Fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) offers superior impact resistance and lightweight properties for helmets, enhancing user safety and comfort. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, provide exceptional tensile strength and thermal stability, making them ideal for high-performance helmet applications requiring durability and ballistic protection.
Table of Comparison
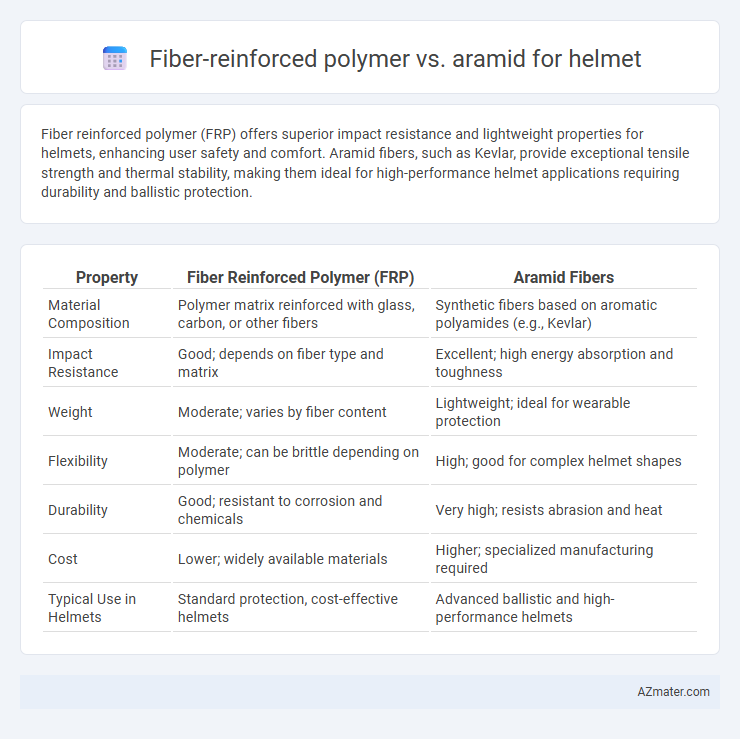
| Property | Fiber Reinforced Polymer (FRP) | Aramid Fibers |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Polymer matrix reinforced with glass, carbon, or other fibers | Synthetic fibers based on aromatic polyamides (e.g., Kevlar) |
| Impact Resistance | Good; depends on fiber type and matrix | Excellent; high energy absorption and toughness |
| Weight | Moderate; varies by fiber content | Lightweight; ideal for wearable protection |
| Flexibility | Moderate; can be brittle depending on polymer | High; good for complex helmet shapes |
| Durability | Good; resistant to corrosion and chemicals | Very high; resists abrasion and heat |
| Cost | Lower; widely available materials | Higher; specialized manufacturing required |
| Typical Use in Helmets | Standard protection, cost-effective helmets | Advanced ballistic and high-performance helmets |
Introduction to Helmet Materials: Fiber Reinforced Polymer vs Aramid
Fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) and aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, are crucial materials in helmet construction due to their high strength-to-weight ratios and impact resistance. FRP offers versatility with customizable layering and resin matrices, enabling tailored stiffness and durability, while aramid fibers provide exceptional tensile strength and energy absorption, making helmets lighter and better at dissipating shock. These material properties directly influence helmet performance, safety standards, and wearer comfort, determining their suitability for various protective applications.
Composition and Structure: FRP Helmets Explained
Fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) helmets utilize a composite material combining a polymer matrix, often epoxy or polyester resin, with reinforcing fibers such as fiberglass or carbon fiber, creating a lightweight yet strong shell. The polymer matrix binds the fibers together, distributing impact forces across the helmet surface, while the fiber layers provide high tensile strength and resistance to deformation. In contrast, aramid helmets, made from Kevlar or similar aramid fibers, offer superior impact resistance and energy absorption due to their unique molecular structure and tightly woven fiber arrangement that effectively dissipates kinetic energy upon impact.
Understanding Aramid: Properties and Applications in Helmets
Aramid fibers, known for their exceptional tensile strength and heat resistance, are widely used in helmets to provide lightweight yet robust protection. These fibers exhibit high impact resistance and superior energy absorption, making them ideal for military and sports helmets requiring durability against ballistic and blunt forces. Compared to fiber reinforced polymer composites, aramid-based helmets offer enhanced flexibility and comfort without compromising safety standards.
Weight Comparison: FRP vs Aramid Helmets
Fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) helmets typically weigh more than aramid-based helmets due to the higher density of FRP materials compared to aramid fibers like Kevlar. Aramid helmets offer superior strength-to-weight ratios, resulting in lighter and more comfortable head protection without compromising impact resistance. This weight advantage makes aramid helmets preferable for long-duration use and reduces user fatigue.
Impact Resistance: Performance Differences
Fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) helmets offer high impact resistance through rigid fiber-matrix bonding, effectively distributing and absorbing energy upon impact. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, provide superior tensile strength and exceptional energy absorption due to their high toughness and flexibility, enhancing helmet resilience against blunt force trauma. Comparative studies show aramid-based helmets typically outperform FRP in multi-impact scenarios by maintaining structural integrity and reducing deformation.
Durability and Longevity: Which Material Lasts Longer?
Fiber reinforced polymer helmets offer superior durability due to their resistance to environmental factors such as UV radiation, moisture, and chemical exposure, which contributes to longer service life. Aramid fibers, known for their exceptional tensile strength and impact resistance, provide excellent protection but may degrade faster under prolonged exposure to certain elements. Overall, fiber reinforced polymers tend to have greater longevity in helmets compared to aramid materials, especially in varying environmental conditions.
Comfort and Ergonomics in Helmet Design
Fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) offers lightweight strength and superior impact resistance, enhancing helmet comfort by reducing pressure on the head during extended wear. Aramid fibers, known for their exceptional flexibility and energy absorption, contribute to ergonomic designs by conforming better to head shapes and improving shock distribution. The combination of FRP's rigidity with aramid's pliability often results in helmets that balance comfort and protection, optimizing both fit and user experience.
Cost Analysis: FRP vs Aramid Helmet Pricing
Fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) helmets typically offer a lower cost compared to aramid helmets due to cheaper raw materials and simpler manufacturing processes. Aramid helmets, such as those made with Kevlar, command higher prices driven by superior impact resistance, lightweight properties, and advanced production techniques. Cost analysis reveals that FRP helmets are budget-friendly options for general protection, while aramid helmets provide premium performance and durability at a significantly increased price.
Industry Standards and Safety Certifications
Fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) helmets meet rigorous industry standards such as DOT, ECE, and Snell, offering high impact resistance and durability while maintaining lightweight properties. Aramid fiber helmets, primarily using Kevlar or Twaron, excel in meeting military-grade specifications like MIL-STD and possess superior tensile strength and thermal stability essential for ballistic protection. Both materials undergo strict safety certifications evaluating impact absorption, penetration resistance, and environmental durability to ensure optimal user protection in various helmet applications.
Choosing the Right Helmet Material: Key Considerations
Fiber reinforced polymer offers superior impact resistance and lightweight properties essential for helmet safety and comfort, making it a popular choice in high-performance protective gear. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, provide exceptional tensile strength and thermal stability, ideal for helmets needing enhanced ballistic protection and durability. When choosing helmet material, prioritize specific use cases, impact absorption capacity, weight constraints, and overall durability to ensure optimal protection and performance.
Infographic: Fiber reinforced polymer vs Aramid for Helmet
 azmater.com
azmater.com