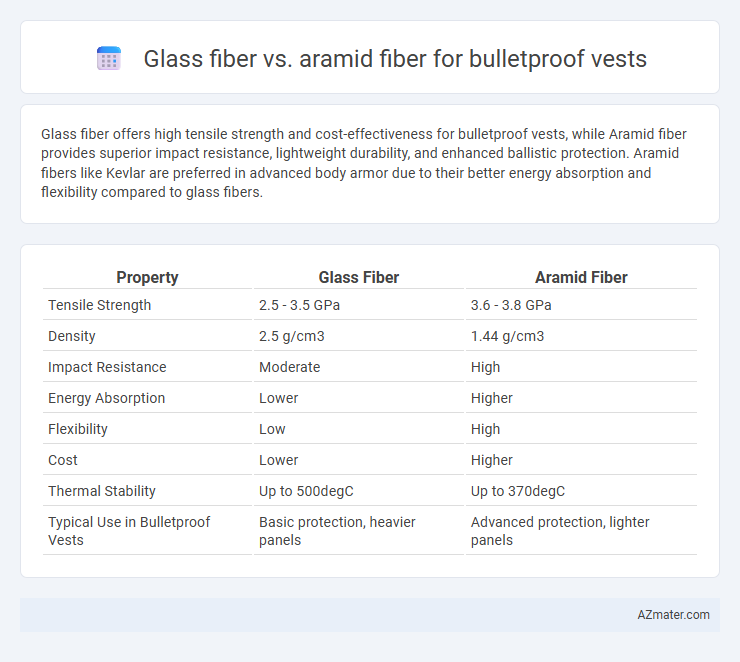
Glass fiber offers high tensile strength and cost-effectiveness for bulletproof vests, while Aramid fiber provides superior impact resistance, lightweight durability, and enhanced ballistic protection. Aramid fibers like Kevlar are preferred in advanced body armor due to their better energy absorption and flexibility compared to glass fibers.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Glass Fiber | Aramid Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 2.5 - 3.5 GPa | 3.6 - 3.8 GPa |
| Density | 2.5 g/cm3 | 1.44 g/cm3 |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Energy Absorption | Lower | Higher |
| Flexibility | Low | High |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 500degC | Up to 370degC |
| Typical Use in Bulletproof Vests | Basic protection, heavier panels | Advanced protection, lighter panels |
Introduction to Ballistic Fibers
Ballistic fibers such as glass fiber and aramid fiber are essential materials in the manufacture of bulletproof vests due to their high tensile strength and lightweight properties. Aramid fibers, including Kevlar and Twaron, offer superior energy absorption and flexibility, providing enhanced ballistic resistance compared to glass fiber. Glass fibers, although less effective in stopping high-velocity projectiles, are often used in composite layers to improve impact resistance and reduce overall vest cost.
Understanding Glass Fiber
Glass fiber offers high tensile strength, lightweight properties, and affordability, making it a common choice for bulletproof vests in cost-sensitive applications. Its excellent impact resistance and stiffness contribute to effective energy dispersion upon ballistic impact, although it generally provides lower toughness compared to aramid fibers like Kevlar. Glass fiber's resistance to moisture and chemicals enhances durability, but it has a higher density and less flexibility than aramid fiber, influencing comfort and wearability in personal armor.
Overview of Aramid Fiber
Aramid fiber, known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, is a synthetic polymer widely used in bulletproof vests due to its high tensile strength and resistance to heat and impact. Unlike glass fiber, aramid fibers such as Kevlar and Twaron offer superior energy absorption and flexibility, making them ideal for personal ballistic protection. The molecular structure of aramid fibers provides enhanced durability and resistance to abrasion, contributing to improved comfort and mobility for wearers in tactical situations.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Glass fiber offers high tensile strength and stiffness with excellent impact resistance, making it effective for dissipating kinetic energy in bulletproof vests. Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar, provides superior tensile strength-to-weight ratio and exceptional toughness, enhancing flexibility and multi-hit protection in ballistic applications. The mechanical properties comparison reveals aramid fiber excels in energy absorption and durability, while glass fiber provides cost-effective rigidity and strong structural support.
Ballistic Performance: Protection Levels
Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar, offers superior ballistic performance compared to glass fiber due to its higher tensile strength and energy absorption capacity, making it effective against higher threat levels like NIJ Level III and IIIA. Glass fiber vests typically provide protection against lower-velocity rounds and are lighter but less capable of stopping rifle rounds or higher-caliber handgun bullets. The enhanced flexibility and durability of aramid fibers enable more layered designs that improve multi-impact resistance and overall protective capabilities in bulletproof vests.
Weight and Comfort Analysis
Glass fiber bulletproof vests are heavier due to the higher density of silica-based fibers, impacting prolonged wear comfort and mobility. Aramid fiber vests, such as those made from Kevlar, offer superior lightweight properties and enhanced flexibility, reducing fatigue during extended use. This combination of lower weight and increased comfort makes aramid fibers the preferred choice for modern ballistic protection.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Aramid fibers offer superior durability and environmental resistance compared to glass fibers, maintaining high tensile strength and flexibility under harsh conditions such as UV exposure, moisture, and temperature fluctuations. Glass fibers tend to degrade faster when exposed to moisture and UV rays, which can compromise the integrity and protective capability of bulletproof vests over time. The enhanced chemical stability and resistance to abrasion in aramid fibers make them more suitable for long-lasting ballistic protection in diverse environmental settings.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Glass fiber offers a more cost-effective solution for bulletproof vests due to its lower raw material and manufacturing expenses, making it widely accessible for mass production. Aramid fiber, while more expensive, provides superior strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced ballistic resistance but is less readily available and incurs higher procurement costs. The trade-off between affordability and advanced protective performance makes glass fiber preferable for budget-conscious applications, whereas aramid fiber suits high-performance needs despite its premium price and limited availability.
Application Scenarios in Body Armor
Glass fiber offers high tensile strength and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for budget-conscious bulletproof vests with moderate threat levels. Aramid fiber excels in lightweight, flexible body armor designed for high-mobility scenarios, such as law enforcement or military operations requiring enhanced ballistic resistance. Both materials serve distinct application scenarios where glass fiber caters to economic mass production and aramid fiber addresses advanced protection needs.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Right Fiber
Aramid fiber exhibits superior ballistic resistance and higher tensile strength compared to glass fiber, making it the preferred choice for bulletproof vests requiring maximum protection. Glass fiber, while more cost-effective and lightweight, typically offers lower impact resistance and durability in high-stress situations. Selecting aramid fiber ensures enhanced flexibility, reduced weight, and improved overall performance in personal body armor applications.
Infographic: Glass fiber vs Aramid fiber for Bulletproof vest
 azmater.com
azmater.com