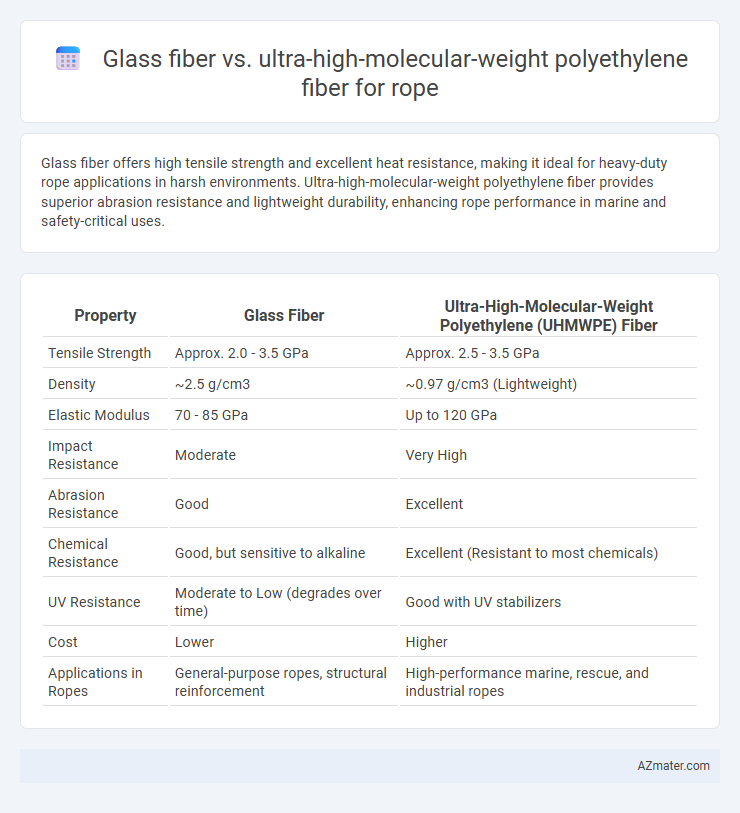
Glass fiber offers high tensile strength and excellent heat resistance, making it ideal for heavy-duty rope applications in harsh environments. Ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene fiber provides superior abrasion resistance and lightweight durability, enhancing rope performance in marine and safety-critical uses.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Glass Fiber | Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | Approx. 2.0 - 3.5 GPa | Approx. 2.5 - 3.5 GPa |
| Density | ~2.5 g/cm3 | ~0.97 g/cm3 (Lightweight) |
| Elastic Modulus | 70 - 85 GPa | Up to 120 GPa |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate | Very High |
| Abrasion Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Chemical Resistance | Good, but sensitive to alkaline | Excellent (Resistant to most chemicals) |
| UV Resistance | Moderate to Low (degrades over time) | Good with UV stabilizers |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Applications in Ropes | General-purpose ropes, structural reinforcement | High-performance marine, rescue, and industrial ropes |
Introduction to Rope Fiber Materials
Glass fiber offers high tensile strength and excellent abrasion resistance, making it suitable for heavy-duty rope applications where durability and load-bearing capacity are critical. Ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) fiber provides exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, superior impact resistance, and low stretch, ideal for lightweight, high-performance ropes used in maritime and rescue operations. Both materials excel in corrosion resistance and longevity, but UHMWPE fibers generally outperform glass fibers in flexibility and fatigue resistance under dynamic loads.
Overview of Glass Fiber Properties
Glass fiber exhibits high tensile strength, excellent heat resistance, and superior durability, making it a reliable choice for rope manufacturing in demanding environments. Its lightweight nature combined with low thermal expansion enhances stability under temperature fluctuations. Resistant to corrosion and chemical degradation, glass fiber maintains performance in harsh industrial and marine applications.
Overview of Ultra-high-molecular-weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) Fiber Properties
Ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength, often exceeding 3 GPa, making it ideal for high-performance rope applications requiring superior load-bearing capacity. Its low density, approximately 0.97 g/cm3, ensures ropes remain lightweight and highly flexible compared to glass fiber counterparts. Additionally, UHMWPE fibers offer excellent abrasion resistance, low moisture absorption, and outstanding chemical resistance, enhancing rope durability in harsh environments.
Tensile Strength Comparison
Ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) fiber exhibits a superior tensile strength, often ranging from 2.4 to 3.1 GPa, compared to glass fiber which typically offers tensile strength between 2.0 to 3.5 GPa. Despite glass fiber's higher modulus, UHMWPE fibers provide higher strength-to-weight ratios and greater energy absorption, making them ideal for high-performance rope applications. UHMWPE fibers also demonstrate excellent fatigue resistance and lower density, enhancing the durability and efficiency of ropes in demanding environments.
Durability and Abrasion Resistance
Ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) fiber offers superior durability and exceptional abrasion resistance compared to glass fiber, making it a preferred choice for high-performance ropes exposed to harsh environments. Glass fiber, while strong and heat resistant, tends to be more brittle and less resistant to wear under repetitive friction or impact. UHMWPE fibers provide enhanced longevity and maintain strength under continuous mechanical stress, ensuring longer service life in demanding applications.
Weight and Flexibility Differences
Glass fiber ropes exhibit higher density ranging from 2.5 to 2.6 g/cm3, resulting in increased weight compared to ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) fibers, which have a density of approximately 0.97 g/cm3. UHMWPE ropes provide superior flexibility due to their low modulus of elasticity, enabling easier handling and greater elongation under load. The significant weight advantage and enhanced flexibility of UHMWPE fibers make them preferable for applications demanding lightweight and maneuverable ropes.
Environmental Resistance and Chemical Stability
Glass fiber offers excellent environmental resistance with high durability against moisture, UV radiation, and temperature fluctuations, making it suitable for harsh outdoor conditions. Ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) fiber exhibits superior chemical stability, resisting solvents, acids, and alkalis while maintaining strength and flexibility in corrosive environments. UHMWPE fibers also demonstrate lower water absorption and better resistance to chemical degradation compared to glass fibers, enhancing their longevity in marine and industrial applications.
Cost Considerations for Glass Fiber vs UHMWPE
Glass fiber ropes generally offer a lower initial cost compared to ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) fiber ropes, making them more budget-friendly for projects with tight financial constraints. However, UHMWPE ropes provide superior durability and resistance to abrasion, potentially resulting in lower long-term replacement and maintenance expenses. When evaluating cost considerations, it is essential to balance the upfront investment of UHMWPE against its extended service life and performance benefits relative to glass fiber.
Common Applications in Industry
Glass fiber ropes are widely used in marine environments, construction, and electrical insulation due to their high tensile strength, durability, and resistance to heat and chemicals. Ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) fiber ropes excel in aerospace, military, and offshore industries, valued for their exceptional abrasion resistance, low stretch, and lightweight properties. Both fiber types provide reliable performance, with glass fiber preferred for thermal stability and UHMWPE chosen for superior strength-to-weight ratios.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Your Rope Needs
Glass fiber offers exceptional tensile strength and resistance to heat, making it suitable for applications requiring durability under high temperatures and abrasive conditions. Ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) fiber provides superior lightweight strength, excellent impact resistance, and high chemical resistance, ideal for ropes used in marine, industrial, and safety equipment where flexibility and corrosion resistance are critical. Selecting the right fiber depends on the environmental factors, load capacity, and specific performance requirements of the rope application.
Infographic: Glass fiber vs Ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene fiber for Rope
 azmater.com
azmater.com