Pre-preg materials offer superior resin control and higher strength-to-weight ratios compared to traditional glass fiber, enhancing boat hull durability and performance. Glass fiber remains cost-effective but typically results in heavier, less consistent laminate quality for marine applications.
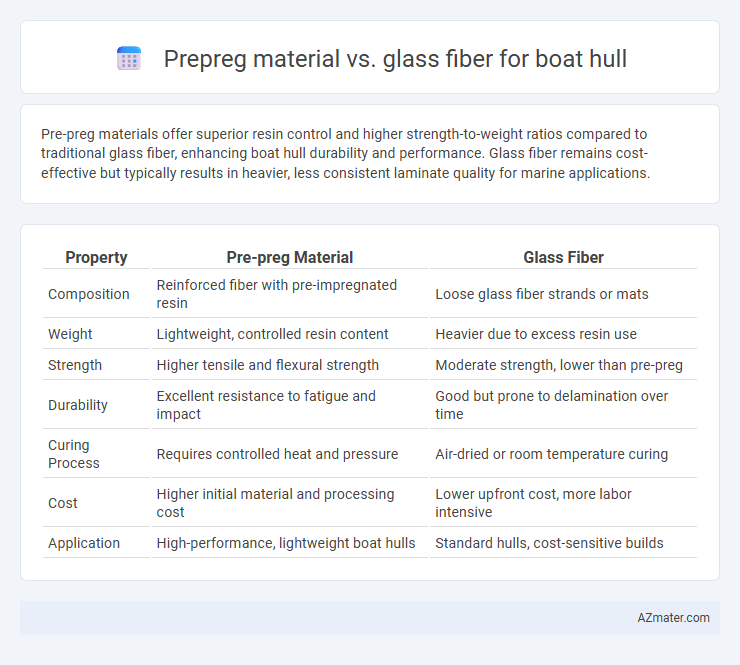
Table of Comparison
| Property | Pre-preg Material | Glass Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Reinforced fiber with pre-impregnated resin | Loose glass fiber strands or mats |
| Weight | Lightweight, controlled resin content | Heavier due to excess resin use |
| Strength | Higher tensile and flexural strength | Moderate strength, lower than pre-preg |
| Durability | Excellent resistance to fatigue and impact | Good but prone to delamination over time |
| Curing Process | Requires controlled heat and pressure | Air-dried or room temperature curing |
| Cost | Higher initial material and processing cost | Lower upfront cost, more labor intensive |
| Application | High-performance, lightweight boat hulls | Standard hulls, cost-sensitive builds |
Introduction: Pre-preg Material vs Glass Fiber in Boat Hull Construction
Pre-preg materials offer superior fiber-resin ratio control and enhanced mechanical properties compared to conventional glass fiber, crucial for high-performance boat hulls. Glass fiber remains a cost-effective option with proven durability and ease of use in large-scale hull manufacturing. Selecting between pre-preg and glass fiber impacts weight reduction, strength, and overall structural integrity in marine applications.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Process
Pre-preg materials consist of fibers pre-impregnated with a precise resin matrix, ensuring uniform resin distribution and reducing voids during curing, typically using epoxy with carbon or glass fibers. Glass fiber for boat hulls involves woven or chopped strand mats combined with resin manually or via infusion, allowing variation in resin content and fiber alignment but often leading to higher void content. The manufacturing process for pre-preg requires controlled temperature and pressure curing in an autoclave, resulting in superior mechanical properties and consistent laminate quality, whereas fiberglass layup uses open molding techniques with less stringent environmental controls, impacting strength and durability.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Pre-preg materials offer superior strength-to-weight ratio compared to traditional glass fiber, resulting in a stiffer and more impact-resistant boat hull. The controlled resin content and uniform fiber distribution in pre-pregs enhance durability by reducing voids and improving fatigue resistance. Glass fiber remains a cost-effective option but generally exhibits lower tensile strength and is more susceptible to water absorption and UV degradation over time.
Weight and Performance Differences
Pre-preg materials offer superior strength-to-weight ratios compared to traditional glass fiber, resulting in lighter boat hulls that enhance speed and fuel efficiency. Pre-preg composites provide better resin control and uniform fiber distribution, leading to improved mechanical performance and durability under marine conditions. Glass fiber remains cost-effective but typically adds more weight and requires thicker laminates to achieve comparable strength, which can reduce overall hull performance.
Cost Considerations and Budget Impact
Pre-preg material, consisting of resin-impregnated fibers, offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and reduced labor costs due to faster curing times but generally comes with a higher upfront price compared to traditional glass fiber. Glass fiber remains more budget-friendly for boat hull construction, with lower initial material costs and widespread availability, making it suitable for cost-sensitive projects despite longer production times and potentially higher labor expenses. Evaluating total project budget impact requires balancing the premium cost of pre-preg with potential savings in performance, durability, and assembly efficiency versus the economical yet labor-intensive glass fiber option.
Ease of Fabrication and Repairs
Pre-preg materials offer superior ease of fabrication for boat hulls due to their pre-impregnated resin systems, ensuring consistent fiber-to-resin ratios and reducing handling time compared to traditional glass fiber fabrics. Repairs on pre-preg composites can be more complex, requiring controlled temperature curing processes and specialized equipment, whereas glass fiber hulls allow simpler, more accessible patching with wet lay-up methods using resin and fiber cloth. The enhanced precision and reduced labor in pre-preg fabrication often justify its use despite maintenance challenges, while glass fiber remains favored for straightforward field repairs and lower initial costs.
Resistance to Environmental Factors
Pre-preg materials offer superior resistance to environmental factors such as UV radiation, moisture, and temperature fluctuations compared to traditional glass fiber, enhancing the durability of boat hulls. The tightly controlled resin-to-fiber ratio in pre-preg composites improves resistance to water absorption and chemical degradation, critical for marine environments. Glass fiber, though cost-effective, typically requires additional coatings to achieve similar environmental protection, making pre-preg a preferred choice for high-performance, long-lasting boat hulls.
Lifespan and Maintenance Requirements
Pre-preg materials offer superior lifespan for boat hulls due to their high fiber-to-resin ratio and consistent curing process, resulting in enhanced durability and resistance to water ingress compared to traditional glass fiber laminates. Maintenance requirements for pre-preg hulls are generally lower, as their tightly controlled resin content minimizes moisture absorption and reduces the risk of delamination, unlike glass fiber which often needs more frequent repairs and refinishing due to fiberglass mat swelling and resin degradation. The improved structural integrity and moisture resistance of pre-preg composites directly contribute to extended hull service life and lower upkeep costs over time.
Suitability for Different Boat Types
Pre-preg materials offer superior strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced resin control, making them ideal for high-performance racing yachts and lightweight sailboats where precision and performance are critical. Glass fiber, known for its affordability and durability, suits larger recreational boats and fishing vessels that require robust construction without the need for advanced manufacturing techniques. Selecting between pre-preg and glass fiber depends largely on the boat's intended use, budget constraints, and performance requirements.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Your Boat Hull
Pre-preg materials offer superior strength-to-weight ratios, enhanced resin control, and improved durability compared to traditional glass fiber, making them ideal for high-performance boat hulls. Glass fiber remains a cost-effective option with good impact resistance and ease of repair, suitable for budget-conscious builds or less demanding applications. Selecting the right material depends on balancing performance requirements, budget constraints, and long-term maintenance considerations for optimal boat hull performance.
Infographic: Pre-preg material vs Glass fiber for Boat hull
 azmater.com
azmater.com