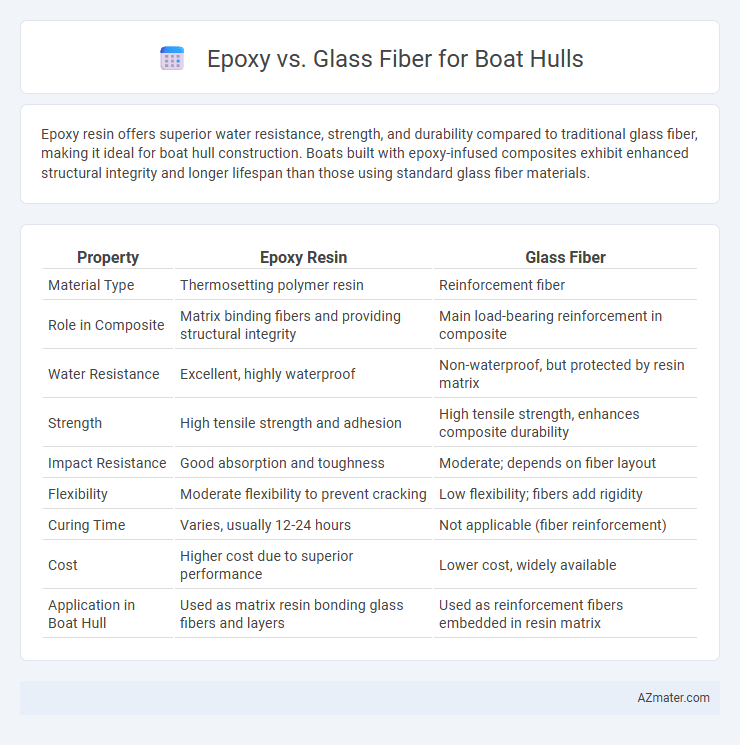
Epoxy resin offers superior water resistance, strength, and durability compared to traditional glass fiber, making it ideal for boat hull construction. Boats built with epoxy-infused composites exhibit enhanced structural integrity and longer lifespan than those using standard glass fiber materials.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Epoxy Resin | Glass Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermosetting polymer resin | Reinforcement fiber |
| Role in Composite | Matrix binding fibers and providing structural integrity | Main load-bearing reinforcement in composite |
| Water Resistance | Excellent, highly waterproof | Non-waterproof, but protected by resin matrix |
| Strength | High tensile strength and adhesion | High tensile strength, enhances composite durability |
| Impact Resistance | Good absorption and toughness | Moderate; depends on fiber layout |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility to prevent cracking | Low flexibility; fibers add rigidity |
| Curing Time | Varies, usually 12-24 hours | Not applicable (fiber reinforcement) |
| Cost | Higher cost due to superior performance | Lower cost, widely available |
| Application in Boat Hull | Used as matrix resin bonding glass fibers and layers | Used as reinforcement fibers embedded in resin matrix |
Introduction to Boat Hull Materials
Epoxy resin and glass fiber are critical materials in constructing durable boat hulls, offering superior strength and water resistance compared to traditional materials. Epoxy provides excellent adhesive properties and resistance to moisture and chemicals, enhancing the hull's durability and longevity. Glass fiber, known for its high tensile strength and lightweight characteristics, complements epoxy resin to create a robust composite material ideal for marine environments.
Understanding Epoxy Resin
Epoxy resin offers superior adhesion and waterproofing properties compared to traditional polyester resins used with glass fiber, resulting in a more durable and impact-resistant boat hull. Its chemical resistance and flexibility reduce the risk of cracks and delamination, enhancing hull longevity in marine environments. Epoxy resin's ability to bond effectively with glass fiber reinforcement creates a lighter, stronger composite ideal for high-performance and repair applications.
Overview of Glass Fiber
Glass fiber, a popular composite material in boat hull construction, offers high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent durability against impact and fatigue. Its corrosion-resistant properties and ability to be molded into complex shapes make it ideal for customizable hull designs. Commonly combined with polyester or vinyl ester resins, glass fiber ensures a lightweight yet strong hull suitable for various marine environments.
Key Differences Between Epoxy and Glass Fiber
Epoxy offers superior adhesion, chemical resistance, and flexibility compared to glass fiber, making it ideal for high-performance boat hulls requiring durability and impact resistance. Glass fiber, or fiberglass, provides a cost-effective and lightweight reinforcement but lacks the enhanced bonding properties and moisture resistance found in epoxy resins. The key differences also include epoxy's ability to create stronger, less brittle composites, whereas glass fiber laminates often require additional layers to achieve similar structural integrity.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Epoxy resin offers superior strength and durability compared to traditional glass fiber for boat hulls due to its enhanced bonding properties and resistance to water absorption. Glass fiber hulls tend to be more prone to delamination and require more maintenance over time, whereas epoxy composites provide increased impact resistance and long-term structural integrity. Choosing epoxy ensures better performance against environmental stressors and prolongs the lifespan of marine vessels.
Weight and Flexibility Considerations
Epoxy resin offers superior strength-to-weight ratio compared to traditional polyester resins used with glass fiber, resulting in lighter boat hulls that enhance fuel efficiency and speed. Glass fiber provides good flexibility and impact resistance but adds more weight, making epoxy a preferred choice for applications demanding reduced weight without compromising durability. The combination of epoxy with fiberglass reinforcement yields a hull that balances flexibility and lightweight performance, crucial for optimizing overall boat handling and longevity.
Resistance to Water and Chemicals
Epoxy resin offers superior resistance to water and chemicals compared to traditional glass fiber, ensuring enhanced durability and longevity for boat hulls in harsh marine environments. Glass fiber provides mechanical strength but relies on the resin matrix for waterproofing and chemical protection, often making epoxy-based composites more effective against water infiltration and chemical corrosion. Choosing epoxy with glass fiber reinforcement maximizes hull integrity by combining strong water and chemical resistance with structural reinforcement.
Cost Analysis: Epoxy vs Glass Fiber
Epoxy resin generally commands a higher upfront cost compared to glass fiber due to its superior adhesive properties and durability, which can reduce long-term maintenance expenses for boat hulls. Glass fiber, while initially more affordable, may incur greater repair and upkeep costs over time due to its lower resistance to water permeability and impact damage. When evaluating cost efficiency, epoxy offers enhanced longevity and performance that can offset its premium price through fewer repairs and extended hull life.
Application and Repair Process
Epoxy resin offers superior adhesion and durability for boat hull applications, providing enhanced water resistance and structural integrity compared to polyester-based glass fiber laminates. Repairing epoxy hulls typically involves thorough surface preparation, including sanding and cleaning, followed by applying compatible epoxy resin and fiberglass cloth for stronger, more seamless patches. Glass fiber repairs are generally quicker but less durable, requiring multiple layers of resin and careful curing to restore hull strength and prevent water intrusion.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Hull Material
Epoxy offers superior adhesion, water resistance, and durability, making it ideal for high-performance and long-lasting boat hulls. Glass fiber provides cost-effective strength and ease of repair but may lack the longevity and structural integrity of epoxy composites. Selecting the best hull material depends on balancing budget constraints with desired performance, durability, and maintenance requirements.
Infographic: Epoxy vs Glass fiber for Boat hull
 azmater.com
azmater.com