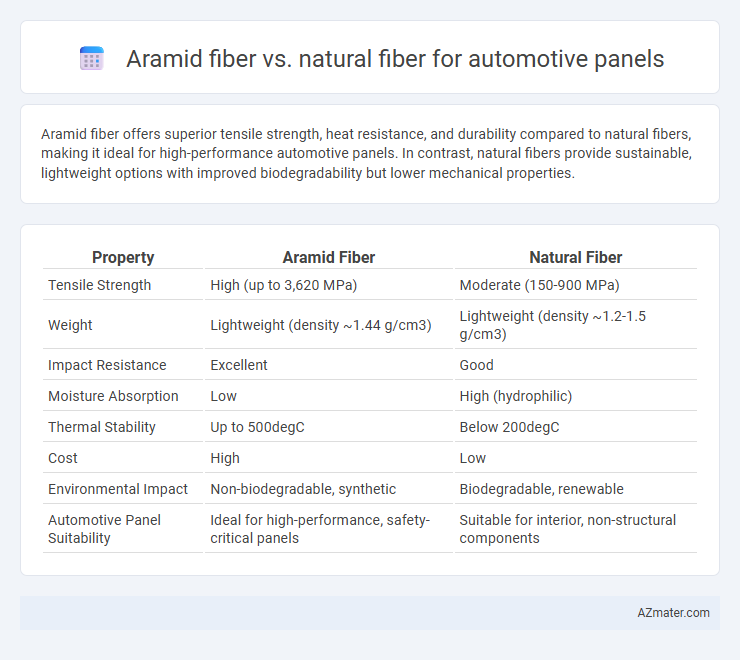
Aramid fiber offers superior tensile strength, heat resistance, and durability compared to natural fibers, making it ideal for high-performance automotive panels. In contrast, natural fibers provide sustainable, lightweight options with improved biodegradability but lower mechanical properties.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aramid Fiber | Natural Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | High (up to 3,620 MPa) | Moderate (150-900 MPa) |
| Weight | Lightweight (density ~1.44 g/cm3) | Lightweight (density ~1.2-1.5 g/cm3) |
| Impact Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Moisture Absorption | Low | High (hydrophilic) |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 500degC | Below 200degC |
| Cost | High | Low |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, synthetic | Biodegradable, renewable |
| Automotive Panel Suitability | Ideal for high-performance, safety-critical panels | Suitable for interior, non-structural components |
Introduction to Automotive Panel Materials
Aramid fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and excellent impact resistance compared to natural fibers, making it ideal for high-performance automotive panels. Natural fibers such as hemp, flax, and jute provide lightweight, sustainable alternatives with good vibration damping but lower durability and moisture resistance. Automotive manufacturers increasingly balance the enhanced mechanical properties of aramid fibers with the eco-friendly advantages of natural fibers to optimize panel performance and sustainability.
Overview of Aramid Fiber Properties
Aramid fibers exhibit exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, high tensile strength, and outstanding thermal stability, making them ideal for automotive panels that demand durability and impact resistance. Their inherent flame retardancy and excellent abrasion resistance enhance safety and longevity in automotive applications. In contrast, natural fibers offer biodegradability and cost-effectiveness but lack the superior mechanical and thermal properties of aramid fibers.
Characteristics of Natural Fibers in Automotive Applications
Natural fibers such as flax, hemp, and jute offer lightweight, renewable, and biodegradable properties, making them increasingly popular in automotive panels. These fibers provide excellent vibration damping, thermal insulation, and energy absorption, with densities typically ranging between 1.2 to 1.5 g/cm3, which contributes to overall weight reduction in vehicles. Despite lower mechanical strength compared to aramid fibers, natural fibers deliver sufficient stiffness and impact resistance for interior components while improving sustainability and reducing carbon footprint in automotive manufacturing.
Mechanical Performance Comparison
Aramid fiber exhibits superior mechanical performance compared to natural fibers for automotive panels, offering high tensile strength (3,000 MPa) and excellent impact resistance. Natural fibers like flax and hemp generally provide lower tensile strength (250-900 MPa) and reduced durability under dynamic loads, limiting their use in high-performance applications. The enhanced stiffness and thermal stability of aramid fibers ensure greater structural integrity and safety in automotive panels.
Weight and Density Considerations
Aramid fiber offers significantly lower density, around 1.44 g/cm3, compared to natural fibers like jute or flax, which range between 1.3 to 1.5 g/cm3 but with varying inconsistencies affecting overall panel weight. The lower density of aramid fibers contributes to lighter automotive panels, enhancing vehicle fuel efficiency and performance. Despite natural fibers providing environmental benefits, aramid fibers deliver superior strength-to-weight ratios crucial for lightweight automotive panel applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Aramid fibers exhibit superior durability and lightweight properties, contributing to reduced vehicle weight and improved fuel efficiency, which lowers overall carbon emissions compared to natural fibers. While natural fibers like hemp or flax offer biodegradability and renewable sourcing, they often require more agricultural inputs and land use, potentially impacting environmental sustainability. The selection between aramid and natural fibers for automotive panels hinges on balancing long-term ecological footprint with material performance and lifecycle emissions.
Cost Analysis: Aramid vs Natural Fibers
Aramid fibers typically cost significantly more than natural fibers due to their complex manufacturing processes and superior performance characteristics such as high tensile strength and thermal resistance. Natural fibers, derived from renewable sources like flax, hemp, or sisal, offer lower material costs and biodegradability but often require additional treatments to meet automotive durability standards. Cost analysis reveals that while aramid fibers increase initial panels production expenses, their enhanced durability and weight savings can reduce overall lifecycle costs in automotive applications compared to natural fibers.
Manufacturing and Processing Differences
Aramid fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and heat resistance compared to natural fibers, making it ideal for high-performance automotive panels requiring durability and thermal stability. Manufacturing aramid fiber panels involves complex processes like polymerization, spinning, and resin impregnation, which require advanced equipment and controlled environments. In contrast, natural fiber panels utilize simpler, eco-friendly processes such as weaving and compression molding, allowing for cost-effective production but with limitations in mechanical properties and uniformity.
Safety and Fire Resistance Evaluation
Aramid fiber offers superior safety performance and fire resistance compared to natural fibers in automotive panels due to its high tensile strength and inherent flame-retardant properties, which reduce the risk of ignition and enhance impact absorption during collisions. Natural fibers, while environmentally friendly and lightweight, generally exhibit lower thermal stability and flammability resistance, making them less effective in meeting stringent automotive fire safety standards. Fire resistance evaluation confirms aramid composites maintain structural integrity at elevated temperatures, providing enhanced protection for vehicle occupants.
Future Trends in Automotive Panel Materials
Aramid fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and heat resistance compared to natural fibers, driving its increased adoption in automotive panels to enhance performance and safety. Emerging trends indicate a shift towards hybrid composites combining aramid fibers with natural fibers to achieve balanced sustainability and durability. Advanced manufacturing techniques and growing demand for lightweight, high-performance materials are accelerating the integration of aramid fibers in future automotive panel designs.
Infographic: Aramid fiber vs Natural fiber for Automotive panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com