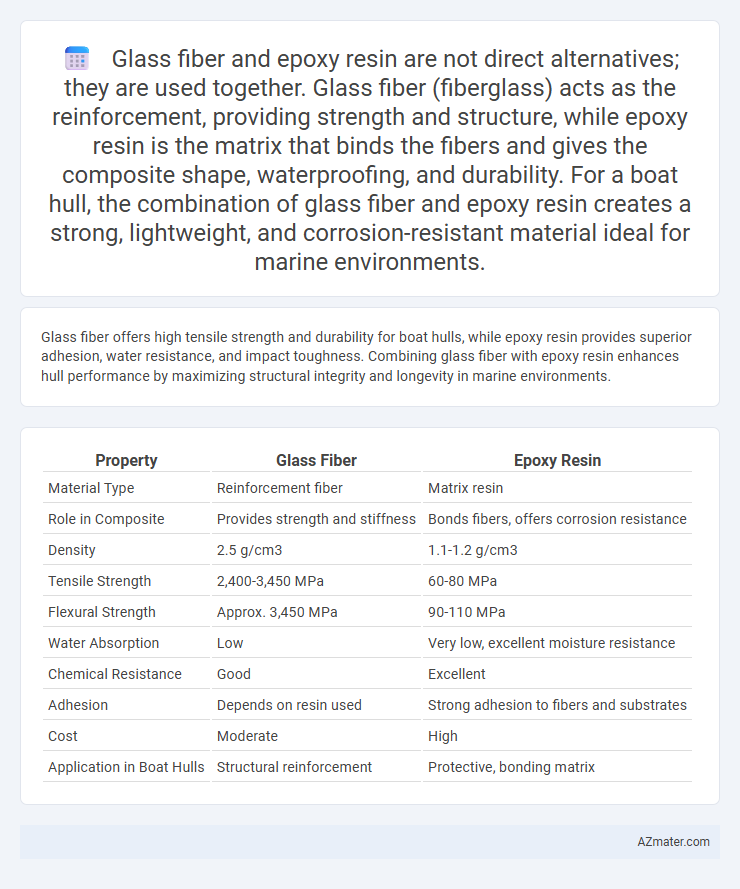
Glass fiber offers high tensile strength and durability for boat hulls, while epoxy resin provides superior adhesion, water resistance, and impact toughness. Combining glass fiber with epoxy resin enhances hull performance by maximizing structural integrity and longevity in marine environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Glass Fiber | Epoxy Resin |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Reinforcement fiber | Matrix resin |
| Role in Composite | Provides strength and stiffness | Bonds fibers, offers corrosion resistance |
| Density | 2.5 g/cm3 | 1.1-1.2 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 2,400-3,450 MPa | 60-80 MPa |
| Flexural Strength | Approx. 3,450 MPa | 90-110 MPa |
| Water Absorption | Low | Very low, excellent moisture resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Adhesion | Depends on resin used | Strong adhesion to fibers and substrates |
| Cost | Moderate | High |
| Application in Boat Hulls | Structural reinforcement | Protective, bonding matrix |
Introduction to Boat Hull Materials
Glass fiber reinforced composites offer high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance, making them a preferred choice for boat hull construction. Epoxy resin acts as a durable matrix that bonds glass fibers, enhancing mechanical properties and resistance to water absorption compared to polyester resins. Combining glass fiber with epoxy resin results in hulls that provide superior structural integrity, impact resistance, and longevity in marine environments.
Overview of Glass Fiber and Epoxy Resin
Glass fiber is a widely used reinforcement material in boat hull construction due to its high tensile strength, lightweight properties, and excellent resistance to corrosion and water absorption. Epoxy resin serves as a superior matrix for bonding glass fibers, offering exceptional adhesion, mechanical strength, and resistance to environmental degradation compared to polyester or vinyl ester resins. The synergy between glass fiber and epoxy resin results in durable, impact-resistant composite hulls that enhance overall boat performance and longevity.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Glass fiber offers excellent tensile strength and impact resistance, making it a popular choice for boat hulls that require robust performance in rough water conditions. Epoxy resin provides superior adhesion and chemical resistance, resulting in enhanced durability and longer lifespan by preventing water absorption and structural degradation. Combining glass fiber with epoxy resin creates hulls with optimal strength and durability, outperforming traditional polyester resin composites.
Weight Considerations for Boat Performance
Glass fiber offers a favorable strength-to-weight ratio, making it a popular choice for lightweight boat hulls that enhance speed and fuel efficiency. Epoxy resin, while generally heavier than polyester alternatives, provides superior bonding and durability that can contribute to a more rigid and resilient hull without excessive weight gain. When optimizing for boat performance, the combination of glass fiber reinforced with epoxy resin achieves an ideal balance between reduced weight and increased structural integrity.
Resistance to Water and Corrosion
Glass fiber reinforced with epoxy resin exhibits exceptional resistance to water absorption and corrosion, making it an ideal material for boat hulls exposed to harsh marine environments. Epoxy resin creates a highly impermeable barrier that prevents water infiltration and protects the glass fibers from hydrolytic degradation. This combination enhances durability, prolongs the lifespan of the hull, and minimizes maintenance caused by water damage and corrosion.
Maintenance and Repair Differences
Glass fiber boat hulls generally require more frequent maintenance due to their susceptibility to surface scratches and delamination, which must be regularly inspected and repaired to prevent water intrusion. Epoxy resin hulls offer superior durability and resistance to moisture absorption, resulting in less frequent repairs and enhanced structural integrity over time. Repairing epoxy resin hulls involves more specialized techniques and materials, often requiring professional expertise, whereas glass fiber repairs are typically more straightforward and suitable for amateur DIY maintenance.
Cost Analysis: Glass Fiber vs Epoxy Resin
Glass fiber remains the most cost-effective material for boat hull construction due to its lower raw material and production expenses compared to epoxy resin. Epoxy resin offers superior strength and durability but comes at a significantly higher price, impacting overall project budgets. Evaluating long-term maintenance and repair costs reveals that epoxy resin may provide better value despite the initial higher investment.
Ease of Fabrication and Application
Glass fiber offers excellent ease of fabrication for boat hulls due to its flexibility, lightweight nature, and ability to conform to complex shapes, making it ideal for mold layup processes. Epoxy resin provides superior adhesion, curing properties, and chemical resistance, ensuring durable bonding with glass fiber layers while allowing precise control over curing time and viscosity during application. The combination of glass fiber reinforcement with epoxy resin results in a high-strength, corrosion-resistant hull that is relatively straightforward to fabricate and apply in marine environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Glass fiber boat hulls rely on energy-intensive production processes and generate non-biodegradable waste, raising concerns about landfill accumulation and recycling difficulties. Epoxy resin, while offering superior durability and resistance, is typically derived from petrochemicals, contributing to carbon emissions and posing challenges in biodegradability and safe disposal. Emerging bio-based epoxy alternatives and improved recycling methods aim to reduce environmental impact and enhance sustainability in marine applications.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Boat Hull
Glass fiber offers excellent tensile strength and flexibility, making it a popular choice for durable and impact-resistant boat hulls, while epoxy resin provides superior adhesion and waterproofing, enhancing structural integrity. Selecting the right material depends on factors such as weight considerations, environmental exposure, and maintenance requirements, with epoxy resin often preferred for high-performance and long-lasting finishes. Combining glass fiber with epoxy resin results in a robust composite that maximizes strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion, ensuring optimal boat hull performance.
Infographic: Glass fiber vs Epoxy resin for Boat hull
 azmater.com
azmater.com