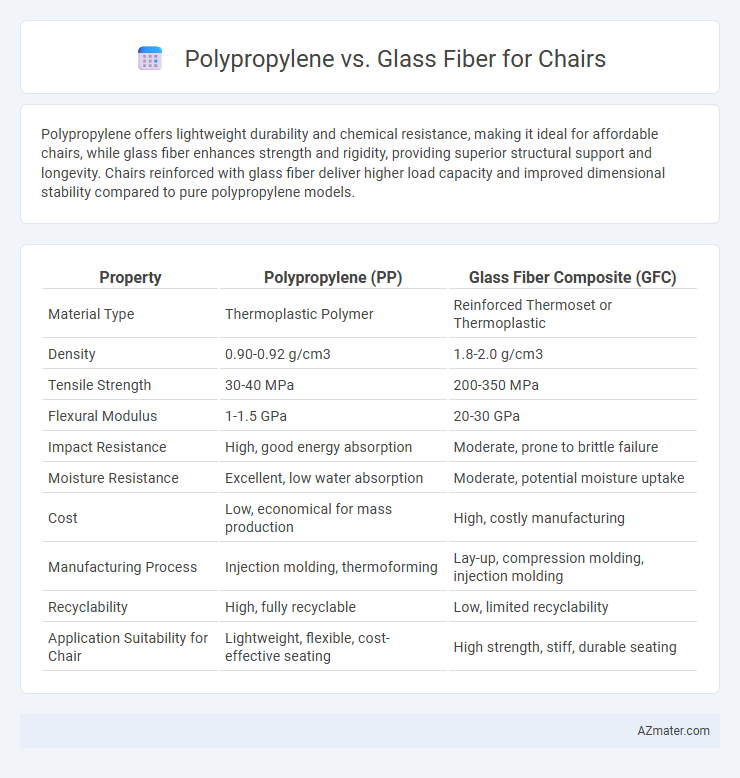
Polypropylene offers lightweight durability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for affordable chairs, while glass fiber enhances strength and rigidity, providing superior structural support and longevity. Chairs reinforced with glass fiber deliver higher load capacity and improved dimensional stability compared to pure polypropylene models.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polypropylene (PP) | Glass Fiber Composite (GFC) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Polymer | Reinforced Thermoset or Thermoplastic |
| Density | 0.90-0.92 g/cm3 | 1.8-2.0 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 30-40 MPa | 200-350 MPa |
| Flexural Modulus | 1-1.5 GPa | 20-30 GPa |
| Impact Resistance | High, good energy absorption | Moderate, prone to brittle failure |
| Moisture Resistance | Excellent, low water absorption | Moderate, potential moisture uptake |
| Cost | Low, economical for mass production | High, costly manufacturing |
| Manufacturing Process | Injection molding, thermoforming | Lay-up, compression molding, injection molding |
| Recyclability | High, fully recyclable | Low, limited recyclability |
| Application Suitability for Chair | Lightweight, flexible, cost-effective seating | High strength, stiff, durable seating |
Introduction to Chair Materials: Polypropylene vs Glass Fiber
Polypropylene offers lightweight durability and flexibility, making it a popular choice for ergonomic and affordable chair designs. Glass fiber enhances strength and rigidity, providing superior structural support and resistance to wear in high-performance seating applications. Comparing these materials reveals a balance between cost-efficiency and long-term durability essential for selecting the ideal chair composition.
Material Composition and Properties
Polypropylene is a thermoplastic polymer known for its lightweight nature, flexibility, and chemical resistance, making it ideal for ergonomic chair designs requiring durability and comfort. Glass fiber, composed of fine strands of glass embedded in a resin matrix, significantly enhances the strength, stiffness, and heat resistance of chair components, resulting in a more rigid and long-lasting structure. Comparing the two, polypropylene offers superior impact resistance and corrosion proofing, while glass fiber provides higher tensile strength and dimensional stability for heavy-duty applications.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Polypropylene offers moderate durability and flexibility, making it resistant to impact and fatigue but less capable of supporting heavy loads over time. Glass fiber-reinforced materials significantly enhance strength and stiffness, providing superior load-bearing capacity and long-term resistance to wear and deformation. Chairs made with glass fiber composites exhibit higher tensile strength and improved durability under stress compared to standard polypropylene counterparts.
Weight and Portability Considerations
Polypropylene chairs typically weigh significantly less than glass fiber alternatives, enhancing portability for various settings such as outdoor events or flexible office layouts. Glass fiber, being denser and heavier, provides superior strength but limits ease of movement and transport. Lightweight polypropylene enables effortless handling without compromising durability, ideal for users prioritizing mobility.
Comfort and Ergonomics
Polypropylene offers lightweight flexibility and cushioning that enhances chair comfort by conforming slightly to body contours, making it suitable for ergonomic designs focused on pressure distribution. Glass fiber, integrated as reinforcement in polypropylene composites, increases structural strength and stability, which supports ergonomic posture alignment but can reduce overall seat flexibility. Chairs using glass fiber-reinforced polypropylene balance durability with ergonomic support, providing firmer comfort ideal for prolonged seating sessions.
Aesthetic and Design Flexibility
Polypropylene offers exceptional design flexibility for chairs due to its ability to be easily molded into complex shapes and vibrant colors, enabling modern, ergonomic aesthetics. Glass fiber-reinforced materials provide a sleek, high-end finish with enhanced structural integrity but limit intricate design variations due to their rigid composite nature. Combining polypropylene with glass fibers can optimize both aesthetic appeal and durability, balancing creative design freedom with strength.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polypropylene chairs offer lower environmental impact due to their recyclable nature and reduced energy consumption during production compared to glass fiber composites. Glass fiber chairs, while durable and strong, involve energy-intensive manufacturing processes and challenges in recycling, which can increase their carbon footprint. Choosing polypropylene supports sustainability through easier end-of-life recycling and less resource-intensive fabrication.
Cost Effectiveness and Affordability
Polypropylene offers greater cost effectiveness and affordability compared to glass fiber, as it is a cheaper raw material with lower manufacturing expenses. Glass fiber chairs typically have higher production costs due to the material's strength and durability, resulting in a pricier end product. For budget-conscious consumers, polypropylene chairs provide a cost-efficient solution without significant compromise in quality.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Polypropylene chairs offer easy maintenance with their smooth, non-porous surface that resists stains and can be cleaned using mild soap and water, making them ideal for environments needing frequent cleaning. Glass fiber chairs require more careful handling as their textured surfaces can trap dirt and may need specialized cleaning agents to avoid damage. Regular inspections and gentle cleaning practices extend the lifespan of glass fiber chairs, while polypropylene demands minimal upkeep, enhancing its appeal for low-maintenance applications.
Best Applications and Use Cases
Polypropylene is ideal for lightweight, flexible chairs used in indoor and outdoor environments where resistance to moisture and chemicals is essential, such as dining or patio furniture. Glass fiber-reinforced chairs offer superior strength and rigidity, making them suitable for ergonomic office seating, industrial applications, and heavy-duty use requiring long-term durability and structural support. Choosing between polypropylene and glass fiber depends on the need for cost-effective, weather-resistant seating versus high-strength, load-bearing furniture solutions.
Infographic: Polypropylene vs Glass fiber for Chair
 azmater.com
azmater.com