Polycarbonate offers high impact resistance and heat stability but lacks nonstick properties, while polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) provides superior nonstick performance and chemical inertness, making PTFE the preferred material for nonstick pans. PTFE coatings reduce food adhesion and simplify cleaning, whereas polycarbonate is typically used for transparent cookware lids rather than cooking surfaces.
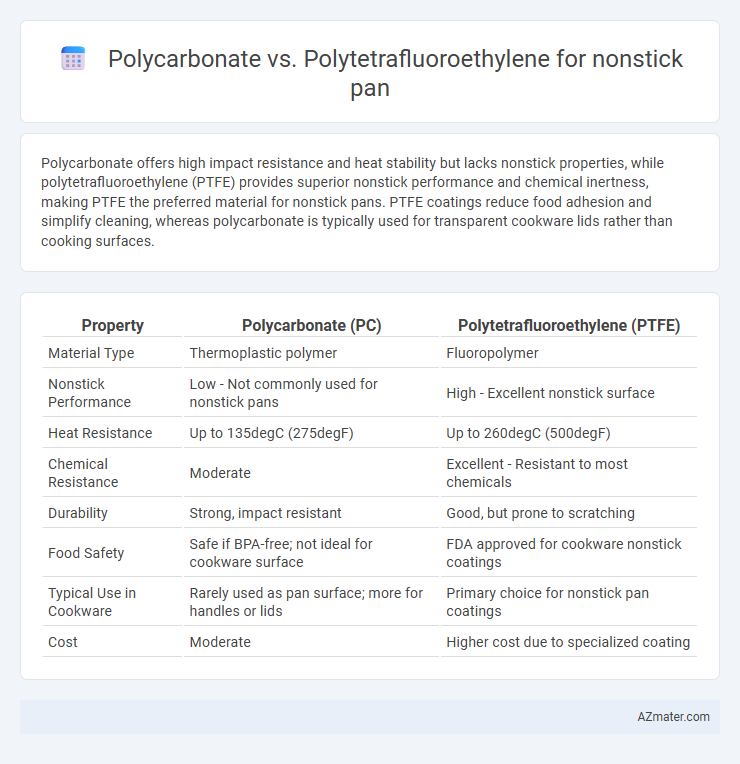
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polycarbonate (PC) | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Fluoropolymer |
| Nonstick Performance | Low - Not commonly used for nonstick pans | High - Excellent nonstick surface |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 135degC (275degF) | Up to 260degC (500degF) |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate | Excellent - Resistant to most chemicals |
| Durability | Strong, impact resistant | Good, but prone to scratching |
| Food Safety | Safe if BPA-free; not ideal for cookware surface | FDA approved for cookware nonstick coatings |
| Typical Use in Cookware | Rarely used as pan surface; more for handles or lids | Primary choice for nonstick pan coatings |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher cost due to specialized coating |
Introduction to Nonstick Pan Materials
Nonstick pans commonly utilize materials like polycarbonate and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) for their coatings due to their heat resistance and durability. Polycarbonate offers impact resistance and clarity but is less heat resistant compared to PTFE, which possesses superior chemical inertness and a high melting point around 327degC, making it ideal for nonstick cooking surfaces. PTFE's low coefficient of friction ensures food release and easy cleaning, whereas polycarbonate is typically used in the manufacturing components rather than the coating itself.
What is Polycarbonate?
Polycarbonate is a durable, transparent thermoplastic known for its impact resistance and heat tolerance, making it ideal for various kitchen applications but not typically used as a nonstick coating. Unlike Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), which provides superior nonstick properties and chemical resistance, polycarbonate serves more structural roles such as in pan lids or handles. Its ability to withstand heat up to around 135degC complements nonstick cookware design without directly affecting cooking surfaces.
What is Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)?
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a synthetic fluoropolymer known for its exceptional nonstick properties, chemical resistance, and high-temperature tolerance, making it a popular material for nonstick cookware coatings. Unlike polycarbonate, which is a durable thermoplastic used primarily for its impact resistance and clarity, PTFE's unique molecular structure provides a smooth, frictionless surface ideal for cooking without food sticking. The high melting point of PTFE, around 327degC (621degF), ensures it maintains nonstick performance even under frequent heating cycles in pans.
Heat Resistance: Polycarbonate vs PTFE
Polycarbonate offers moderate heat resistance, withstanding temperatures up to approximately 125degC (257degF), making it less suitable for high-heat cooking applications in nonstick pans. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly known as Teflon, demonstrates superior heat resistance, tolerating temperatures up to 260degC (500degF) before degradation, ensuring safer use during typical frying and sauteing processes. The significant difference in thermal stability makes PTFE the preferred nonstick coating material for high-temperature cooking compared to polycarbonate.
Nonstick Performance Comparison
Polycarbonate offers moderate nonstick performance with reasonable durability but can degrade under high heat, leading to reduced slickness over time. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly known as Teflon, provides superior nonstick capabilities due to its low friction surface and high heat tolerance up to 260degC (500degF), ensuring easier food release and cleaning. PTFE's chemical stability and resistance to food residue buildup make it the preferred coating for high-performance nonstick cookware compared to polycarbonate-based alternatives.
Durability and Longevity
Polycarbonate offers moderate durability in nonstick pans but tends to degrade faster under high heat compared to Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), which is renowned for its exceptional heat resistance and longevity. PTFE-coated pans resist scratches and chemical breakdown, maintaining their nonstick properties over extended use, making them more suitable for long-term cooking applications. The superior thermal stability of PTFE ensures it outperforms polycarbonate in durability, providing a longer-lasting nonstick surface ideal for frequent and high-temperature cooking.
Safety and Health Considerations
Polycarbonate is generally not used as a nonstick coating due to its potential to release bisphenol A (BPA) when heated, posing health risks, while polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly known as Teflon, offers superior nonstick properties and heat resistance but can emit toxic fumes if overheated above 260degC (500degF). PTFE-coated pans are safe for cooking at recommended temperatures, but caution is advised to avoid high heat to prevent polymer degradation and respiratory issues from fumes. Overall, PTFE remains the preferred and safer option for nonstick cookware with proper usage, whereas polycarbonate is unsuitable for direct cooking surfaces.
Ease of Cleaning and Maintenance
Polycarbonate nonstick pans are generally easier to clean due to their smooth, scratch-resistant surface that resists staining and allows food to release effortlessly, minimizing residue buildup. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) pans, known for their superior nonstick properties, require careful maintenance to prevent damage from metal utensils and abrasive cleaners, as scratches can compromise their coating and complicate cleaning. Both materials benefit from gentle hand washing with mild detergents, but polycarbonate surfaces typically demand less meticulous upkeep for long-term cleanliness.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polycarbonate and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability for nonstick pans. PTFE, commonly known as Teflon, has faced scrutiny due to its production process involving perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA), a persistent environmental pollutant linked to health risks, whereas polycarbonate does not use such harmful substances but raises concerns due to bisphenol A (BPA) residues. Polycarbonate offers better recyclability and lower greenhouse gas emissions during manufacturing compared to PTFE, making it a more sustainable option when considering nonstick cookware.
Which Material is Best for Your Nonstick Pan?
Polycarbonate offers high impact resistance and heat tolerance up to 135degC, making it durable but less suitable for direct cooking surfaces in nonstick pans. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), known as Teflon, excels with its superior nonstick properties and heat resistance up to 260degC, providing easier food release and effortless cleanup. For nonstick pans, PTFE is generally the best material due to its exceptional nonstick performance and higher temperature tolerance, ensuring both safety and cooking efficiency.
Infographic: Polycarbonate vs Polytetrafluoroethylene for Nonstick pan
 azmater.com
azmater.com