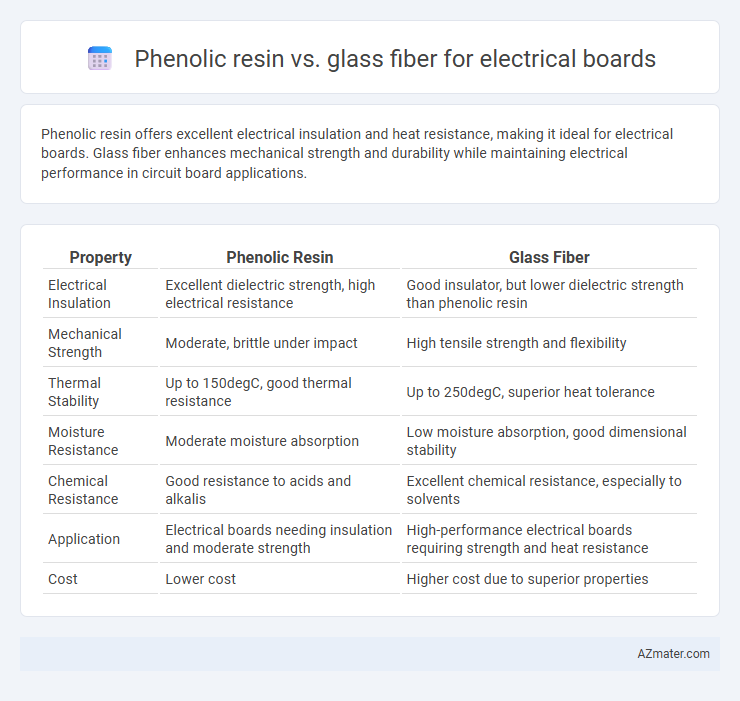
Phenolic resin offers excellent electrical insulation and heat resistance, making it ideal for electrical boards. Glass fiber enhances mechanical strength and durability while maintaining electrical performance in circuit board applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Phenolic Resin | Glass Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent dielectric strength, high electrical resistance | Good insulator, but lower dielectric strength than phenolic resin |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate, brittle under impact | High tensile strength and flexibility |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 150degC, good thermal resistance | Up to 250degC, superior heat tolerance |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate moisture absorption | Low moisture absorption, good dimensional stability |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to acids and alkalis | Excellent chemical resistance, especially to solvents |
| Application | Electrical boards needing insulation and moderate strength | High-performance electrical boards requiring strength and heat resistance |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to superior properties |
Introduction to Electrical Board Materials
Phenolic resin and glass fiber are two common materials used in electrical board manufacturing, each offering distinct properties tailored for specific applications. Phenolic resin provides excellent thermal resistance, electrical insulation, and mechanical strength, making it suitable for standard electrical components and circuit boards. Glass fiber enhances rigidity, dimensional stability, and dielectric strength, often utilized in high-performance printed circuit boards (PCBs) requiring superior durability and heat tolerance.
Overview of Phenolic Resin
Phenolic resin, a thermosetting polymer derived from phenol and formaldehyde, offers high mechanical strength, excellent electrical insulation, and superior heat resistance, making it ideal for electrical boards. It provides excellent flame retardancy and low moisture absorption, ensuring durability and safety in high-performance electrical applications. Phenolic resin's cost-efficiency and ease of molding contribute to its widespread use in printed circuit boards and other electrical components.
Overview of Glass Fiber
Glass fiber offers superior mechanical strength and excellent electrical insulation properties, making it a preferred material for electrical boards in high-performance applications. Its resistance to heat, moisture, and chemicals enhances board durability and reliability under extreme conditions. Compared to phenolic resin, glass fiber provides better dimensional stability and lower dielectric loss, ensuring efficient signal integrity in electronic devices.
Key Properties Comparison
Phenolic resin offers excellent electrical insulation, high thermal stability up to 150degC, and superior chemical resistance, making it ideal for electrical board substrates. Glass fiber provides enhanced mechanical strength, improved dimensional stability, and higher dielectric strength, which boosts the board's durability and performance under mechanical stress. The combination of phenolic resin with glass fiber reinforcement results in a composite material that balances electrical insulation and structural integrity, meeting stringent industry standards like UL94 V-0 flame retardancy.
Electrical Insulation Performance
Phenolic resin offers excellent electrical insulation properties due to its high dielectric strength and low moisture absorption, making it suitable for electrical boards in high-voltage applications. Glass fiber, when combined with phenolic resin, enhances mechanical strength but slightly reduces overall insulation performance due to increased dielectric constant. The balance between phenolic resin's insulating capabilities and glass fiber's reinforcement is critical for optimizing electrical insulation and mechanical durability in printed circuit boards.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Phenolic resin offers excellent mechanical strength and high thermal stability, making it suitable for electrical boards exposed to moderate stress and heat. Glass fiber, integrated into composite materials like FR-4, significantly enhances tensile strength, impact resistance, and durability, ensuring superior performance in high-stress electrical applications. The combination of glass fiber reinforcement with phenolic resin provides improved mechanical durability and dimensional stability under electrical and thermal loads.
Thermal Stability Analysis
Phenolic resin exhibits superior thermal stability with a high glass transition temperature (Tg) around 130-150degC, making it ideal for electrical boards exposed to moderate heat levels. Glass fiber reinforcement enhances mechanical strength and dimensional stability, improving the overall heat resistance of phenolic composites by limiting thermal expansion and deformation. Thermal stability analysis typically shows phenolic resin composites maintain structural integrity and electrical insulation properties under continuous thermal stress up to 150degC, outperforming many other materials in electrical applications.
Fire Resistance Capabilities
Phenolic resin offers superior fire resistance for electrical boards due to its inherent self-extinguishing properties and low smoke emission during combustion. Glass fiber, while enhancing mechanical strength and thermal stability, is inherently non-flammable but requires resin matrixes for fire resistance, which are less effective than phenolic resin alone. Combining phenolic resin with glass fiber creates a composite material that maximizes both fire resistance and structural integrity for electrical board applications.
Cost and Availability
Phenolic resin offers a cost-effective solution for electrical boards due to its low production expenses and wide availability, making it a popular choice in budget-sensitive applications. Glass fiber, while generally more expensive because of its enhanced mechanical strength and thermal stability, may have limited availability depending on regional supply chains and specialized manufacturing processes. Choosing between phenolic resin and glass fiber depends on balancing cost constraints and the required durability for specific electrical board applications.
Best Applications and Industry Recommendations
Phenolic resin is best suited for electrical boards requiring high thermal resistance and excellent electrical insulation, commonly used in consumer electronics and automotive industry components. Glass fiber-reinforced boards offer superior mechanical strength and dimensional stability, making them ideal for industrial machinery and high-performance printed circuit boards (PCBs). Industry recommendations emphasize phenolic resin for cost-effective, low-current applications, while glass fiber is preferred for high-frequency, high-stress environments demanding durability and precision.
Infographic: Phenolic resin vs Glass fiber for Electrical board
 azmater.com
azmater.com