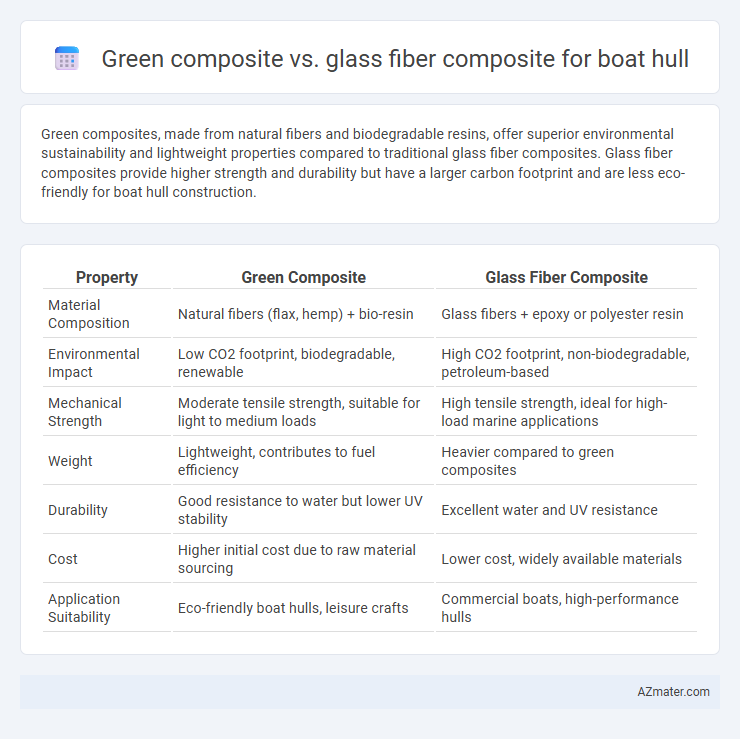
Green composites, made from natural fibers and biodegradable resins, offer superior environmental sustainability and lightweight properties compared to traditional glass fiber composites. Glass fiber composites provide higher strength and durability but have a larger carbon footprint and are less eco-friendly for boat hull construction.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Green Composite | Glass Fiber Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural fibers (flax, hemp) + bio-resin | Glass fibers + epoxy or polyester resin |
| Environmental Impact | Low CO2 footprint, biodegradable, renewable | High CO2 footprint, non-biodegradable, petroleum-based |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate tensile strength, suitable for light to medium loads | High tensile strength, ideal for high-load marine applications |
| Weight | Lightweight, contributes to fuel efficiency | Heavier compared to green composites |
| Durability | Good resistance to water but lower UV stability | Excellent water and UV resistance |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to raw material sourcing | Lower cost, widely available materials |
| Application Suitability | Eco-friendly boat hulls, leisure crafts | Commercial boats, high-performance hulls |
Introduction to Boat Hull Materials
Boat hull materials significantly impact vessel performance, durability, and environmental footprint. Green composites, made from natural fibers like flax or hemp combined with bio-based resins, offer enhanced sustainability and reduced weight compared to traditional glass fiber composites, which consist of glass fibers embedded in polyester or epoxy resins. While glass fiber composites provide proven strength and corrosion resistance suited for marine environments, green composites present a promising eco-friendly alternative with competitive mechanical properties for boat hull construction.
Overview of Green Composites
Green composites for boat hulls combine natural fibers like flax, hemp, or jute with bio-based or recyclable resins, offering enhanced environmental sustainability compared to traditional glass fiber composites. These composites reduce carbon footprint and promote biodegradability without significantly compromising mechanical properties such as tensile strength and impact resistance. Advances in green composite technology improve water resistance and durability, making them a viable and eco-friendly alternative in marine applications.
Glass Fiber Composites Explained
Glass fiber composites are widely used for boat hulls due to their superior strength-to-weight ratio, excellent durability, and corrosion resistance in marine environments. The fiberglass matrix combines glass fibers with resin, providing high tensile strength and impact resistance, essential for withstanding harsh ocean conditions. Compared to green composites, glass fiber composites offer proven performance, easier manufacturing processes, and greater availability of materials and repair options in the boating industry.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Green composites for boat hulls use renewable materials like flax or hemp fibers combined with bio-based resins, significantly reducing carbon emissions and dependence on fossil fuels compared to traditional glass fiber composites. Glass fiber composites rely heavily on energy-intensive production processes and non-recyclable thermoset resins, resulting in higher environmental pollution and landfill waste. The biodegradability and lower lifecycle environmental footprint of green composites make them a sustainable alternative for marine applications.
Mechanical Properties and Performance
Green composites, made from natural fibers like flax or hemp combined with bio-based resins, offer comparable tensile strength and stiffness to glass fiber composites while significantly reducing environmental impact. Glass fiber composites exhibit superior impact resistance, fatigue endurance, and water absorption control, making them highly durable for boat hull applications. Performance-wise, green composites provide enhanced vibration damping and lighter weight but may require additional treatments to match the longevity and mechanical resilience of traditional glass fiber hulls.
Weight and Durability Factors
Green composites for boat hulls offer significantly lower weight compared to traditional glass fiber composites, enhancing fuel efficiency and maneuverability. Despite the lightweight advantage, green composites maintain competitive durability, exhibiting strong resistance to impact and fatigue through natural fiber reinforcements combined with bio-based resins. Glass fiber composites remain favored for superior abrasion resistance and long-term structural integrity, but advances in green composite technology continue to close the performance gap while prioritizing sustainability.
Cost Analysis: Green vs. Glass Fiber
Green composites for boat hulls offer a cost advantage primarily due to lower raw material expenses compared to glass fiber composites, which require energy-intensive manufacturing processes for glass fibers. Although green composites may incur higher initial processing costs and potential variability in material performance, long-term savings arise from reduced environmental compliance fees and potential tax incentives. Glass fiber composites remain cost-effective for high-strength requirements but often result in increased lifecycle costs due to recycling challenges and disposal fees.
Manufacturing and Processing Differences
Green composites for boat hulls utilize natural fibers like flax or hemp combined with bio-based resins, offering lighter weight and enhanced environmental benefits during manufacturing compared to traditional glass fiber composites. Processing green composites involves lower energy consumption and reduced emissions due to the use of renewable materials and simpler curing methods, while glass fiber composites require energy-intensive production with synthetic resins and extensive curing cycles. The variance in fiber-matrix bonding characteristics also impacts manufacturing techniques, as green composites often demand specialized surface treatments to optimize adhesion, contrasting with the well-established processes developed for glass fiber composites.
Case Studies in Marine Applications
Case studies in marine applications reveal that green composites, made from natural fibers like flax or hemp combined with bio-resins, offer superior environmental benefits and reduced weight compared to traditional glass fiber composites, enhancing fuel efficiency and reducing carbon emissions. Performance tests demonstrate that while glass fiber composites maintain higher tensile strength and impact resistance, green composites exhibit sufficient durability for small to medium-sized boat hulls under moderate sea conditions. Lifecycle assessments confirm green composites' advantages in sustainability, making them increasingly attractive for eco-friendly marine vessel construction and regulatory compliance.
Future Trends in Boat Hull Materials
Green composites for boat hulls are gaining traction due to their bio-based resins and natural fibers, reducing environmental impact and enhancing sustainability in marine applications. Glass fiber composites remain popular for their superior strength-to-weight ratio and cost efficiency but face challenges from increasingly stringent environmental regulations and growing demand for eco-friendly alternatives. Future trends indicate a shift toward hybrid composites that combine green materials with advanced fibers to achieve optimal performance while minimizing carbon footprint in boat construction.
Infographic: Green composite vs Glass fiber composite for Boat Hull
 azmater.com
azmater.com