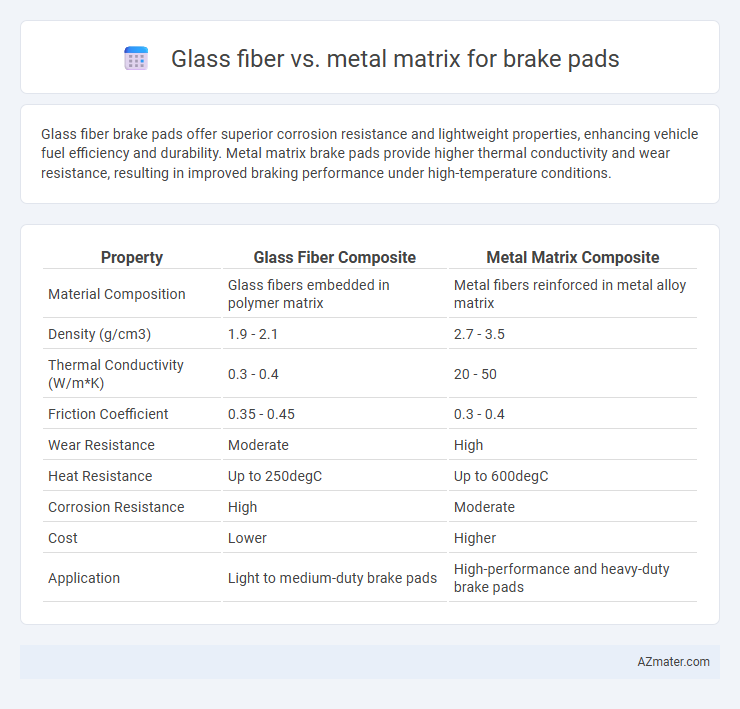
Glass fiber brake pads offer superior corrosion resistance and lightweight properties, enhancing vehicle fuel efficiency and durability. Metal matrix brake pads provide higher thermal conductivity and wear resistance, resulting in improved braking performance under high-temperature conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Glass Fiber Composite | Metal Matrix Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Glass fibers embedded in polymer matrix | Metal fibers reinforced in metal alloy matrix |
| Density (g/cm3) | 1.9 - 2.1 | 2.7 - 3.5 |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m*K) | 0.3 - 0.4 | 20 - 50 |
| Friction Coefficient | 0.35 - 0.45 | 0.3 - 0.4 |
| Wear Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 250degC | Up to 600degC |
| Corrosion Resistance | High | Moderate |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Application | Light to medium-duty brake pads | High-performance and heavy-duty brake pads |
Introduction to Brake Pad Materials
Brake pad materials critically influence vehicle braking performance, with glass fiber and metal matrix composites being prominent options. Glass fiber brake pads offer high thermal stability and lightweight properties, enhancing heat dissipation and reducing brake fade during intensive use. Metal matrix brake pads provide superior durability and wear resistance, ensuring consistent friction performance under extreme temperatures and mechanical stress.
Overview of Glass Fiber in Brake Pads
Glass fiber in brake pads offers exceptional thermal stability and high tensile strength, making it ideal for withstanding the intense heat and stress during braking. Its lightweight nature contributes to reduced overall vehicle weight, enhancing fuel efficiency and performance. The material's excellent wear resistance and noise-dampening properties improve brake longevity and reduce operational noise compared to traditional metal matrix composites.
Understanding Metal Matrix Composites
Metal matrix composites (MMCs) used in brake pads offer superior thermal stability, wear resistance, and mechanical strength compared to glass fiber composites. MMCs typically combine aluminum or magnesium matrices reinforced with ceramic particles, enhancing heat dissipation and reducing brake fade under high stress conditions. The integration of MMCs in brake pads ensures consistent performance, longer lifespan, and improved safety in automotive applications.
Performance Comparison: Glass Fiber vs Metal Matrix
Glass fiber brake pads offer superior noise reduction and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for everyday driving conditions. Metal matrix brake pads excel in thermal stability and wear resistance, providing enhanced performance under extreme braking and high-temperature environments. The choice between glass fiber and metal matrix depends on balancing durability, heat dissipation, and noise levels for specific vehicle requirements.
Durability and Longevity Analysis
Glass fiber brake pads demonstrate superior resistance to wear and thermal degradation, resulting in enhanced durability compared to conventional metal matrix counterparts. Metal matrix brake pads tend to experience faster deterioration under high-temperature conditions due to metal fatigue and oxidation, reducing their operational lifespan. The composite nature of glass fiber materials provides consistent friction performance and structural integrity, contributing to prolonged longevity and decreased maintenance costs in brake system applications.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Management
Glass fiber composites exhibit superior heat resistance and thermal insulation compared to metal matrix materials in brake pads, reducing heat transfer to brake components. Metal matrix brake pads offer excellent thermal conductivity, enabling efficient heat dissipation and preventing brake fade during high-temperature operations. Optimal thermal management in brake pads balances the insulating properties of glass fiber with the heat conduction capabilities of metal matrices to enhance braking performance and durability.
Cost Efficiency and Economic Impact
Glass fiber brake pads offer significant cost efficiency due to lower raw material and manufacturing expenses compared to metal matrix alternatives, making them more economical for mass production. Metal matrix brake pads, while offering superior thermal conductivity and durability, incur higher initial costs and complex processing, which can increase overall expenditure in automotive applications. The economic impact of choosing glass fiber materials is notable in reducing vehicle maintenance costs and promoting affordability, whereas metal matrix pads often justify their cost through enhanced performance and longer service life.
Safety and Environmental Considerations
Glass fiber brake pads offer enhanced safety through superior heat resistance and reduced brake fade, ensuring consistent braking performance under extreme conditions. Metal matrix brake pads exhibit excellent strength and wear resistance but may generate higher levels of metal particulates, raising environmental concerns. Considering environmental impact, glass fiber composites generally produce lower emissions and are easier to recycle, making them a more sustainable choice for eco-conscious braking systems.
Applications and Industry Preferences
Glass fiber brake pads offer superior noise reduction and thermal stability, making them ideal for passenger vehicles and light-duty applications. Metal matrix brake pads provide enhanced wear resistance and high-temperature performance, preferred in heavy-duty trucks, racing cars, and industrial machinery. Automotive manufacturers favor glass fiber composites for cost-effective, low-noise braking solutions, while metal matrix composites dominate in performance-driven and industrial sectors demanding durability under extreme conditions.
Future Trends in Brake Pad Material Technology
Future trends in brake pad material technology emphasize the shift from traditional metal matrix composites to advanced glass fiber-reinforced polymers, driven by the need for lightweight, high-performance solutions that enhance fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. Innovations in glass fiber composites enable superior thermal stability and wear resistance, addressing the challenges of high-speed braking and electric vehicle applications. Research continues to optimize hybrid composites combining glass fibers with nano-additives to achieve optimal friction coefficients and durability, signaling a transformative approach in brake pad design.
Infographic: Glass fiber vs Metal matrix for Brake pad
 azmater.com
azmater.com