, and high mechanical strength compared to polyethylene, making it ideal for high-performance packaging applications. Polyethylene is cost-effective and flexible with good moisture barrier properties but lacks the durability and heat resistance required for demanding packaging environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK) | Polyethylene (PE) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | High-performance thermoplastic polymer | Thermoplastic polymer |
| Mechanical Strength | Very high tensile and impact resistance | Moderate tensile strength, flexible |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to chemicals and solvents | Good resistance, vulnerable to strong solvents |
| Temperature Resistance | Continuous use up to 250degC | Typically up to 80degC |
| Barrier Properties | Superior barrier against gases and moisture | Lower gas and moisture barrier |
| Cost | High cost, suitable for premium applications | Low cost, widely used in mass packaging |
| Applications in Packaging | Specialty packaging requiring durability and heat resistance | Common packaging for food, consumer goods |
| Recyclability | Recyclable but limited infrastructure | Widely recyclable |
Introduction to Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK) and Polyethylene
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its exceptional mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability, making it suitable for advanced packaging applications requiring durability and sterilization. Polyethylene (PE), one of the most widely used plastics, offers excellent flexibility, moisture barrier properties, and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for everyday packaging solutions like films and containers. While PEEK excels in harsh environments and high-temperature conditions, polyethylene dominates mass-market packaging due to its versatility and affordability.
Chemical Structure and Properties Comparison
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) features a rigid aromatic backbone with alternating ketone and ether linkages, providing exceptional thermal stability and chemical resistance superior to polyethylene's saturated hydrocarbon chain. PEEK's high glass transition temperature around 143degC and melting point near 343degC enable it to maintain mechanical integrity under harsh conditions, whereas polyethylene typically melts between 105-135degC and is prone to oxidation and permeation. These structural and thermal property differences position PEEK as a premium material for high-performance packaging requiring durability and barrier properties, while polyethylene remains favored for cost-effective, flexible packaging applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) exhibits superior mechanical strength and durability compared to polyethylene, making it ideal for high-performance packaging applications requiring resistance to wear, impact, and harsh environments. PEEK maintains dimensional stability and mechanical integrity under high temperatures and chemical exposure, whereas polyethylene often deforms or degrades under similar conditions. This enhanced durability and robust mechanical profile enable PEEK to provide long-term protection and reliability in demanding packaging scenarios.
Barrier Performance: Moisture and Gas Permeability
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) offers superior barrier performance compared to polyethylene, exhibiting significantly lower moisture and gas permeability rates essential for high-performance packaging applications. PEEK's high crystallinity and dense molecular structure reduce oxygen and water vapor transmission, enhancing product shelf life and protection against environmental contaminants. In contrast, polyethylene, while cost-effective, has higher permeability, making it less suitable for packaging sensitive goods requiring stringent barrier properties.
Temperature Resistance and Stability
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) exhibits superior temperature resistance, maintaining mechanical stability and chemical resistance up to 250degC, making it ideal for high-performance packaging applications. In contrast, polyethylene (PE) typically withstands temperatures only up to 80-100degC before deformation and degradation occur, limiting its use in heat-sensitive packaging environments. The enhanced thermal stability and rigidity of PEEK provide prolonged durability and resistance to thermal cycling compared to the more flexible but less heat-resistant polyethylene.
Safety and Food Compatibility
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) exhibits superior chemical resistance and thermal stability compared to polyethylene (PE), making it highly suitable for food packaging applications requiring stringent safety standards. PEEK's inert nature prevents leaching of harmful substances, ensuring food compatibility and reducing contamination risks, whereas polyethylene may release additives or degrade under high temperatures. Regulatory approvals for PEEK in food contact materials highlight its advantage for packaging demanding enhanced safety and durability.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) exhibits high thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it suitable for specialized packaging applications but presents challenges in recycling due to its complex molecular structure and energy-intensive processing requirements. Polyethylene (PE), widely used in packaging, offers excellent recyclability through established methods like mechanical recycling and chemical depolymerization, contributing to lower environmental impact in large-scale waste management. Despite polyethylene's lower mechanical performance, its widespread recyclability and lower carbon footprint render it more environmentally favorable compared to PEEK in typical packaging scenarios.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) offers superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance compared to polyethylene, but its high raw material and processing costs significantly increase overall packaging expenses. Polyethylene remains the preferred choice for cost-sensitive packaging applications due to its low price, ease of processing, and widespread availability, despite lower durability and heat resistance. Economic considerations prioritize polyethylene for mass-market packaging, while PEEK is reserved for specialized, high-performance needs where higher costs are justified by enhanced functionality.
Common Applications in Packaging
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) is utilized in high-performance packaging applications requiring exceptional chemical resistance and thermal stability, such as medical device packaging and aerospace component protection. Polyethylene (PE) dominates everyday packaging solutions due to its flexibility, moisture barrier properties, and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for food wrappers, grocery bags, and shrink films. The contrast in applications stems from PEEK's superior durability for specialized uses versus PE's widespread adaptability in mass-market packaging.
Choosing the Right Material: PEEK vs Polyethylene for Packaging
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) offers superior mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability compared to polyethylene, making it ideal for high-performance packaging applications requiring durability and heat resistance. Polyethylene excels in cost-effectiveness, flexibility, and moisture barrier properties, which suits disposable or flexible packaging needs. Selecting between PEEK and polyethylene depends on balancing performance requirements against budget constraints and specific packaging environmental conditions.
Infographic: Polyether ether ketone vs Polyethylene for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com