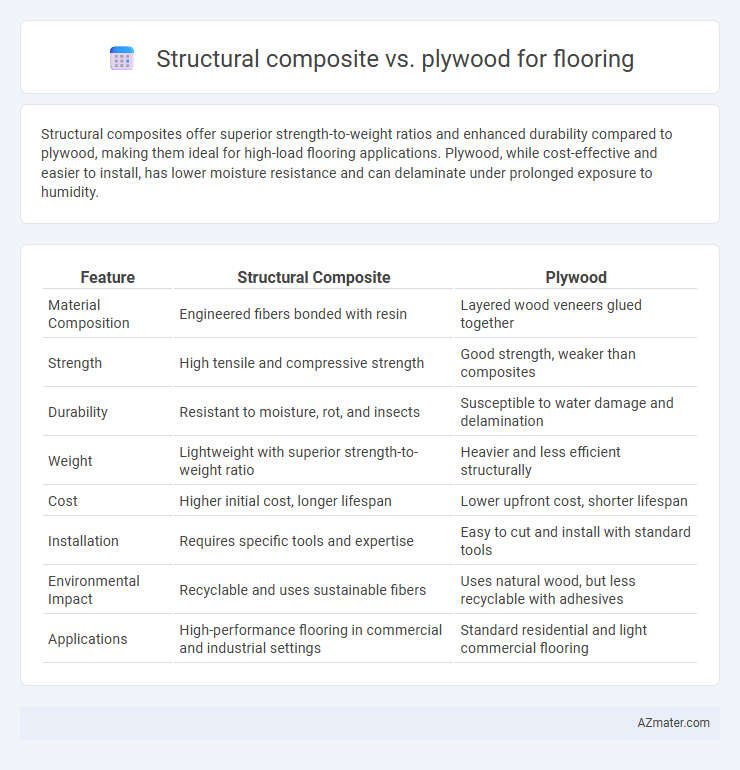
Structural composites offer superior strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced durability compared to plywood, making them ideal for high-load flooring applications. Plywood, while cost-effective and easier to install, has lower moisture resistance and can delaminate under prolonged exposure to humidity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Structural Composite | Plywood |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Engineered fibers bonded with resin | Layered wood veneers glued together |
| Strength | High tensile and compressive strength | Good strength, weaker than composites |
| Durability | Resistant to moisture, rot, and insects | Susceptible to water damage and delamination |
| Weight | Lightweight with superior strength-to-weight ratio | Heavier and less efficient structurally |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, longer lifespan | Lower upfront cost, shorter lifespan |
| Installation | Requires specific tools and expertise | Easy to cut and install with standard tools |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable and uses sustainable fibers | Uses natural wood, but less recyclable with adhesives |
| Applications | High-performance flooring in commercial and industrial settings | Standard residential and light commercial flooring |
Introduction to Flooring Material Choices
Structural composite flooring combines engineered wood fibers and adhesives, offering enhanced strength and moisture resistance compared to traditional plywood. Plywood consists of multiple thin layers of wood veneer, providing durability and a natural wood appearance but is more susceptible to water damage. Both materials serve as reliable subfloor options, with structural composites favored in environments demanding superior stability and longevity.
What is Structural Composite?
Structural composite is an engineered wood product made by bonding layers of wood veneers, strands, or fibers with adhesives under heat and pressure, designed to provide superior strength and stability compared to traditional wood materials. It offers increased resistance to warping, moisture, and load-bearing forces, making it ideal for flooring applications where durability and performance are critical. Unlike plywood, which consists of thin wood veneers glued in alternating grain directions, structural composites utilize advanced manufacturing processes to enhance mechanical properties and uniformity.
Overview of Plywood for Flooring
Plywood for flooring consists of thin layers of wood veneers glued together with alternating grain patterns, providing enhanced strength and durability compared to solid wood. It offers excellent dimensional stability, resistance to warping, and a smooth surface ideal for various floor finishes. Plywood is widely used in subfloor applications due to its cost-effectiveness, ease of installation, and compatibility with underfloor heating systems.
Comparative Strength and Durability
Structural composite flooring offers superior strength and durability compared to plywood due to its engineered layers that resist warping, splitting, and moisture damage more effectively. Plywood tends to have natural inconsistencies and is more prone to delamination and weakening under prolonged exposure to humidity and heavy loads. The composite materials and bonding techniques in structural composites provide enhanced load-bearing capacity and longer lifespan in demanding flooring applications.
Moisture Resistance and Stability
Structural composite panels exhibit superior moisture resistance compared to plywood, minimizing swelling, warping, and delamination in high-humidity or wet environments. Their engineered composition enhances dimensional stability, reducing movement and maintaining flatness under fluctuating moisture levels. Plywood, while commonly used, tends to absorb water more readily, leading to potential structural degradation and decreased lifespan in moisture-prone flooring applications.
Installation Ease and Techniques
Structural composites offer streamlined installation for flooring due to their uniformity, consistent thickness, and pre-finished surfaces, reducing the need for extensive sanding or preparation. Plywood requires careful alignment and fastening to avoid warping or uneven surfaces, often demanding more skilled labor and time-intensive techniques such as staggered joints and moisture barriers. Both materials benefit from adhesive and mechanical fasteners, but composites generally enable faster installations with fewer adjustments.
Cost Analysis: Structural Composite vs Plywood
Structural composite flooring generally incurs a higher initial cost compared to plywood due to advanced manufacturing processes and engineered material properties. Plywood remains more cost-effective upfront, with variable pricing influenced by thickness, grade, and wood species, often making it a budget-friendly choice for large-scale projects. Long-term expenses for structural composites may be lower because of improved durability, moisture resistance, and reduced maintenance requirements, which contribute to overall lifecycle savings despite the higher initial investment.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Structural composite flooring, made from engineered wood fibers and adhesives, offers a more sustainable alternative to traditional plywood due to its efficient use of raw materials and ability to incorporate recycled content. Plywood production often involves higher energy consumption and emits more volatile organic compounds (VOCs) because of the formaldehyde-based adhesives typically used. Choosing structural composites can reduce deforestation and lower the carbon footprint of flooring projects, aligning better with environmentally conscious building practices.
Best Use Cases for Each Material
Structural composite flooring excels in commercial and industrial applications due to its superior strength-to-weight ratio and moisture resistance, making it ideal for high-traffic areas and environments prone to humidity. Plywood flooring is best suited for residential and light commercial uses where cost-effectiveness, ease of installation, and versatility are prioritized, especially in dry conditions. Each material's performance varies significantly based on load requirements, environmental exposure, and budget constraints.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Flooring Option
Structural composite flooring offers superior strength, moisture resistance, and dimensional stability compared to plywood, making it ideal for high-traffic or moisture-prone areas. Plywood remains a cost-effective and widely available option with adequate performance for standard residential flooring. Selecting between structural composite and plywood depends on budget constraints, environmental conditions, and long-term durability requirements.
Infographic: Structural composite vs Plywood for Flooring
 azmater.com
azmater.com