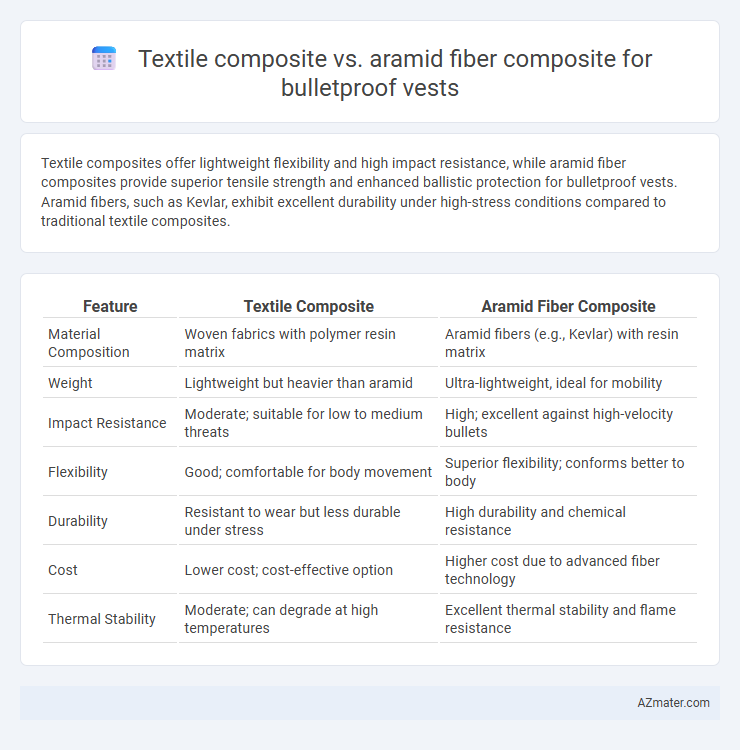
Textile composites offer lightweight flexibility and high impact resistance, while aramid fiber composites provide superior tensile strength and enhanced ballistic protection for bulletproof vests. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, exhibit excellent durability under high-stress conditions compared to traditional textile composites.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Textile Composite | Aramid Fiber Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Woven fabrics with polymer resin matrix | Aramid fibers (e.g., Kevlar) with resin matrix |
| Weight | Lightweight but heavier than aramid | Ultra-lightweight, ideal for mobility |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate; suitable for low to medium threats | High; excellent against high-velocity bullets |
| Flexibility | Good; comfortable for body movement | Superior flexibility; conforms better to body |
| Durability | Resistant to wear but less durable under stress | High durability and chemical resistance |
| Cost | Lower cost; cost-effective option | Higher cost due to advanced fiber technology |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate; can degrade at high temperatures | Excellent thermal stability and flame resistance |
Introduction to Bulletproof Vest Materials
Bulletproof vest materials primarily include textile composites and aramid fiber composites, each offering distinct protective benefits. Textile composites combine various fibers and resin matrices to enhance flexibility and ballistic resistance, while aramid fiber composites, such as Kevlar, provide high tensile strength and exceptional energy absorption for impact resistance. Selection of these materials depends on balancing weight, durability, and bullet penetration prevention in body armor design.
Overview of Textile Composites
Textile composites used in bulletproof vests primarily consist of tightly woven fibers such as aramid, polyethylene, or glass, offering a balance of lightweight properties and high tensile strength for effective ballistic resistance. These composites are engineered to absorb and disperse kinetic energy, enhancing protection while maintaining flexibility and comfort for the wearer. Compared to aramid fiber composites, textile composites often integrate multiple fiber types or weaves to optimize durability, impact resistance, and breathability in personal armor applications.
Understanding Aramid Fiber Composites
Aramid fiber composites exhibit exceptional tensile strength and impact resistance, making them ideal for bulletproof vests requiring lightweight yet durable protection. Their molecular structure consists of long-chain synthetic aromatic polyamides, which provide high thermal stability and resistance to abrasion compared to traditional textile composites. These properties result in superior ballistic performance, energy absorption, and multi-hit capability essential in advanced personal armor systems.
Comparative Ballistic Performance
Textile composites for bulletproof vests typically consist of materials like Kevlar or Twaron, offering high tensile strength and flexibility crucial for dissipating ballistic energy. Aramid fiber composites, specifically engineered from aramid fibers, demonstrate superior ballistic performance by providing enhanced energy absorption and reduced penetration depth due to their molecular structure and fiber alignment. Comparative tests reveal that aramid fiber composites generally outperform traditional textile composites in multi-hit scenarios, maintaining integrity and stopping projectiles more effectively.
Weight and Comfort Considerations
Textile composites used in bulletproof vests typically offer lighter weight options, enhancing wearer comfort and mobility during extended use. Aramid fiber composites, such as Kevlar, provide excellent ballistic protection while maintaining a favorable strength-to-weight ratio, though they may feel stiffer compared to flexible textile composites. Balancing weight and comfort, aramid composites are often preferred for high-threat environments, whereas textile composites suit scenarios requiring greater flexibility and reduced fatigue.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Textile composites, often made from high-strength woven fibers like Kevlar, offer excellent durability with high tensile strength and impact resistance but may degrade over prolonged exposure to UV light and moisture. Aramid fiber composites, such as those using Twaron or Nomex, provide superior environmental resistance, maintaining structural integrity against heat, chemicals, and humidity, which enhances long-term performance in harsh conditions. These properties make aramid fiber composites preferable for bulletproof vests requiring consistent protection in diverse and demanding environments.
Flexibility and Wearability Factors
Textile composites, often made from materials like Kevlar or Twaron, offer superior flexibility and comfort due to their woven construction, which allows better movement and breathability in bulletproof vests. Aramid fiber composites, while providing high tensile strength and excellent ballistic resistance, tend to be stiffer and less comfortable during extended wear because of their denser fiber arrangement and resin impregnation. The balance between flexibility and wearability in bulletproof vests depends on the specific layering and fabric treatments used in textile composites compared to the rigidity often inherent in aramid fiber composite panels.
Cost Analysis: Textile vs Aramid Fiber
Textile composites generally offer a lower cost alternative compared to aramid fiber composites due to the use of less expensive raw materials such as high-performance polyesters or nylon blends. Aramid fiber composites, while providing superior ballistic resistance and durability, incur higher costs because of the complex manufacturing processes and premium materials like Kevlar or Twaron. Cost analysis must weigh the balance between budget constraints and performance requirements, with textile composites favored for budget-sensitive applications and aramid fibers chosen for high-threat protection.
Manufacturing and Design Differences
Textile composites for bulletproof vests typically utilize woven fabrics like Kevlar or UHMWPE, offering flexibility and easier layering during manufacturing, while aramid fiber composites involve more rigid, resin-impregnated fibers that enhance structural integrity but require precise curing processes. Manufacturing textile composites emphasizes multi-layer lamination and heat pressing to achieve desired ballistic resistance, whereas aramid fiber composites demand controlled resin infusion and autoclave curing for optimal strength and durability. Design-wise, textile composites provide lightweight, ergonomic vests suitable for extended wear, whereas aramid fiber composites prioritize enhanced protection with increased stiffness, often resulting in heavier, less flexible armor plates.
Future Trends in Bulletproof Vest Materials
Textile composites and aramid fiber composites represent two critical materials in bulletproof vest innovation, with future trends emphasizing enhanced multi-threat protection and weight reduction. Research is progressing towards hybrid composites combining aramid fibers with ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) to improve ballistic resistance and flexibility. Advances in nanotechnology and smart textiles aim to integrate sensor capabilities and adaptive protection, setting a new standard for next-generation bulletproof vests.
Infographic: Textile composite vs Aramid fiber composite for Bulletproof vest
 azmater.com
azmater.com