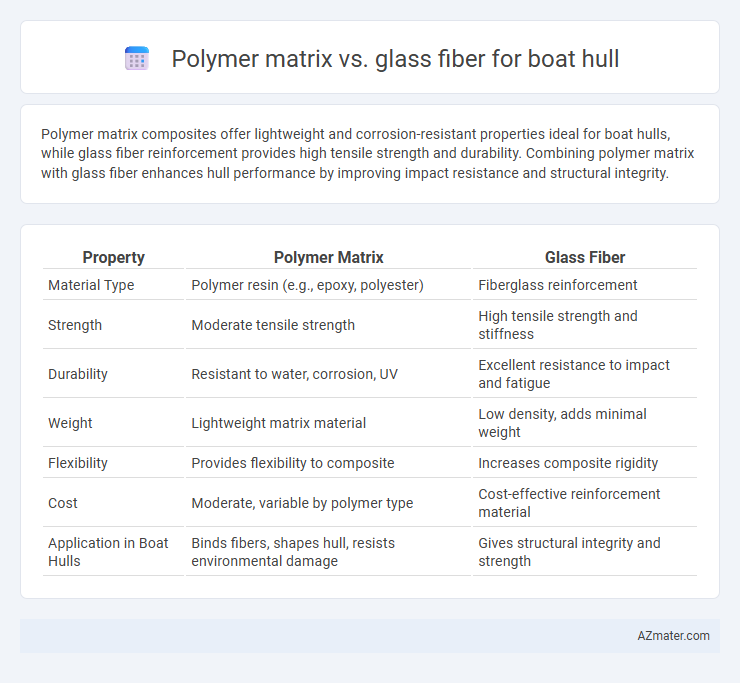
Polymer matrix composites offer lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties ideal for boat hulls, while glass fiber reinforcement provides high tensile strength and durability. Combining polymer matrix with glass fiber enhances hull performance by improving impact resistance and structural integrity.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polymer Matrix | Glass Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Polymer resin (e.g., epoxy, polyester) | Fiberglass reinforcement |
| Strength | Moderate tensile strength | High tensile strength and stiffness |
| Durability | Resistant to water, corrosion, UV | Excellent resistance to impact and fatigue |
| Weight | Lightweight matrix material | Low density, adds minimal weight |
| Flexibility | Provides flexibility to composite | Increases composite rigidity |
| Cost | Moderate, variable by polymer type | Cost-effective reinforcement material |
| Application in Boat Hulls | Binds fibers, shapes hull, resists environmental damage | Gives structural integrity and strength |
Introduction to Boat Hull Materials
Boat hull materials commonly include polymer matrix composites and glass fiber due to their strength-to-weight ratios and corrosion resistance. Polymer matrix composites provide lightweight and durable structures, enhancing fuel efficiency and performance. Glass fiber reinforcements offer excellent tensile strength and impact resistance, making them ideal for marine environments where durability and flexibility are critical.
Overview of Polymer Matrix Composites
Polymer matrix composites (PMCs) consist of a polymer resin combined with reinforcing fibers, typically providing high strength-to-weight ratios crucial for boat hull construction. Unlike traditional Glass fiber composites, PMCs offer enhanced corrosion resistance, improved fatigue durability, and greater design flexibility. These materials contribute to lighter, more fuel-efficient vessels while maintaining structural integrity in marine environments.
Understanding Glass Fiber Reinforcement
Glass fiber reinforcement in polymer matrix composites significantly enhances the mechanical properties of boat hulls, offering high tensile strength and excellent impact resistance crucial for marine environments. The interfacial bonding between the polymer matrix and glass fibers ensures load transfer efficiency, which improves durability and reduces hull weight compared to traditional materials. This combination provides corrosion resistance and flexibility, making glass fiber-reinforced polymers a preferred choice for lightweight, strong, and long-lasting boat hull construction.
Key Differences: Polymer Matrix vs Glass Fiber
Polymer matrix and glass fiber differ primarily in composition and performance for boat hull construction. Polymer matrix, typically resin-based, acts as the binding agent providing corrosion resistance and flexibility, while glass fiber serves as the reinforcing material, offering high tensile strength and impact resistance. The combination of a polymer matrix with glass fiber reinforcement results in a composite material that balances durability, weight, and structural integrity essential for marine applications.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Polymer matrix composites, commonly reinforced with glass fibers, provide high tensile strength and excellent impact resistance crucial for boat hull performance. Glass fiber reinforcements significantly enhance the composite's durability by offering superior resistance to fatigue, corrosion, and environmental degradation in marine conditions. Comparing strength, glass fiber composites deliver an optimal balance of stiffness and flexibility, ensuring long-term structural integrity and reliable performance in harsh aquatic environments.
Weight and Performance Implications
Polymer matrix composites in boat hulls offer significant weight reduction compared to traditional materials, enhancing fuel efficiency and speed. Glass fiber reinforcements provide robust mechanical strength and impact resistance, crucial for durability in marine environments. The combination of lightweight polymer matrices with glass fiber optimizes hull performance by balancing strength, stiffness, and corrosion resistance.
Corrosion and Water Resistance
Polymer matrix composites exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to glass fiber materials, making them ideal for boat hulls exposed to harsh marine environments. Glass fiber tends to absorb water over time, leading to potential swelling, delamination, and reduced structural integrity, while polymer matrices provide enhanced water resistance and durability. The non-porous nature of polymer matrices significantly reduces the risk of corrosion and water ingress, ensuring longer lifespan and lower maintenance for boat hulls.
Cost Analysis and Long-term Value
Polymer matrix composites typically offer lower initial costs compared to glass fiber due to simpler processing and material expenses, making them attractive for budget-conscious boat hull manufacturing. Glass fiber reinforcement, while potentially more expensive upfront, provides superior durability and impact resistance, resulting in lower maintenance costs and enhanced long-term value. Over the vessel's lifecycle, the investment in glass fiber hulls often yields higher resale value and reduced repair frequency, justifying the initial cost premium for many boat owners.
Maintenance and Repair Considerations
Polymer matrix composites in boat hulls offer superior resistance to corrosion and mildew, reducing maintenance frequency compared to glass fiber hulls that are prone to water absorption and osmosis. Repairing polymer matrix hulls typically requires specialized resins and curing processes, while glass fiber hull repairs are more straightforward and can often be performed DIY with polyester or epoxy resins. Long-term durability of polymer matrix materials may lower overall lifecycle repair costs despite higher initial repair complexity relative to glass fiber alternatives.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Boat Hull
Selecting the appropriate material for a boat hull significantly impacts durability and performance, with polymer matrix composites offering lightweight properties and corrosion resistance, while glass fiber provides high strength and affordability. Polymer matrix systems typically enhance flexibility and impact resistance, making them ideal for dynamic marine environments, whereas glass fiber's proven reliability and ease of repair suit economical builds. Evaluating specific application needs, including exposure conditions and maintenance capacity, ensures the right balance between longevity and cost-effectiveness in hull construction.
Infographic: Polymer matrix vs Glass fiber for Boat hull
 azmater.com
azmater.com