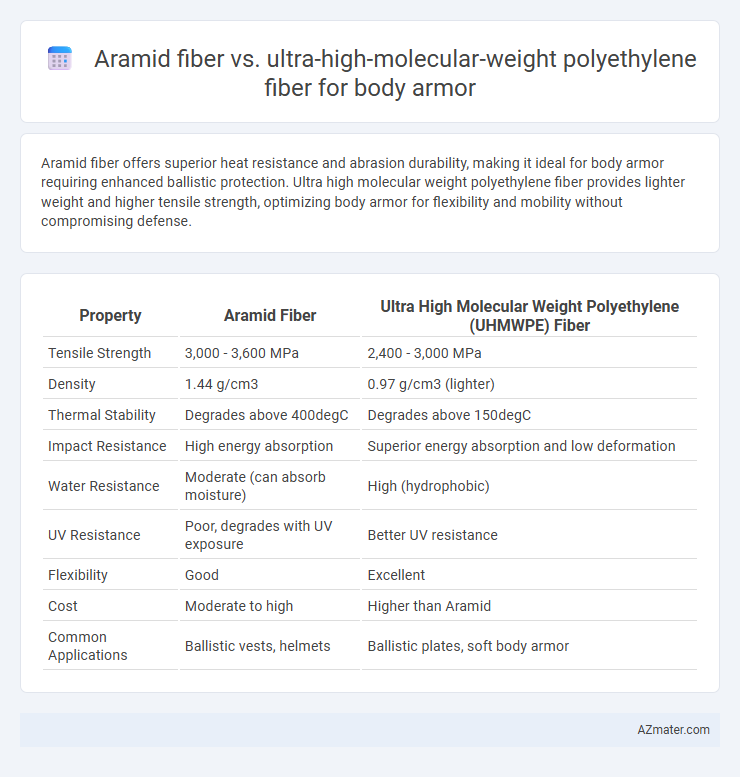
Aramid fiber offers superior heat resistance and abrasion durability, making it ideal for body armor requiring enhanced ballistic protection. Ultra high molecular weight polyethylene fiber provides lighter weight and higher tensile strength, optimizing body armor for flexibility and mobility without compromising defense.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aramid Fiber | Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 3,000 - 3,600 MPa | 2,400 - 3,000 MPa |
| Density | 1.44 g/cm3 | 0.97 g/cm3 (lighter) |
| Thermal Stability | Degrades above 400degC | Degrades above 150degC |
| Impact Resistance | High energy absorption | Superior energy absorption and low deformation |
| Water Resistance | Moderate (can absorb moisture) | High (hydrophobic) |
| UV Resistance | Poor, degrades with UV exposure | Better UV resistance |
| Flexibility | Good | Excellent |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Higher than Aramid |
| Common Applications | Ballistic vests, helmets | Ballistic plates, soft body armor |
Introduction to Body Armor Materials
Aramid fiber and ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) fiber are two primary materials used in body armor due to their exceptional strength-to-weight ratios and ballistic resistance. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, offer high tensile strength and thermal stability, while UHMWPE fibers provide superior energy absorption and lighter weight properties. Selection between aramid and UHMWPE depends on factors like intended ballistic protection level, flexibility, and environmental resistance.
Overview of Aramid Fiber
Aramid fiber, known for its exceptional heat resistance and tensile strength, is a commonly used material in body armor due to its lightweight and impact-absorbing properties. Its molecular structure provides high durability and resistance to abrasion, making it effective against ballistic threats. Aramid fibers such as Kevlar and Twaron are engineered to disperse energy from projectiles, enhancing wearer protection without sacrificing flexibility.
Overview of Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) Fiber
Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) fiber, prized for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to abrasion, outperforms Aramid fiber in specific body armor applications. UHMWPE demonstrates superior ballistic protection with enhanced energy absorption capabilities while maintaining a lighter weight, contributing to increased wearer mobility and comfort. Its resistance to moisture, chemicals, and UV degradation makes UHMWPE an optimal choice for durable, high-performance ballistic protection.
Mechanical Properties: Aramid vs UHMWPE
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, demonstrate high tensile strength and exceptional thermal stability, with tensile strengths ranging from 2.4 to 3.6 GPa and a modulus of 70 to 125 GPa, making them highly resistant to heat and impact. Ultra high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) fibers like Dyneema exhibit superior tensile strength up to 3.6 GPa but with a lower modulus around 100 GPa, offering excellent energy absorption and impact resistance combined with lighter weight. Both fibers provide high-performance mechanical properties for body armor, but UHMWPE offers enhanced ballistic protection at reduced weight, whereas aramid fibers deliver greater heat resistance and structural rigidity.
Ballistic Performance Comparison
Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar, offers excellent ballistic resistance due to its high tensile strength and energy-absorbing properties, making it effective in dissipating the impact of projectiles. Ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) fibers provide superior strength-to-weight ratios with lower density, resulting in lighter body armor while maintaining comparable or better ballistic protection against high-velocity threats. Performance tests indicate UHMWPE fibers typically outperform aramid in multi-hit scenarios and impact resistance, contributing to enhanced durability and user mobility in ballistic armor applications.
Weight and Comfort Considerations
Aramid fiber offers a lightweight yet rigid structure ideal for body armor, but it tends to be less breathable and can retain heat, affecting overall comfort during extended wear. Ultra high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) fiber is lighter than aramid and provides superior flexibility and moisture resistance, enhancing comfort without compromising protection. Both fibers are effective, but UHMWPE is often favored in body armor applications where reduced weight and improved comfort are critical for mobility and user endurance.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, exhibit superior heat resistance and maintain structural integrity under high temperatures, making them highly durable against thermal degradation in body armor applications. Ultra high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) fibers offer exceptional chemical resistance and moisture resistance but can degrade when exposed to prolonged UV radiation and heat, impacting long-term durability. In terms of environmental resistance, aramid fibers withstand harsh conditions better, while UHMWPE fibers require protective coatings to enhance their resistance against environmental factors.
Cost Analysis
Aramid fiber body armor typically costs between $30 and $70 per square meter, with prices influenced by weaving techniques and resin coatings, whereas Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) fiber ranges from $50 to $100 per square meter due to advanced processing and higher raw material costs. UHMWPE offers lighter weight and better fatigue resistance, but its higher initial investment can impact budget considerations in large-scale procurement. Cost efficiency depends on balancing material performance, lifecycle durability, and application-specific protective requirements.
Application Suitability in Body Armor
Aramid fibers such as Kevlar offer excellent ballistic resistance and heat stability, making them suitable for soft body armor designed to stop handgun rounds and provide flexibility. Ultra high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) fibers deliver superior impact resistance and lighter weight, ideal for hard body armor plates and multi-threat protection while maintaining enhanced mobility. The choice depends on desired protection level, weight constraints, and operational environment, with UHMWPE favored for lightweight, multi-hit scenarios and aramid preferred for thermal resistance and pliability.
Future Trends in Body Armor Materials
Advancements in body armor materials increasingly favor Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) fiber for its superior strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced ballistic resistance compared to traditional Aramid fibers like Kevlar. Emerging trends highlight the integration of nanotechnology and composite layering, optimizing UHMWPE's durability and flexibility to meet evolving threat levels. Research focuses on hybrid fibers combining Aramid's thermal stability with UHMWPE's impact absorption, driving the next generation of lightweight, high-performance protective gear.
Infographic: Aramid fiber vs Ultra high molecular weight polyethylene fiber for Body armor
 azmater.com
azmater.com