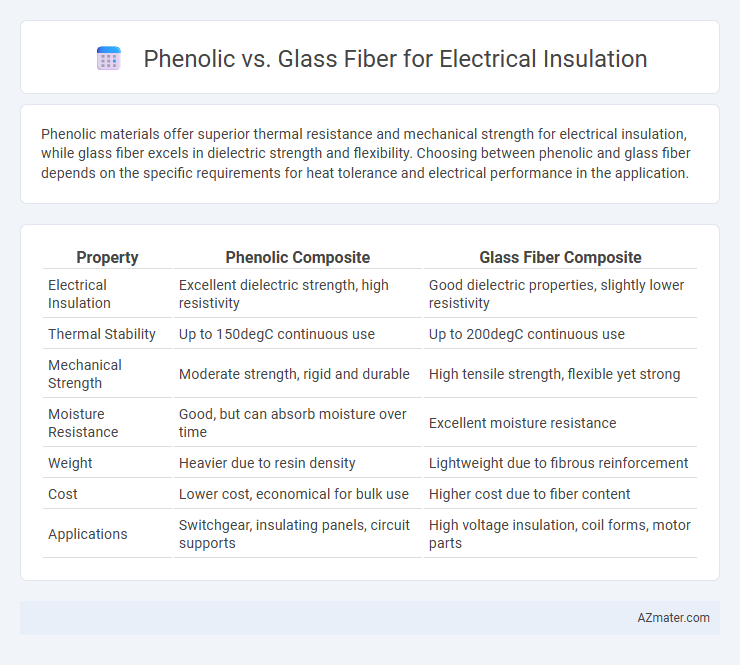
Phenolic materials offer superior thermal resistance and mechanical strength for electrical insulation, while glass fiber excels in dielectric strength and flexibility. Choosing between phenolic and glass fiber depends on the specific requirements for heat tolerance and electrical performance in the application.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Phenolic Composite | Glass Fiber Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent dielectric strength, high resistivity | Good dielectric properties, slightly lower resistivity |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 150degC continuous use | Up to 200degC continuous use |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate strength, rigid and durable | High tensile strength, flexible yet strong |
| Moisture Resistance | Good, but can absorb moisture over time | Excellent moisture resistance |
| Weight | Heavier due to resin density | Lightweight due to fibrous reinforcement |
| Cost | Lower cost, economical for bulk use | Higher cost due to fiber content |
| Applications | Switchgear, insulating panels, circuit supports | High voltage insulation, coil forms, motor parts |
Introduction to Electrical Insulation Materials
Phenolic and glass fiber materials serve distinct roles in electrical insulation, with phenolic offering excellent thermal resistance and mechanical strength due to its thermoset resin composition. Glass fiber provides superior dielectric properties and high tensile strength, making it ideal for high-frequency and high-voltage applications. Both materials are critical in preventing electrical conduction and ensuring device safety by maintaining insulation integrity under diverse operational conditions.
Overview of Phenolic Resin Insulation
Phenolic resin insulation offers excellent thermal stability, chemical resistance, and electrical insulation properties, making it ideal for high-voltage applications and electrical components exposed to heat and moisture. Its rigid, heat-cured thermosetting structure provides superior mechanical strength and dimensional stability compared to glass fiber insulation. Phenolic materials typically deliver enhanced arc resistance and flame retardancy, contributing to safer and more reliable electrical systems.
Overview of Glass Fiber Insulation
Glass fiber insulation offers superior electrical insulation properties due to its high dielectric strength and excellent resistance to moisture, heat, and chemical exposure. Its fine glass strands provide mechanical strength and dimensional stability, making it ideal for high-performance electrical applications such as transformers and motors. Compared to phenolic insulation, glass fiber maintains integrity in extreme temperatures and harsh environments, ensuring reliable long-term electrical protection.
Electrical Properties Comparison
Phenolic resin exhibits superior electrical insulation properties with high dielectric strength and excellent resistance to electrical tracking, making it ideal for high-voltage applications. Glass fiber composites provide enhanced mechanical strength and dimensional stability while maintaining good electrical insulation, but their dielectric strength typically falls below that of phenolic materials. Phenolic insulation materials also offer lower moisture absorption than glass fiber composites, contributing to more consistent electrical performance in varying environmental conditions.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Phenolic composites exhibit high mechanical strength and excellent thermal resistance, making them suitable for electrical insulation in high-stress environments. Glass fiber reinforced materials provide superior durability and impact resistance, enhancing longevity under mechanical fatigue and harsh conditions. The choice between phenolic and glass fiber insulation depends on the specific application's requirements for strength, thermal stability, and exposure to mechanical wear.
Thermal Resistance and Stability
Phenolic materials exhibit superior thermal resistance, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 130degC to 150degC, making them ideal for moderate heat environments in electrical insulation. Glass fiber offers enhanced thermal stability, withstanding continuous exposure to temperatures around 250degC, providing reliability in high-temperature electrical applications. Both materials ensure excellent electrical insulation properties, but glass fiber composites are preferred when higher thermal endurance and long-term dimensional stability are required.
Moisture and Chemical Resistance
Phenolic materials exhibit superior moisture resistance compared to glass fiber, preventing water absorption and maintaining electrical insulation integrity in humid environments. Glass fiber provides excellent chemical resistance to acids and alkalis but can degrade when exposed to prolonged moisture or certain solvents. Selecting phenolic insulation ensures enhanced durability in moist and chemically aggressive conditions, crucial for reliable electrical performance.
Safety and Environmental Considerations
Phenolic insulation offers excellent flame resistance and low smoke emission, enhancing safety by reducing fire hazards in electrical applications, while glass fiber provides superior mechanical strength and thermal stability but can pose inhalation risks during handling. Phenolic materials are typically more environmentally friendly due to their biodegradability and lower toxic emissions compared to synthetic glass fibers, which may contribute to environmental pollution if not properly managed. Selecting the appropriate insulation involves balancing phenolic's safer combustion properties with glass fiber's durability, considering both operational safety and environmental impact.
Cost and Ease of Manufacturing
Phenolic materials offer lower cost and simpler manufacturing processes due to their ease of molding and curing, making them economically attractive for electrical insulation. Glass fiber composites, while generally more expensive, provide superior mechanical strength and thermal stability but require more complex manufacturing techniques such as filament winding or lamination. Cost-efficiency favors phenolic for high-volume, low-stress applications, whereas glass fiber suits applications demanding higher performance despite higher production costs.
Application Suitability: Phenolic vs Glass Fiber
Phenolic materials offer excellent thermal resistance and mechanical strength, making them suitable for high-temperature electrical insulation applications such as transformers and switchgear components. Glass fiber insulation provides superior electrical performance and flexibility, ideal for coil insulation, circuit boards, and high-frequency electronic devices. Choosing between phenolic and glass fiber depends on the specific insulation requirements, including thermal endurance, mechanical durability, and electrical properties.
Infographic: Phenolic vs Glass fiber for Electrical insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com