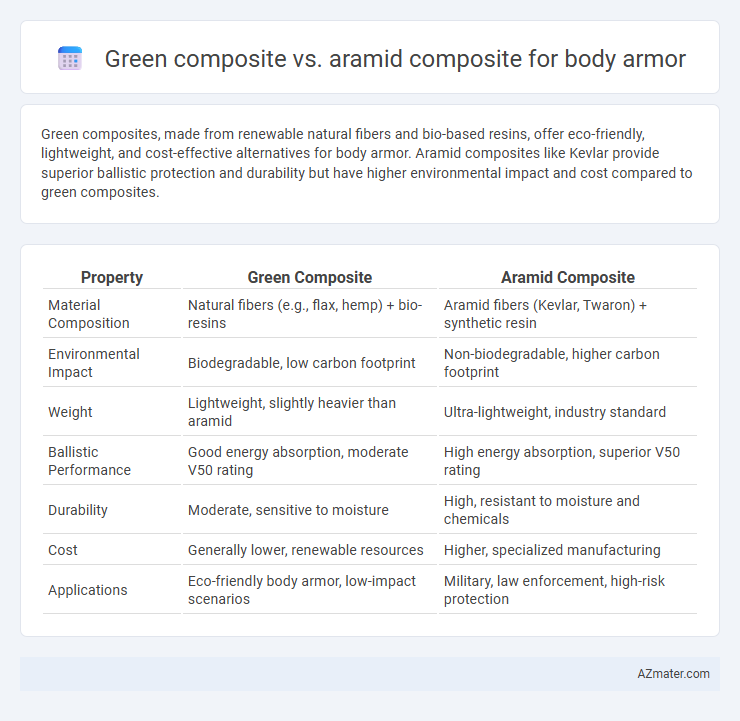
Green composites, made from renewable natural fibers and bio-based resins, offer eco-friendly, lightweight, and cost-effective alternatives for body armor. Aramid composites like Kevlar provide superior ballistic protection and durability but have higher environmental impact and cost compared to green composites.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Green Composite | Aramid Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural fibers (e.g., flax, hemp) + bio-resins | Aramid fibers (Kevlar, Twaron) + synthetic resin |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, higher carbon footprint |
| Weight | Lightweight, slightly heavier than aramid | Ultra-lightweight, industry standard |
| Ballistic Performance | Good energy absorption, moderate V50 rating | High energy absorption, superior V50 rating |
| Durability | Moderate, sensitive to moisture | High, resistant to moisture and chemicals |
| Cost | Generally lower, renewable resources | Higher, specialized manufacturing |
| Applications | Eco-friendly body armor, low-impact scenarios | Military, law enforcement, high-risk protection |
Introduction to Body Armor Materials
Body armor materials primarily consist of synthetic fibers such as aramid composites and natural fiber-based green composites, each offering distinct protective properties. Aramid composites, including Kevlar, provide high tensile strength and impact resistance, making them industry standards for ballistic protection. Green composites, derived from bio-based fibers like flax or hemp combined with polymer matrices, present an eco-friendly alternative with promising mechanical performance and reduced environmental impact.
Overview of Green Composites
Green composites for body armor utilize natural fibers such as hemp, flax, or kenaf combined with bio-based resins, offering sustainable alternatives to traditional synthetic materials like aramid composites. These composites provide benefits including reduced environmental impact, biodegradability, and comparable mechanical properties such as high tensile strength and impact resistance essential for protective gear. Research demonstrates that green composites can achieve adequate ballistic performance while lowering carbon footprint, making them an emerging choice in eco-friendly body armor design.
Understanding Aramid Composites
Aramid composites, such as Kevlar and Twaron, are renowned for their exceptional tensile strength and resistance to impact, making them a preferred choice in body armor applications. These composites consist of aramid fibers embedded in a polymer matrix, providing lightweight protection with high energy absorption capabilities against ballistic threats. Understanding the molecular structure and fiber alignment in aramid composites is crucial for optimizing armor performance, balancing durability, flexibility, and wearer comfort.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Green composites, composed of natural fibers like flax or hemp combined with biodegradable resins, exhibit moderate tensile strength ranging from 150 to 300 MPa and impact resistance suitable for lightweight body armor applications. Aramid composites, made from synthetic fibers such as Kevlar, provide superior mechanical properties with tensile strengths exceeding 3,000 MPa and exceptional energy absorption, making them ideal for high-performance ballistic protection. The stiffness and durability of aramid composites significantly outperform green composites, though green composites offer advantages in environmental sustainability and reduced weight for non-military protective gear.
Ballistic Performance Analysis
Green composites, incorporating natural fibers like hemp or flax, offer lower density and enhanced environmental sustainability compared to traditional Aramid composites such as Kevlar. Ballistic performance analysis reveals Aramid composites exhibit superior multi-hit resistance and higher tensile strength critical for dissipating projectile energy effectively. However, advancements in green composite matrix resins and fiber treatments are narrowing the ballistic protection gap, presenting a promising alternative for eco-friendly body armor without significant compromise on impact resistance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Green composites for body armor utilize natural fibers like flax or hemp combined with bio-based resins, significantly reducing carbon footprint and promoting biodegradability compared to synthetic materials. Aramid composites, such as Kevlar, rely on petrochemical-based fibers with high energy-intensive manufacturing processes and limited recyclability, resulting in greater environmental pollution. Sustainable body armor solutions increasingly favor green composites due to their renewable resources, lower toxicity, and potential for end-of-life composting or recycling.
Weight and Comfort Considerations
Green composites for body armor typically utilize natural fibers like hemp or flax combined with bio-based resins, resulting in lighter weight materials that enhance wearer comfort and reduce fatigue during prolonged use. Aramid composites, such as Kevlar, offer exceptional strength and ballistic resistance but tend to be heavier and less breathable, potentially causing discomfort and heat retention under extended wear. Weight and breathability advantages of green composites can improve mobility and comfort, making them a compelling alternative for personal protective equipment in less extreme threat environments.
Cost Efficiency and Market Availability
Green composites, primarily made from natural fibers and biodegradable matrices, offer significant cost efficiency due to lower raw material expenses and reduced manufacturing energy requirements compared to traditional Aramid composites like Kevlar. Despite these cost advantages, the market availability of green composites remains limited owing to slower development cycles and less established supply chains, whereas Aramid composites benefit from widespread industry adoption and robust distribution networks. For body armor applications, Aramid composites still dominate the market given their proven performance, though green composites are gaining attention as a sustainable and cost-effective alternative in niche segments.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Green composites for body armor utilize bio-based fibers and resins, offering moderate durability with enhanced environmental benefits, but they typically require more frequent inspection and maintenance due to susceptibility to moisture and UV degradation. Aramid composites, such as Kevlar, provide superior durability with high tensile strength and excellent resistance to abrasion, chemicals, and heat, resulting in lower maintenance demands and longer service life. In terms of maintenance, aramid composites are more robust and require less frequent checks, while green composites need careful handling and routine upkeep to maintain protective performance.
Future Trends in Body Armor Materials
Green composites for body armor leverage sustainable, biodegradable fibers and resins, aiming to reduce environmental impact without compromising ballistic performance. Aramid composites, known for their high tensile strength and lightweight properties, continue to dominate but face challenges related to cost and environmental sustainability. Future trends emphasize hybrid solutions combining green composites with aramid layers to enhance eco-friendliness, durability, and multi-threat protection in body armor technology.
Infographic: Green composite vs Aramid composite for Body armor
 azmater.com
azmater.com