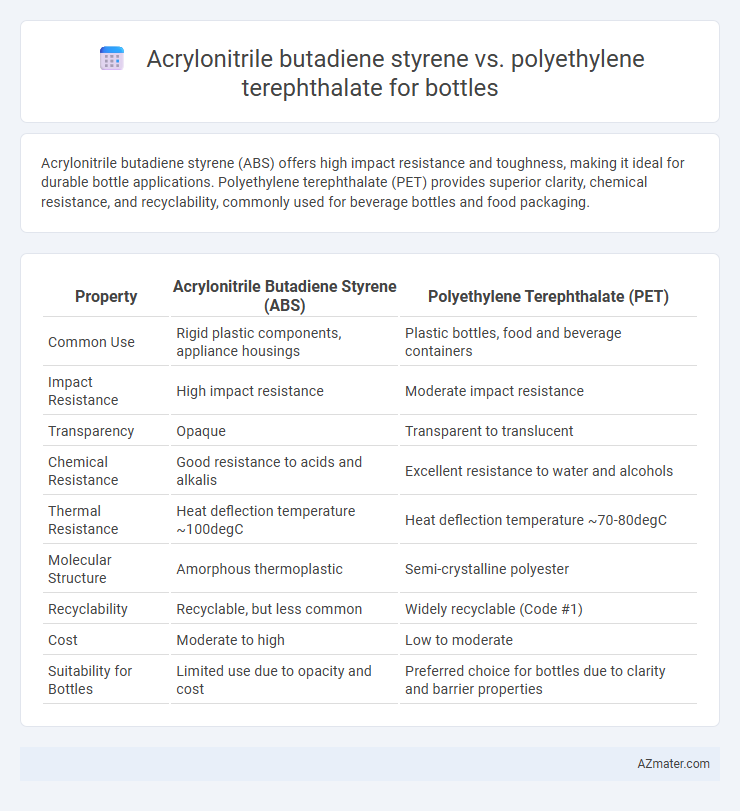
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers high impact resistance and toughness, making it ideal for durable bottle applications. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) provides superior clarity, chemical resistance, and recyclability, commonly used for beverage bottles and food packaging.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) |
|---|---|---|
| Common Use | Rigid plastic components, appliance housings | Plastic bottles, food and beverage containers |
| Impact Resistance | High impact resistance | Moderate impact resistance |
| Transparency | Opaque | Transparent to translucent |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to acids and alkalis | Excellent resistance to water and alcohols |
| Thermal Resistance | Heat deflection temperature ~100degC | Heat deflection temperature ~70-80degC |
| Molecular Structure | Amorphous thermoplastic | Semi-crystalline polyester |
| Recyclability | Recyclable, but less common | Widely recyclable (Code #1) |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
| Suitability for Bottles | Limited use due to opacity and cost | Preferred choice for bottles due to clarity and barrier properties |
Introduction: ABS vs PET for Bottles
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) and Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) are widely used thermoplastics in bottle manufacturing with distinct properties. ABS offers high impact resistance and toughness, making it suitable for durable, reusable bottles, while PET provides excellent clarity, chemical resistance, and is highly recyclable, ideal for single-use beverage containers. The choice between ABS and PET for bottles largely depends on the intended application, durability requirements, and environmental considerations such as recyclability and chemical stability.
Material Composition: ABS and PET Explained
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is a terpolymer composed of acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene, offering high impact resistance and rigidity, ideal for durable bottle applications requiring toughness. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is a polyester formed from terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol, known for its excellent clarity, chemical resistance, and recyclability, making it a preferred choice for beverage bottles. The material composition differences between ABS and PET influence factors like transparency, mechanical strength, and environmental sustainability in bottle manufacturing.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior mechanical strength with high impact resistance and rigidity, making it ideal for durable, impact-resistant bottles. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) provides excellent tensile strength and good chemical resistance, ensuring long-term durability and lightweight properties suitable for beverage containers. ABS excels in toughness under mechanical stress, while PET outperforms in maintaining structural integrity against environmental factors and repeated use.
Chemical Resistance: Performance in Various Environments
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) exhibits moderate chemical resistance, with strong performance against acids and alkalis but limited resistance to solvents and alcohols, making it suitable for bottles exposed to harsher chemical environments. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers excellent chemical resistance, particularly against water, alcohols, and most oils, ensuring durable performance for beverage and food bottles under various storage conditions. PET's superior barrier properties also protect contents from contamination, while ABS may degrade faster when exposed to certain chemicals or UV light.
Weight and Density Differences
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) exhibits a higher density, approximately 1.04 g/cm3, compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET), which typically ranges around 1.38 g/cm3, influencing the overall weight of bottles made from these materials. Bottles fabricated from PET tend to be heavier due to its greater density, impacting transportation costs and handling. The weight difference between ABS and PET bottles affects durability and application suitability, with PET favored for strength and clarity despite its increased mass.
Manufacturing Processes for ABS and PET Bottles
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) bottles are typically produced using injection molding, which allows for high precision and complex shapes but requires higher processing temperatures and specialized equipment. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) bottles are predominantly manufactured through injection stretch blow molding (ISBM), combining injection molding for preform creation and stretch blow molding for shaping the bottle, optimizing clarity and barrier properties. The PET manufacturing process offers faster cycle times and better scalability for mass production compared to the more flexible but slower ABS injection molding.
Safety and Food Contact Suitability
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is generally not recommended for direct food contact due to potential chemical leaching and limited FDA approval, whereas polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is widely recognized as safe and approved for food and beverage containers because of its excellent chemical resistance and low permeability. PET exhibits superior barrier properties against moisture and gases, enhancing product safety and shelf life, while ABS lacks these essential characteristics for effective food containment. For applications involving bottle manufacturing, PET is preferred for its proven safety profile in food contact use, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and minimizing health risks.
Sustainability and Recyclability
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers strong impact resistance and durability but is less sustainable due to its complex chemical structure, which complicates recycling processes and limits the number of recycling facilities. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is highly favored for bottle manufacturing because of its excellent recyclability, widespread collection systems, and ability to be recycled multiple times into food-grade products, significantly reducing environmental impact. PET's lower carbon footprint and better compatibility with circular economy initiatives make it the preferred sustainable option over ABS in bottle applications.
Cost Analysis: Production and Pricing
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) generally incurs higher production costs due to its complex polymerization process and raw material expenses compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET), which benefits from widespread availability and lower-cost manufacturing techniques. PET production leverages efficient continuous polymerization, leading to more economical scaling and cost-effective bottle manufacturing, making PET bottles typically less expensive on a per-unit basis. Market pricing reflects these factors, with PET bottles dominating cost-sensitive applications like beverage packaging, while ABS bottles are reserved for specialty uses demanding greater toughness and thermal resistance despite their higher price point.
Industry Use Cases: Choosing Between ABS and PET Bottles
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) bottles offer superior impact resistance and structural rigidity, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications like chemical storage and industrial packaging. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) bottles excel in clarity, lightweight design, and barrier properties, preferred for beverage, cosmetic, and food packaging industries. The choice between ABS and PET depends on required durability, transparency, and chemical resistance for specific industry use cases.
Infographic: Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene vs Polyethylene terephthalate for Bottle
 azmater.com
azmater.com