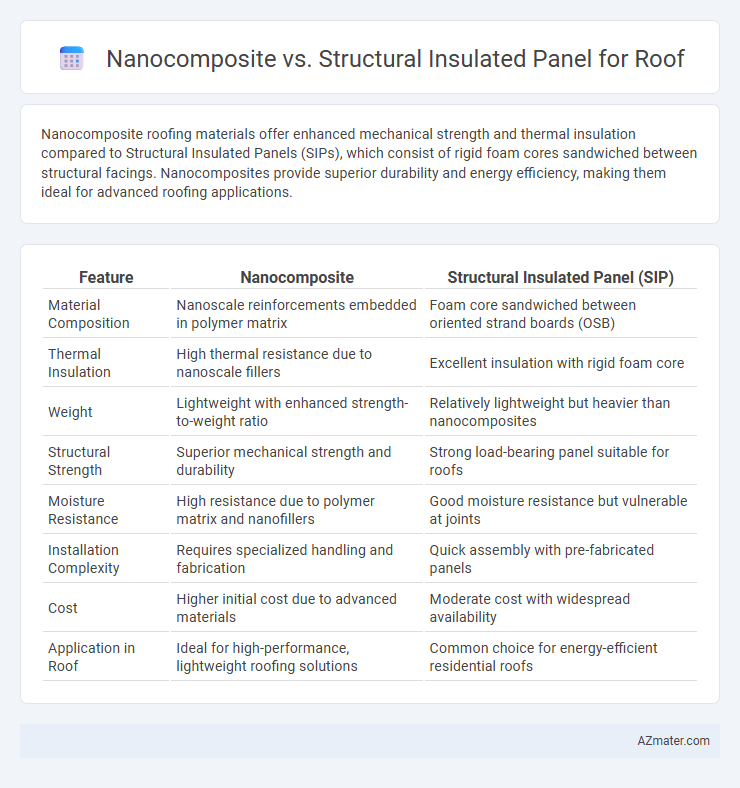
Nanocomposite roofing materials offer enhanced mechanical strength and thermal insulation compared to Structural Insulated Panels (SIPs), which consist of rigid foam cores sandwiched between structural facings. Nanocomposites provide superior durability and energy efficiency, making them ideal for advanced roofing applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Nanocomposite | Structural Insulated Panel (SIP) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Nanoscale reinforcements embedded in polymer matrix | Foam core sandwiched between oriented strand boards (OSB) |
| Thermal Insulation | High thermal resistance due to nanoscale fillers | Excellent insulation with rigid foam core |
| Weight | Lightweight with enhanced strength-to-weight ratio | Relatively lightweight but heavier than nanocomposites |
| Structural Strength | Superior mechanical strength and durability | Strong load-bearing panel suitable for roofs |
| Moisture Resistance | High resistance due to polymer matrix and nanofillers | Good moisture resistance but vulnerable at joints |
| Installation Complexity | Requires specialized handling and fabrication | Quick assembly with pre-fabricated panels |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to advanced materials | Moderate cost with widespread availability |
| Application in Roof | Ideal for high-performance, lightweight roofing solutions | Common choice for energy-efficient residential roofs |
Introduction to Roofing Materials: Nanocomposites vs SIPs
Nanocomposites enhance roofing materials by integrating nanoparticles into polymers, resulting in superior thermal insulation, increased strength, and improved durability compared to conventional materials. Structural Insulated Panels (SIPs) consist of an insulating foam core sandwiched between oriented strand boards (OSB), offering high rigidity, energy efficiency, and faster installation for roofing systems. Evaluating nanocomposites versus SIPs involves considering factors like thermal resistance (R-value), load-bearing capacity, environmental impact, and long-term performance in various climatic conditions.
Composition and Structure of Nanocomposite Roof Panels
Nanocomposite roof panels consist of a polymer matrix infused with nanoparticles such as carbon nanotubes or nanoclays, enhancing strength, thermal insulation, and durability at a microscopic level. These panels exhibit a multi-scale structure where nanoparticles uniformly disperse within the polymer, leading to improved mechanical properties and resistance to UV degradation. In contrast, structural insulated panels (SIPs) typically comprise rigid foam cores sandwiched between oriented strand board (OSB) layers, focusing on bulk insulation and structural support rather than nanoscale material enhancement.
Structural Insulated Panels (SIPs): Design and Functionality
Structural Insulated Panels (SIPs) consist of an insulating foam core sandwiched between two structural facings, usually oriented strand board (OSB), offering high thermal resistance and structural strength for roofing applications. Their design enables rapid assembly and airtight construction, significantly reducing energy loss and improving building durability. Compared to nanocomposites, SIPs provide a balanced solution with predictable load-bearing capacity and enhanced insulation performance specific to roof structures.
Thermal Performance Comparison: Nanocomposites vs SIPs
Nanocomposites exhibit superior thermal insulation due to their nanoparticle-enhanced matrix, allowing reduced thermal conductivity and improved energy efficiency in roofing applications. Structural Insulated Panels (SIPs) offer consistent thermal performance with rigid insulation cores, but generally have higher thermal conductivity compared to nanocomposite-enhanced materials. The integration of nanocomposites in roof systems can reduce heat transfer more effectively than traditional SIPs, contributing to better thermal regulation and lower energy consumption.
Mechanical Strength and Durability in Roofing Applications
Nanocomposite materials exhibit superior mechanical strength and enhanced durability in roofing applications due to their nanoscale reinforcement, which improves impact resistance and load-bearing capacity. Structural insulated panels (SIPs) provide excellent thermal insulation and moderate strength but may be more susceptible to moisture-related degradation over time. The integration of nanocomposites in roofing systems can significantly increase resistance to environmental stressors while maintaining lightweight properties compared to conventional SIPs.
Energy Efficiency: Which Panel Performs Better?
Nanocomposite panels offer superior energy efficiency due to their enhanced thermal insulation properties and lower thermal conductivity compared to traditional structural insulated panels (SIPs). The integration of nanoparticles in nanocomposites improves heat resistance and reduces thermal bridging, leading to better temperature regulation in roofing applications. Structural insulated panels, while effective, generally have higher R-values but less adaptability in thermal performance optimization compared to advanced nanocomposite variants.
Installation Processes and Flexibility
Nanocomposite roofing materials offer enhanced installation flexibility due to their lightweight composition and adaptability to complex roof shapes, reducing labor time and minimizing structural load. In contrast, Structural Insulated Panels (SIPs) provide rapid, large-panel installation that ensures high energy efficiency but require precise handling and skilled labor to maintain structural integrity during assembly. The choice between nanocomposites and SIPs hinges on balancing installation speed, design versatility, and mechanical performance tailored to specific roofing demands.
Fire Resistance and Safety Features
Nanocomposite materials in roofing offer superior fire resistance due to their high thermal stability and ability to inhibit flame spread, enhancing overall safety in hazardous conditions. Structural insulated panels (SIPs) provide excellent insulation and structural strength but may require additional fire-resistant treatments to meet stringent safety codes. Both roofing options can be optimized for fire safety, with nanocomposites inherently offering advanced protection through nano-engineered fire retardants.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nanocomposite materials for roofing offer enhanced thermal insulation and durability with reduced weight, contributing to lower energy consumption and decreased carbon footprint over the building's lifecycle. Structural insulated panels (SIPs) combine rigid foam insulation with OSB, providing high energy efficiency and reduced thermal bridging while facilitating rapid construction, often sourced from renewable materials. Both options improve sustainability, but nanocomposites typically exhibit superior longevity and recyclability, whereas SIPs excel in ease of installation and use of eco-friendly components.
Cost Effectiveness and Long-Term Value
Nanocomposites offer superior cost effectiveness in roofing due to their lightweight properties and enhanced durability, reducing installation time and maintenance expenses. Structural insulated panels (SIPs) provide excellent long-term energy efficiency and thermal insulation, which translates to significant utility savings over time. While nanocomposites lower upfront and lifecycle costs through material innovation, SIPs deliver consistent performance and structural integrity that support enduring value in roofing applications.
Infographic: Nanocomposite vs Structural insulated panel for Roof
 azmater.com
azmater.com