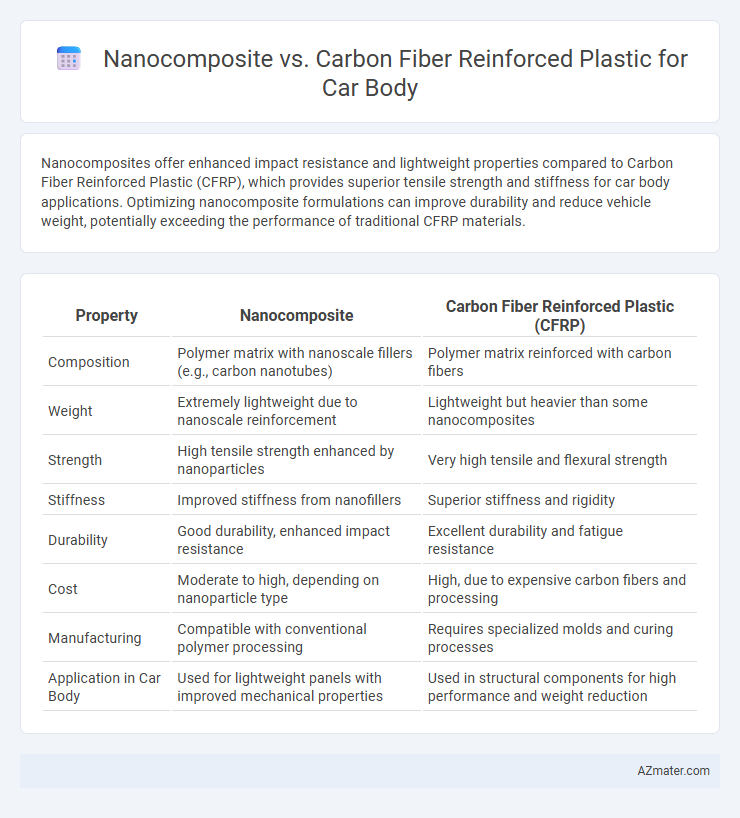
Nanocomposites offer enhanced impact resistance and lightweight properties compared to Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastic (CFRP), which provides superior tensile strength and stiffness for car body applications. Optimizing nanocomposite formulations can improve durability and reduce vehicle weight, potentially exceeding the performance of traditional CFRP materials.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nanocomposite | Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastic (CFRP) |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Polymer matrix with nanoscale fillers (e.g., carbon nanotubes) | Polymer matrix reinforced with carbon fibers |
| Weight | Extremely lightweight due to nanoscale reinforcement | Lightweight but heavier than some nanocomposites |
| Strength | High tensile strength enhanced by nanoparticles | Very high tensile and flexural strength |
| Stiffness | Improved stiffness from nanofillers | Superior stiffness and rigidity |
| Durability | Good durability, enhanced impact resistance | Excellent durability and fatigue resistance |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depending on nanoparticle type | High, due to expensive carbon fibers and processing |
| Manufacturing | Compatible with conventional polymer processing | Requires specialized molds and curing processes |
| Application in Car Body | Used for lightweight panels with improved mechanical properties | Used in structural components for high performance and weight reduction |
Introduction to Advanced Automotive Materials
Nanocomposites and Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastics (CFRP) represent cutting-edge materials revolutionizing automotive body construction with superior strength-to-weight ratios. Nanocomposites incorporate nanoscale fillers such as carbon nanotubes or graphene into polymer matrices, enhancing mechanical properties, thermal stability, and impact resistance beyond conventional composites. CFRP utilizes woven carbon fibers embedded in a resin matrix, offering exceptional stiffness and lightweight benefits critical for fuel efficiency and crash safety improvements in modern vehicles.
What are Nanocomposites?
Nanocomposites are advanced materials composed of a polymer matrix embedded with nanoparticles such as clay, carbon nanotubes, or graphene, offering enhanced mechanical, thermal, and barrier properties. These nanoparticles improve the strength, stiffness, and impact resistance of car body components while reducing weight compared to conventional materials. Nanocomposites provide superior corrosion resistance and better energy absorption, making them a promising alternative to traditional carbon fiber reinforced plastics (CFRP) in automotive applications.
Understanding Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastics (CFRP)
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastics (CFRP) consist of carbon fibers embedded in a polymer matrix, providing exceptional strength-to-weight ratio critical for automotive applications. CFRP offers superior tensile strength, stiffness, and corrosion resistance compared to traditional materials, making it ideal for lightweight car body structures. Its high durability and fatigue resistance improve vehicle performance and fuel efficiency by significantly reducing overall weight without compromising safety.
Material Properties Comparison: Nanocomposite vs CFRP
Nanocomposites exhibit superior tensile strength and impact resistance compared to Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastic (CFRP), enhancing durability in automotive body panels. The high surface area of nanoparticles enables improved matrix reinforcement, resulting in better stiffness and thermal stability than traditional CFRP composites. Additionally, nanocomposites demonstrate lower weight while maintaining structural integrity, contributing to overall vehicle weight reduction and fuel efficiency improvement.
Weight and Strength: Which Material Leads?
Nanocomposites offer superior weight reduction compared to carbon fiber reinforced plastics (CFRP) due to their enhanced matrix-filler interaction and nanoscale reinforcement, resulting in lighter car bodies without compromising structural integrity. CFRP exhibits exceptional tensile strength and stiffness, making it highly effective for load-bearing automotive components, although typically at a higher weight than optimized nanocomposites. Comparative studies show that nanocomposites can achieve a better strength-to-weight ratio, positioning them as a promising material for next-generation lightweight automotive body structures.
Manufacturing Process and Scalability
Nanocomposites offer a manufacturing advantage by enabling easier integration into existing automotive production lines through processes like injection molding and resin transfer molding, promoting higher throughput and reduced cycle times. Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastic (CFRP) typically involves more complex and labor-intensive methods such as hand lay-up or autoclave curing, which can limit scalability due to longer production durations and higher costs. Scalability challenges are more pronounced for CFRP because of the need for specialized equipment and skilled labor, whereas nanocomposites facilitate mass production with potential for cost reduction and enhanced material performance.
Cost Analysis: Nanocomposite vs CFRP
Nanocomposites offer a cost advantage over Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastic (CFRP) due to lower raw material expenses and simpler manufacturing processes. While CFRP provides superior strength-to-weight ratios, its production involves energy-intensive steps and expensive carbon fibers, driving up costs. Considering automotive applications, nanocomposites present a more economical option for lightweight car bodies without significantly compromising performance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nanocomposites offer enhanced mechanical properties and lower weight compared to traditional Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastics (CFRP), contributing to improved fuel efficiency and reduced vehicle emissions. The production of nanocomposites generally consumes less energy and generates fewer greenhouse gases, supporting a smaller carbon footprint over the vehicle lifecycle. Recycling nanocomposites remains challenging but presents opportunities for sustainability improvements, whereas CFRP recycling technologies are more developed yet still limited in scalability and environmental benefits.
Application Performance in Car Bodies
Nanocomposites offer enhanced impact resistance and improved thermal stability compared to Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastics (CFRP), making them suitable for car body panels exposed to varying environmental conditions. CFRP exhibits superior strength-to-weight ratio and stiffness, providing exceptional structural integrity for critical load-bearing components in automobiles. The application of nanocomposite materials enables better crack propagation resistance, while CFRP ensures lightweight design optimizing fuel efficiency and performance.
Future Prospects and Industry Trends
Nanocomposites are gaining traction in the automotive industry due to their superior mechanical properties, lightweight nature, and cost-effective scalability compared to Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastics (CFRPs). Industry trends indicate a growing investment in nanomaterial research aimed at enhancing durability, impact resistance, and recyclability, positioning nanocomposites as a promising alternative for mass-market car body applications. The future prospects highlight a shift toward integrating environmentally sustainable materials with advanced manufacturing techniques, promoting nanocomposites as key to achieving higher performance and reduced production costs in automotive body design.
Infographic: Nanocomposite vs Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastic for Car Body
 azmater.com
azmater.com