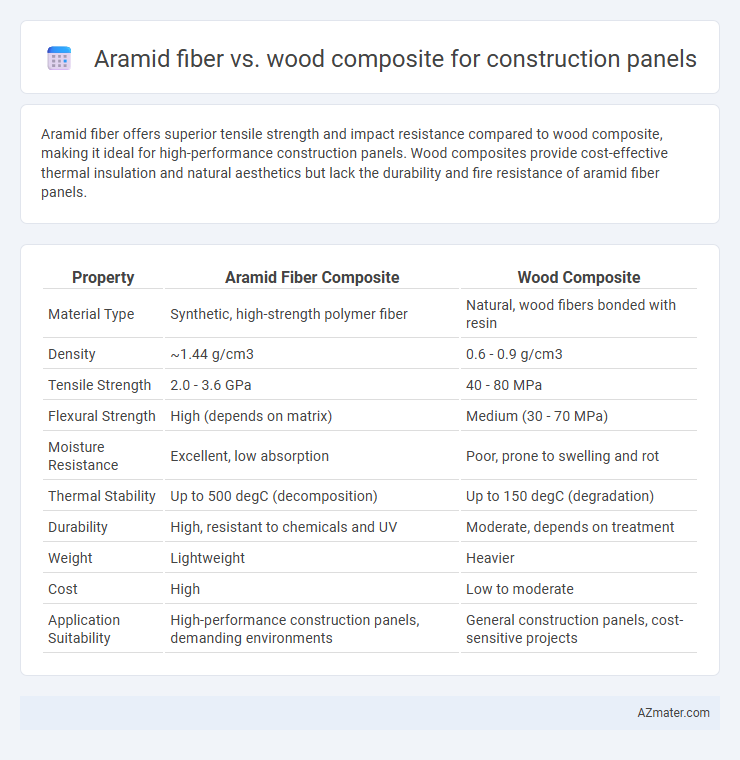
Aramid fiber offers superior tensile strength and impact resistance compared to wood composite, making it ideal for high-performance construction panels. Wood composites provide cost-effective thermal insulation and natural aesthetics but lack the durability and fire resistance of aramid fiber panels.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aramid Fiber Composite | Wood Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic, high-strength polymer fiber | Natural, wood fibers bonded with resin |
| Density | ~1.44 g/cm3 | 0.6 - 0.9 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 2.0 - 3.6 GPa | 40 - 80 MPa |
| Flexural Strength | High (depends on matrix) | Medium (30 - 70 MPa) |
| Moisture Resistance | Excellent, low absorption | Poor, prone to swelling and rot |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 500 degC (decomposition) | Up to 150 degC (degradation) |
| Durability | High, resistant to chemicals and UV | Moderate, depends on treatment |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Cost | High | Low to moderate |
| Application Suitability | High-performance construction panels, demanding environments | General construction panels, cost-sensitive projects |
Introduction to Construction Panel Materials
Aramid fiber and wood composite represent two advanced materials used in construction panels, each offering unique benefits for structural applications. Aramid fiber panels provide exceptional strength-to-weight ratios, high impact resistance, and superior durability against environmental factors, making them ideal for high-performance constructions. Wood composite panels combine natural wood fibers with resin binders to deliver eco-friendly, cost-effective solutions featuring thermal insulation and aesthetic versatility for building interiors and exteriors.
Overview of Aramid Fiber Panels
Aramid fiber panels offer exceptional strength-to-weight ratios, superior impact resistance, and enhanced durability compared to traditional wood composite panels commonly used in construction. Engineered from synthetic aromatic polyamides, these panels exhibit high tensile strength and flame retardancy, making them ideal for structural applications demanding long-term performance under stress. Aramid fiber panels also provide better moisture resistance and dimensional stability, reducing maintenance needs in various environmental conditions.
Properties of Wood Composite Panels
Wood composite panels exhibit high durability, excellent moisture resistance, and superior thermal insulation, making them suitable for various construction applications. Their dimensional stability and resistance to warping enhance long-term performance in structural and decorative uses. These panels also provide good sound insulation and are environmentally friendly due to the utilization of recycled wood fibers and binders.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Aramid fiber-reinforced panels exhibit superior tensile strength and impact resistance compared to wood composites, making them ideal for high-load construction applications. Wood composite panels provide moderate mechanical strength with good flexibility but lack the high stiffness and durability of aramid fiber composites. The enhanced fatigue resistance and lightweight nature of aramid fibers contribute to longer lifespan and improved structural performance in demanding environments.
Durability and Longevity
Aramid fiber composite panels exhibit superior durability and longevity compared to wood composites, thanks to their high tensile strength, resistance to moisture, and excellent impact resistance. Wood composites are prone to swelling, rot, and insect damage, reducing their lifespan in construction applications. Aramid fiber materials maintain structural integrity under harsh environmental conditions, making them ideal for long-term use in construction panels.
Weight and Structural Efficiency
Aramid fiber composites exhibit significantly lower weight compared to wood composites, offering enhanced structural efficiency in construction panels due to their superior strength-to-weight ratio. Wood composites, while heavier, provide adequate load-bearing capacity but often require thicker panels to achieve similar performance levels. The lightweight nature of aramid fiber panels enables easier handling and installation, reducing overall structural demands and improving material longevity in construction applications.
Fire and Moisture Resistance
Aramid fiber composite panels exhibit superior fire resistance due to their inherent flame-retardant properties, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures above 400degC, whereas wood composites are prone to charring and combustion. In terms of moisture resistance, aramid fibers resist water absorption and dimensional changes, preventing warping and fungal growth common in wood-based panels exposed to humidity. These characteristics make aramid fiber composites a more durable option for construction panels in fire-prone and damp environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Aramid fiber panels exhibit superior environmental benefits due to their high durability and resistance to degradation, reducing the need for frequent replacements in construction projects. Wood composites, while biodegradable and sourced from renewable materials, often require energy-intensive processing and may involve adhesives with volatile organic compounds (VOCs), impacting indoor air quality. Sustainable construction practices prioritize the use of wood composites from certified forests combined with manufacturing improvements to minimize environmental impact, whereas aramid fiber panels contribute to longevity and reduced waste over the building lifecycle.
Cost and Installation Considerations
Aramid fiber panels typically incur higher upfront costs compared to wood composites due to the advanced manufacturing and material qualities like superior strength-to-weight ratio and durability. Wood composite panels offer more cost-effective solutions with easier installation processes, leveraging familiarity and existing tools within the construction industry. Installation time and labor costs for aramid fiber can be reduced by its lighter weight, but material expenses remain the primary economic challenge.
Best Applications and Use Cases
Aramid fiber composites excel in high-performance construction panels requiring superior strength-to-weight ratio, impact resistance, and durability, making them ideal for aerospace, automotive, and protective infrastructure applications. Wood composites are best suited for residential and commercial building panels where cost-effectiveness, ease of fabrication, thermal insulation, and sustainability are priorities. Combining both materials can optimize construction panels for hybrid applications demanding a balance of mechanical strength and environmental benefits.
Infographic: Aramid fiber vs Wood composite for Construction panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com