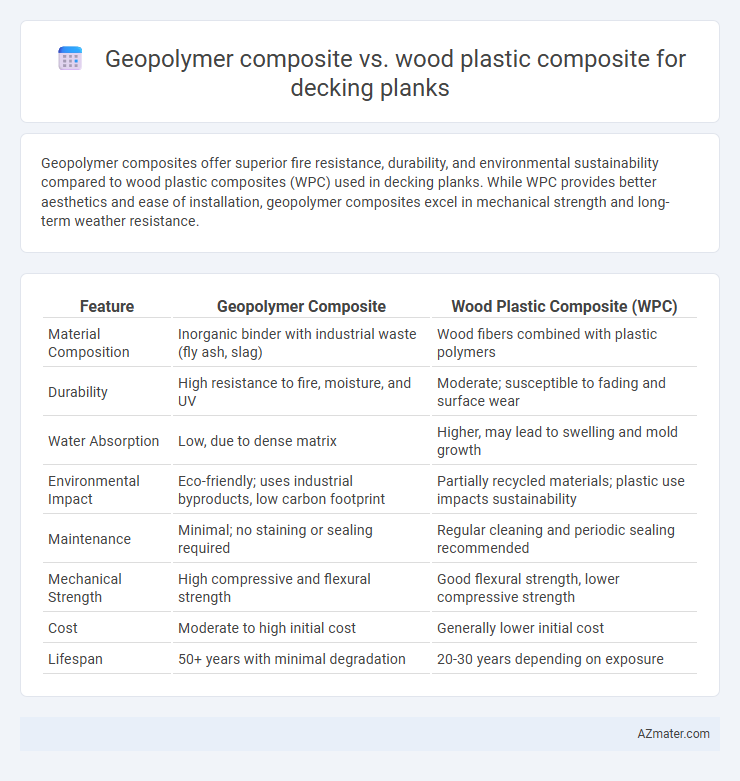
Geopolymer composites offer superior fire resistance, durability, and environmental sustainability compared to wood plastic composites (WPC) used in decking planks. While WPC provides better aesthetics and ease of installation, geopolymer composites excel in mechanical strength and long-term weather resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Geopolymer Composite | Wood Plastic Composite (WPC) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Inorganic binder with industrial waste (fly ash, slag) | Wood fibers combined with plastic polymers |
| Durability | High resistance to fire, moisture, and UV | Moderate; susceptible to fading and surface wear |
| Water Absorption | Low, due to dense matrix | Higher, may lead to swelling and mold growth |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly; uses industrial byproducts, low carbon footprint | Partially recycled materials; plastic use impacts sustainability |
| Maintenance | Minimal; no staining or sealing required | Regular cleaning and periodic sealing recommended |
| Mechanical Strength | High compressive and flexural strength | Good flexural strength, lower compressive strength |
| Cost | Moderate to high initial cost | Generally lower initial cost |
| Lifespan | 50+ years with minimal degradation | 20-30 years depending on exposure |
Introduction to Decking Plank Materials
Decking plank materials vary widely, with geopolymer composites and wood plastic composites (WPC) being notable options for outdoor applications. Geopolymer composites offer superior durability, fire resistance, and environmental sustainability due to their inorganic silica-alumina matrix derived from industrial byproducts. Wood plastic composites combine wood fibers and thermoplastics, providing a balance of natural aesthetics and resistance to moisture and decay, but may have lower fire resistance and strength compared to geopolymer alternatives.
Overview of Geopolymer Composite
Geopolymer composite decking planks offer superior durability and fire resistance compared to traditional wood plastic composites, making them ideal for outdoor applications exposed to harsh weather conditions. These composites are synthesized from industrial byproducts like fly ash and slag, resulting in a low-carbon, eco-friendly material with enhanced structural strength and moisture resistance. Their inorganic polymer matrix provides excellent resistance to UV degradation, rot, and insect damage, significantly extending the lifespan of decking installations.
Overview of Wood Plastic Composite
Wood Plastic Composite (WPC) decking planks combine recycled wood fibers and thermoplastics, offering enhanced durability, low maintenance, and resistance to rot, insects, and weathering compared to traditional wood. WPC materials exhibit improved dimensional stability and require less frequent sealing or staining, making them popular for outdoor applications. Despite environmental benefits from recycled content, WPC can have lower mechanical strength and heat resistance than Geopolymer composites, impacting long-term performance in high-load or extreme weather conditions.
Material Composition and Properties Comparison
Geopolymer composites consist of inorganic aluminosilicate materials activated by alkaline solutions, offering superior fire resistance, thermal stability, and durability compared to wood plastic composites (WPC), which combine wood fibers with thermoplastic resins like polyethylene or polypropylene. WPCs provide better flexibility, moisture resistance, and ease of processing, but they are prone to UV degradation and lower mechanical strength than geopolymer composites. The inorganic matrix in geopolymer composites imparts enhanced structural integrity and environmental resistance, making them suitable for heavy-load decking applications where longevity and minimal maintenance are critical.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Geopolymer composites exhibit superior durability and weather resistance compared to wood plastic composites, with enhanced resistance to UV radiation, moisture, and temperature fluctuations, significantly reducing warping and degradation over time. The inorganic matrix in geopolymer composites provides excellent resistance to fungal decay, insect attacks, and chemical corrosion, extending the lifespan of decking planks in harsh outdoor environments. Wood plastic composites, while moderately weather-resistant, often suffer from swelling, color fading, and mechanical wear under prolonged exposure to extreme weather conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Geopolymer composite decking planks offer a significant environmental advantage by utilizing industrial byproducts such as fly ash and slag, reducing landfill waste and lowering carbon emissions compared to traditional wood plastic composites (WPC), which primarily rely on virgin plastics and wood fibers. The production of geopolymer composites consumes less energy and generates fewer greenhouse gases, contributing to a more sustainable lifecycle and improved durability, which extends the service life of decking surfaces. Wood plastic composites often face challenges in biodegradability and recycling, while geopolymer composites provide enhanced chemical resistance and are more easily recyclable, making them a more ecologically responsible choice for decking applications.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Geopolymer composite decking planks offer more straightforward installation due to their consistent dimensions and higher resistance to warping, eliminating the need for extensive acclimation compared to wood plastic composites. Maintenance for geopolymer composites is minimal, requiring only occasional cleaning without concerns of rot, insect damage, or mold growth, which commonly impact wood plastic composites. Wood plastic composites demand regular sealing and monitoring for surface scratches or fading, increasing long-term upkeep efforts.
Aesthetic Options and Design Flexibility
Geopolymer composite decking planks offer versatile aesthetic options with customizable colors and textures that mimic natural stone while providing superior durability. Wood plastic composites (WPC) provide a wood-like appearance with grain patterns and color variations but may fade or wear over time. The inorganic matrix of geopolymer composites allows greater design flexibility, including intricate shapes and embossing, compared to the limited moldability of WPC materials.
Cost Analysis and Lifespan
Geopolymer composite decking planks generally incur higher initial costs than wood plastic composites (WPC) due to advanced material processing and raw material expenses. Despite this, geopolymer composites offer superior durability and resist degradation from moisture, UV exposure, and biological factors, extending their lifespan up to 50 years compared to WPC's typical 15-25 years. When factoring long-term maintenance, replacement, and lifecycle costs, geopolymer composites provide a more cost-effective solution for decking applications over multiple decades.
Pros and Cons: Geopolymer vs Wood Plastic Composite for Decking
Geopolymer composite decking offers superior durability, fire resistance, and low maintenance compared to wood plastic composite, which can be prone to fading and moisture absorption. Wood plastic composite decking provides a more natural wood look, greater flexibility, and is often easier to install due to its lighter weight. However, geopolymer composites excel in longevity and environmental resistance, making them ideal for harsh weather conditions, while wood plastic composites may suffer from warping and require periodic sealing.
Infographic: Geopolymer composite vs Wood plastic composite for Decking plank
 azmater.com
azmater.com