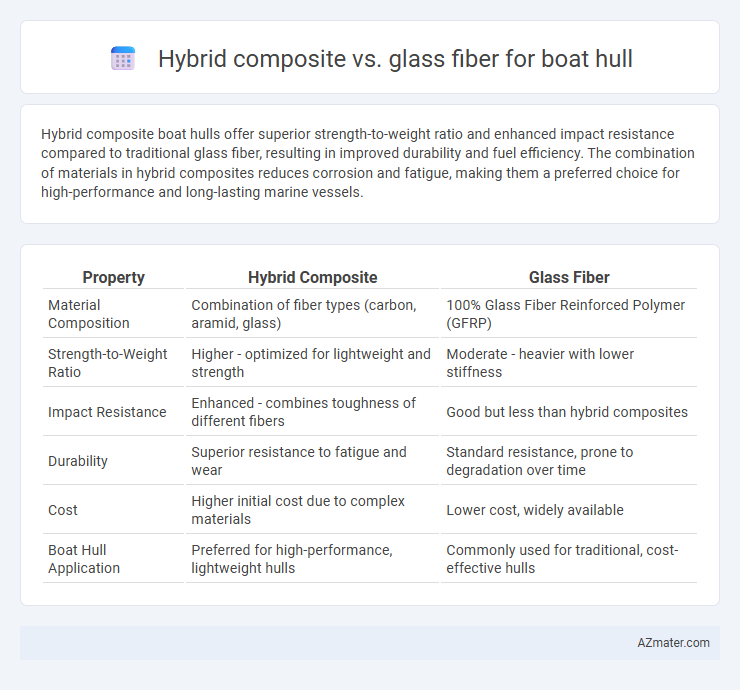
Hybrid composite boat hulls offer superior strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced impact resistance compared to traditional glass fiber, resulting in improved durability and fuel efficiency. The combination of materials in hybrid composites reduces corrosion and fatigue, making them a preferred choice for high-performance and long-lasting marine vessels.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hybrid Composite | Glass Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Combination of fiber types (carbon, aramid, glass) | 100% Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer (GFRP) |
| Strength-to-Weight Ratio | Higher - optimized for lightweight and strength | Moderate - heavier with lower stiffness |
| Impact Resistance | Enhanced - combines toughness of different fibers | Good but less than hybrid composites |
| Durability | Superior resistance to fatigue and wear | Standard resistance, prone to degradation over time |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to complex materials | Lower cost, widely available |
| Boat Hull Application | Preferred for high-performance, lightweight hulls | Commonly used for traditional, cost-effective hulls |
Introduction to Boat Hull Materials
Boat hulls rely on advanced materials to ensure durability, strength, and weight efficiency, with hybrid composites and glass fiber being prominent choices. Hybrid composites combine fibers like carbon and glass to optimize mechanical properties and resistance to impact, surpassing traditional glass fiber in stiffness and fatigue performance. Glass fiber remains widely used due to its cost-effectiveness, corrosion resistance, and ease of fabrication, but hybrid composites offer superior structural integrity and weight savings crucial for high-performance marine vessels.
Overview of Hybrid Composites
Hybrid composites for boat hulls combine glass fibers with other reinforcing materials such as carbon or aramid fibers to optimize strength, stiffness, and durability. These composites offer superior impact resistance and weight savings compared to standard glass fiber, resulting in enhanced performance and fuel efficiency. Hybrid systems balance cost-effectiveness with mechanical properties, making them increasingly popular in marine applications requiring high structural integrity and corrosion resistance.
Glass Fiber Composites Explained
Glass fiber composites dominate boat hull construction due to their high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness compared to hybrid composites. These composites consist of woven glass fibers embedded in a resin matrix, offering excellent durability and impact resistance crucial for marine environments. The predictable performance and ease of repair make glass fiber composites a preferred choice over hybrid composites, which often combine multiple fibers but can complicate manufacturing and maintenance.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Hybrid composites for boat hulls combine fibers like carbon and glass, offering superior strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced impact resistance compared to traditional glass fiber alone. Glass fiber provides good durability and cost-effectiveness but lacks the stiffness and fatigue resistance found in hybrid composites, leading to potential limitations in high-performance marine applications. Hybrid composites exhibit improved longevity and structural integrity under dynamic loads, making them ideal for demanding marine environments.
Weight and Performance Considerations
Hybrid composite boat hulls combine materials such as carbon fiber and glass fiber, resulting in significantly reduced weight compared to traditional glass fiber hulls. This weight reduction enhances vessel speed and fuel efficiency, improving overall performance in marine environments. Glass fiber hulls offer durability and cost-effectiveness but typically increase hull weight, which can limit acceleration and agility in performance-driven boating applications.
Cost Analysis: Hybrid Composite vs Glass Fiber
Hybrid composites typically offer a more cost-effective solution for boat hulls by combining materials like carbon fiber and glass fiber, which balance performance and price. Glass fiber remains the most economical option due to its lower raw material and manufacturing costs, though it may require more maintenance over the boat's lifetime. Evaluating total lifecycle costs, hybrid composites can provide better long-term value through enhanced durability and reduced repair frequency compared to glass fiber hulls.
Maintenance and Longevity Factors
Hybrid composite boat hulls exhibit superior resistance to environmental degradation, combining carbon fiber and glass fiber strengths to reduce maintenance frequency compared to pure glass fiber hulls. Glass fiber hulls are prone to osmotic blistering and require more frequent inspections and repairs, impacting long-term durability. The synergistic properties of hybrid composites offer enhanced toughness and corrosion resistance, extending hull lifespan and lowering upkeep costs significantly.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hybrid composites for boat hulls combine natural fibers with synthetic materials, reducing reliance on non-renewable resources and lowering carbon footprints compared to traditional glass fiber composites. Glass fiber composites often involve energy-intensive manufacturing and are challenging to recycle, leading to significant environmental burdens over their lifecycle. The integration of bio-based fibers in hybrid composites enhances biodegradability and supports sustainable marine applications by minimizing waste and pollution.
Applications in Modern Boat Design
Hybrid composites in boat hull construction combine carbon fiber with glass fiber to enhance strength-to-weight ratio, offering superior impact resistance and fatigue durability compared to traditional glass fiber hulls. Modern boat design leverages hybrid composites for high-performance vessels, including racing yachts and luxury yachts, where weight reduction directly correlates with speed and fuel efficiency. Glass fiber remains widely used for recreational boats and commercial fishing vessels due to its cost-effectiveness, ease of repair, and proven long-term durability in marine environments.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Boat Hull
Hybrid composites combine carbon and glass fibers, offering superior strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced durability compared to traditional glass fiber alone. Glass fiber remains a cost-effective choice with good impact resistance and ease of repair, making it suitable for budget-conscious builds without compromising basic performance. Selecting the right material depends on your priorities for weight savings, structural performance, and maintenance requirements in marine environments.
Infographic: Hybrid composite vs Glass fiber for Boat hull
 azmater.com
azmater.com