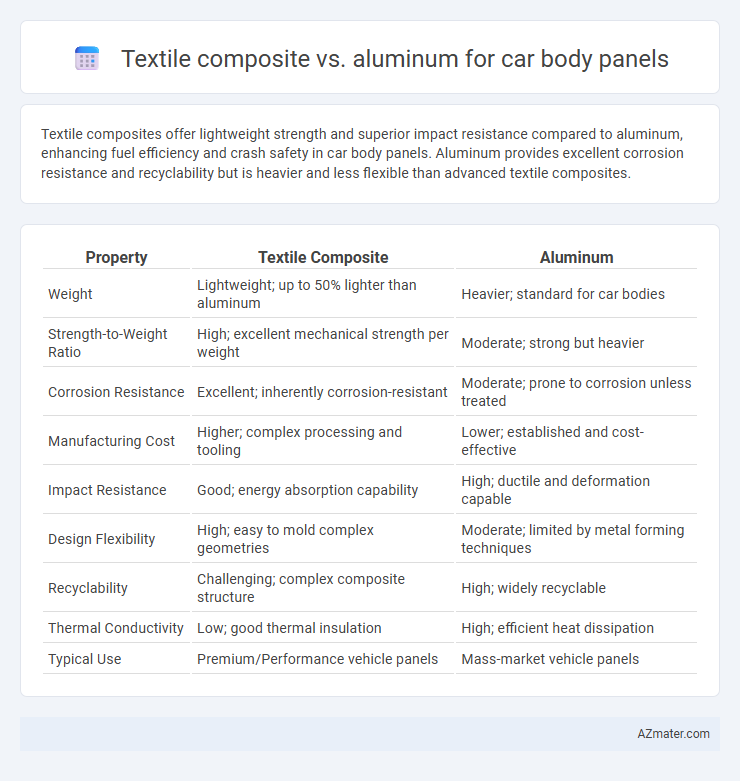
Textile composites offer lightweight strength and superior impact resistance compared to aluminum, enhancing fuel efficiency and crash safety in car body panels. Aluminum provides excellent corrosion resistance and recyclability but is heavier and less flexible than advanced textile composites.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Textile Composite | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Lightweight; up to 50% lighter than aluminum | Heavier; standard for car bodies |
| Strength-to-Weight Ratio | High; excellent mechanical strength per weight | Moderate; strong but heavier |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent; inherently corrosion-resistant | Moderate; prone to corrosion unless treated |
| Manufacturing Cost | Higher; complex processing and tooling | Lower; established and cost-effective |
| Impact Resistance | Good; energy absorption capability | High; ductile and deformation capable |
| Design Flexibility | High; easy to mold complex geometries | Moderate; limited by metal forming techniques |
| Recyclability | Challenging; complex composite structure | High; widely recyclable |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low; good thermal insulation | High; efficient heat dissipation |
| Typical Use | Premium/Performance vehicle panels | Mass-market vehicle panels |
Introduction to Car Body Materials
Textile composites offer lightweight properties and high strength-to-weight ratios, enhancing fuel efficiency and reducing emissions in car body panels. Aluminum provides excellent corrosion resistance and good formability, contributing to durability and crash safety in automotive applications. Both materials play critical roles in advancing vehicle structural performance and weight reduction strategies in modern car manufacturing.
Overview of Textile Composites
Textile composites for car body panels offer high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent impact resistance, surpassing traditional aluminum in reducing vehicle weight and improving fuel efficiency. These composites consist of woven fibers like carbon or glass embedded in resin matrices, providing enhanced flexibility and damage tolerance. Advances in manufacturing techniques allow for complex shapes and superior corrosion resistance compared to aluminum, making textile composites a viable alternative in automotive design.
Properties of Aluminum in Automotive Applications
Aluminum offers a high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance, and superior thermal conductivity, making it ideal for car body panels to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. Its malleability allows for complex shapes and precise engineering, enhancing vehicle design flexibility without compromising durability. Aluminum's recyclability further supports sustainable automotive manufacturing by lowering environmental impact compared to traditional materials.
Weight Comparison: Textile Composite vs Aluminum
Textile composites offer a significant weight advantage over aluminum in car body panels, with densities typically around 1.5 g/cm3 compared to aluminum's 2.7 g/cm3, resulting in up to 40% lighter components. The reduced weight of textile composites contributes to improved fuel efficiency and enhanced vehicle dynamics without compromising structural integrity. These lightweight characteristics make textile composites increasingly favored in automotive applications aiming for performance and sustainability.
Strength and Durability Analysis
Textile composites exhibit high strength-to-weight ratios and superior fatigue resistance compared to aluminum, making them ideal for enhancing car body panel durability. Aluminum, while offering excellent impact resistance and corrosion protection, typically experiences metal fatigue under cyclic loading conditions. Advanced textile composites maintain structural integrity over extended use, outperforming aluminum in long-term durability and weight reduction critical for automotive applications.
Impact Resistance and Safety Considerations
Textile composites exhibit superior impact resistance compared to aluminum, as their high energy absorption capacity reduces deformation during collisions, enhancing occupant safety. Unlike aluminum, which may dent or crack under high impact, textile composites maintain structural integrity and dissipate crash forces more efficiently. Safety regulations increasingly favor textile composites in car body panels due to their lightweight nature combined with enhanced impact resilience, contributing to improved crashworthiness and pedestrian protection.
Corrosion and Environmental Resistance
Textile composites exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to aluminum in car body panels due to their inherent non-metallic nature, which prevents oxidation and rust formation. Aluminum, while lightweight and strong, is prone to surface corrosion and requires protective coatings to maintain durability in harsh environmental conditions. The environmental resistance of textile composites also includes excellent resistance to UV radiation and chemicals, extending their lifespan in automotive applications.
Manufacturing and Production Costs
Textile composites offer significant reductions in manufacturing and production costs for car body panels due to lower material weight and simplified molding processes compared to aluminum. Aluminum requires energy-intensive casting or stamping and high-cost machining, increasing overall expenses. The production cycle for textile composites is faster, reducing labor costs and enabling more cost-effective mass production in the automotive industry.
Sustainability and Recycling Potential
Textile composites offer significant sustainability advantages over aluminum in car body panels due to their lower carbon footprint during production and potential for bio-based fiber integration. Recycling aluminum is energy-intensive but well-established through widespread industrial processes, whereas textile composites face challenges in recycling due to material heterogeneity and lack of economies of scale in composite recycling infrastructure. Innovations in chemical recycling and fiber recovery technologies are improving the recyclability of textile composites, positioning them as a promising, eco-friendly alternative to aluminum in automotive applications.
Future Trends in Car Body Panel Materials
Textile composites are emerging as a lightweight alternative to aluminum in car body panels, offering enhanced strength-to-weight ratios and improved fuel efficiency. Innovations in bio-based fibers and resin matrices promise greater sustainability and recyclability compared to traditional aluminum, which remains valued for its corrosion resistance and structural integrity. Future trends indicate a shift toward hybrid materials combining textile composites with aluminum to optimize performance, reduce emissions, and meet stringent environmental regulations.
Infographic: Textile composite vs Aluminum for Car body panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com