Green composites offer superior environmental benefits and enhanced biodegradability compared to wood plastic composites, which provide greater durability and moisture resistance for decking applications. Selecting green composites reduces carbon footprint, while wood plastic composites deliver long-lasting performance and low maintenance.
Table of Comparison
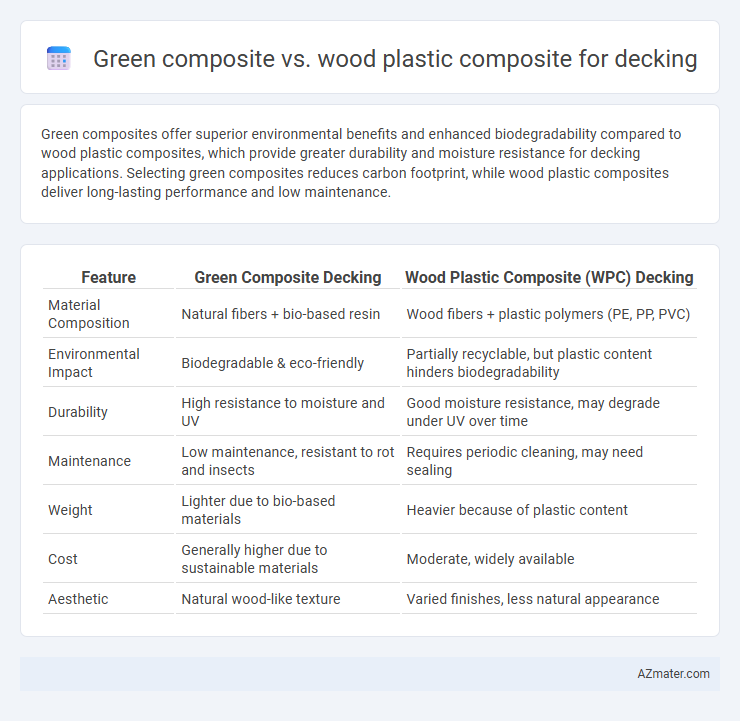
| Feature | Green Composite Decking | Wood Plastic Composite (WPC) Decking |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural fibers + bio-based resin | Wood fibers + plastic polymers (PE, PP, PVC) |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable & eco-friendly | Partially recyclable, but plastic content hinders biodegradability |
| Durability | High resistance to moisture and UV | Good moisture resistance, may degrade under UV over time |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, resistant to rot and insects | Requires periodic cleaning, may need sealing |
| Weight | Lighter due to bio-based materials | Heavier because of plastic content |
| Cost | Generally higher due to sustainable materials | Moderate, widely available |
| Aesthetic | Natural wood-like texture | Varied finishes, less natural appearance |
Introduction to Decking Materials
Green composite decking combines recycled wood fibers and plastic, offering enhanced durability, low maintenance, and resistance to moisture and insects compared to traditional wood. Wood plastic composite (WPC) decking integrates wood flour and thermoplastics, providing a sustainable alternative with improved dimensional stability and reduced splintering. Both materials support eco-friendly construction trends, but green composites often emphasize higher recycled content and environmental benefits.
What Are Green Composites?
Green composites are environmentally friendly materials consisting of natural fibers combined with biodegradable or recyclable resins, designed to reduce carbon footprint and enhance sustainability. Unlike wood plastic composites (WPCs), which typically blend wood fibers with non-biodegradable plastics like polyethylene or polypropylene, green composites emphasize renewable resources and lower environmental impact throughout their lifecycle. These composites offer comparable durability and weather resistance ideal for decking applications while promoting eco-conscious construction choices.
Understanding Wood Plastic Composites (WPC)
Wood Plastic Composites (WPC) are engineered materials combining wood fibers or flour with thermoplastics such as polyethylene, polypropylene, or PVC, designed for durability and low maintenance in decking applications. WPC decking offers resistance to rot, decay, and insect damage while mimicking the aesthetics of natural wood, making it an advantageous alternative to traditional lumber. The composite structure enhances moisture resistance and dimensional stability, reducing warping and splintering compared to solid wood.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Green composites, often made from natural fibers and biodegradable resins, offer a significantly lower carbon footprint and enhanced recyclability compared to traditional wood plastic composites (WPCs), which combine wood fibers with non-biodegradable plastics. WPC decking contributes to plastic pollution due to its polymer content, whereas green composites promote sustainable sourcing and reduce landfill waste through compostability. The environmental impact of green composites is further minimized by their renewable raw materials and lower energy consumption during production, making them a superior eco-friendly choice for decking applications.
Material Composition and Sustainability
Green composite decking typically incorporates natural fibers like bamboo or hemp combined with biodegradable resins, enhancing its eco-friendly profile through renewable and recyclable materials. Wood plastic composites (WPC) blend wood flour or sawdust with thermoplastics such as polyethylene or polypropylene, resulting in durable, low-maintenance boards but with a higher reliance on non-renewable plastics. Sustainability assessments favor green composites for their lower carbon footprint and reduced plastic content, while WPC offers longevity and recyclability benefits that contribute to waste reduction in outdoor decking applications.
Durability and Longevity
Green composites for decking often feature natural fibers combined with biodegradable resins, offering moderate durability but limited resistance to moisture and UV exposure compared to traditional wood. Wood plastic composites (WPC) blend wood fibers with plastic polymers, providing enhanced resistance to rot, insects, and weathering, which significantly extends the decking lifespan. WPC decks typically last 25-30 years with minimal maintenance, outperforming green composites that may degrade faster under harsh environmental conditions.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Flexibility
Green composite decking offers superior aesthetic appeal through its natural wood-like appearance and rich color variations, closely mimicking traditional hardwoods. It provides enhanced design flexibility by allowing customizable textures and profiles that can seamlessly blend with various architectural styles. In contrast, wood plastic composite decking tends to have a more uniform look with limited color options, restricting its application in highly customized or intricate design projects.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Green composite decking offers easier installation due to lighter weight and uniform dimensions, reducing labor time compared to wood plastic composite (WPC), which can be denser and heavier. In terms of maintenance, green composite materials typically resist mold, moisture, and UV damage better than WPC, requiring less frequent cleaning and sealing. While both options benefit from routine upkeep, green composite decking generally demands lower maintenance efforts to preserve appearance and durability over time.
Cost Analysis and Value for Money
Green composite decking typically costs 10-15% more than wood plastic composite (WPC) due to its eco-friendly materials like recycled wood fibers and bio-based resins, offering enhanced durability and UV resistance. Wood plastic composite is generally more affordable upfront, averaging $2 to $5 per linear foot, but may require more frequent maintenance or replacement, impacting long-term value. Considering lifespan and maintenance, green composite provides better value for money by reducing repairs and replacements, making it cost-effective over a 20-30 year period.
Choosing the Right Composite for Your Deck
Green composite decking offers superior environmental benefits with recycled materials and reduced carbon footprint, ideal for eco-conscious projects. Wood plastic composite (WPC) decking emphasizes durability and low maintenance, combining wood fibers and plastic for resistance against moisture and pests. Selecting the right decking composite depends on priorities like sustainability, lifespan, appearance, and budget, ensuring long-term satisfaction and performance.
Infographic: Green composite vs Wood plastic composite for Decking
 azmater.com
azmater.com