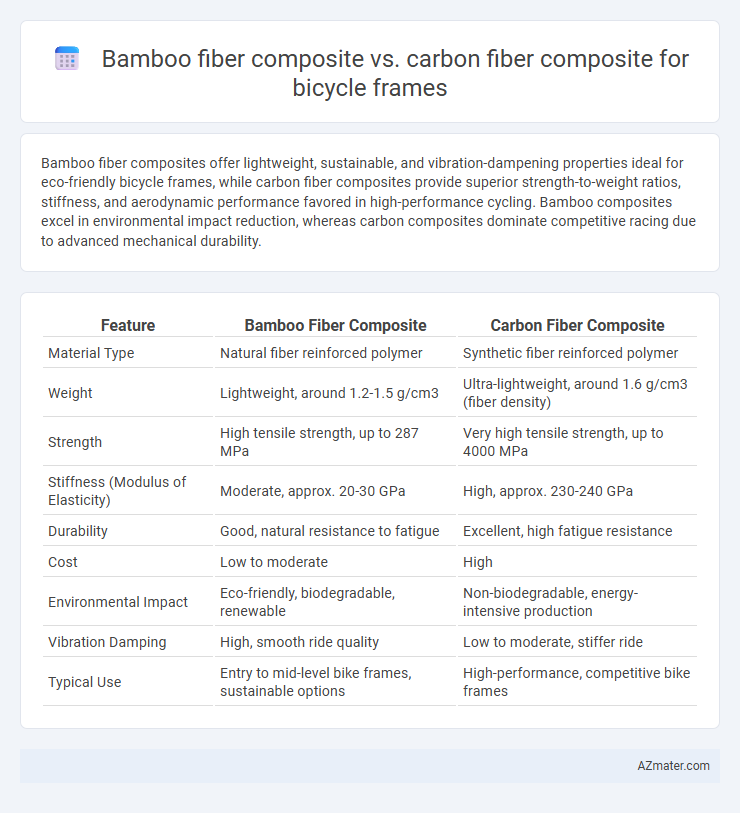
Bamboo fiber composites offer lightweight, sustainable, and vibration-dampening properties ideal for eco-friendly bicycle frames, while carbon fiber composites provide superior strength-to-weight ratios, stiffness, and aerodynamic performance favored in high-performance cycling. Bamboo composites excel in environmental impact reduction, whereas carbon composites dominate competitive racing due to advanced mechanical durability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bamboo Fiber Composite | Carbon Fiber Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Natural fiber reinforced polymer | Synthetic fiber reinforced polymer |
| Weight | Lightweight, around 1.2-1.5 g/cm3 | Ultra-lightweight, around 1.6 g/cm3 (fiber density) |
| Strength | High tensile strength, up to 287 MPa | Very high tensile strength, up to 4000 MPa |
| Stiffness (Modulus of Elasticity) | Moderate, approx. 20-30 GPa | High, approx. 230-240 GPa |
| Durability | Good, natural resistance to fatigue | Excellent, high fatigue resistance |
| Cost | Low to moderate | High |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, biodegradable, renewable | Non-biodegradable, energy-intensive production |
| Vibration Damping | High, smooth ride quality | Low to moderate, stiffer ride |
| Typical Use | Entry to mid-level bike frames, sustainable options | High-performance, competitive bike frames |
Introduction to Bicycle Frame Materials
Bamboo fiber composite and carbon fiber composite are prominent materials used in bicycle frame construction, each offering distinct advantages in strength-to-weight ratio and environmental impact. Carbon fiber composite excels in providing exceptional stiffness, lightweight performance, and aerodynamic efficiency, making it ideal for professional racing and high-performance bicycles. Bamboo fiber composite emphasizes sustainability and vibration damping, combining natural fibers with resin to create a durable, eco-friendly frame that appeals to environmentally conscious riders.
Overview of Bamboo Fiber Composites
Bamboo fiber composites offer a sustainable alternative to traditional carbon fiber composites for bicycle frames, combining natural fibers with resin matrices to achieve notable strength and flexibility. These composites provide excellent vibration damping and shock absorption, resulting in a smoother ride, while maintaining competitive tensile strength and durability. Bamboo's rapid renewability and lower environmental impact make bamboo fiber composites increasingly attractive for eco-friendly bicycle manufacturing.
Overview of Carbon Fiber Composites
Carbon fiber composites are renowned for their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, making them a preferred material for high-performance bicycle frames. These composites consist of carbon fibers embedded in a resin matrix, providing rigidity, impact resistance, and fatigue durability. The advanced manufacturing techniques enable precise tailoring of fiber orientation, resulting in lightweight frames with superior stiffness and vibration dampening compared to bamboo fiber composites.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Bamboo fiber composites exhibit high tensile strength and excellent vibration damping, making them suitable for resilient bicycle frames with natural shock absorption. In contrast, carbon fiber composites provide superior stiffness-to-weight ratios and enhanced fatigue resistance, resulting in frames that deliver maximum performance and durability under extreme conditions. While bamboo offers renewable sustainability and moderate durability, carbon fiber remains the benchmark for elite strength and long-term structural integrity in high-performance cycling applications.
Weight and Performance Differences
Bamboo fiber composites for bicycle frames offer lightweight properties with a typical density of around 1.2 g/cm3, which is higher than carbon fiber composites, usually around 1.6 g/cm3, but the natural fibers result in excellent vibration damping and a more comfortable ride. Carbon fiber composites outperform in stiffness-to-weight ratio and tensile strength, often exceeding 700 MPa in tensile strength and 70 GPa in modulus of elasticity, translating to superior performance in competitive cycling scenarios. Weight differences see carbon fiber frames typically ranging from 700 to 1,000 grams, while bamboo fiber frames tend to be slightly heavier, usually between 1,200 and 1,500 grams, but bamboo's sustainability and shock absorption make it a viable option for casual and endurance cycling.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bamboo fiber composites demonstrate superior sustainability due to their rapid renewability, biodegradability, and low energy consumption during production compared to carbon fiber composites, which rely heavily on fossil fuel-based raw materials and energy-intensive manufacturing processes. Bamboo's natural carbon sequestration and biodegradability substantially reduce the environmental footprint, whereas carbon fiber composites pose significant end-of-life disposal challenges and contribute to microplastic pollution. The choice of bamboo fiber composites enhances circular economy principles in bicycle frame manufacturing by promoting resource efficiency and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Cost Analysis and Affordability
Bamboo fiber composites for bicycle frames offer significantly lower production costs compared to carbon fiber composites due to the abundant availability and sustainable sourcing of bamboo, resulting in affordable pricing for entry-level to mid-range bicycles. Carbon fiber composites require expensive raw materials and energy-intensive manufacturing processes, leading to higher costs that restrict their use primarily to high-performance and premium frames. When assessing cost analysis and affordability, bamboo fiber composites present a more budget-friendly alternative while still providing reasonable durability and strength for everyday cycling needs.
Comfort and Ride Quality
Bamboo fiber composites offer superior vibration damping and natural flexibility, resulting in enhanced comfort and smoother ride quality compared to carbon fiber composites. Carbon fiber composites provide exceptional stiffness and strength, delivering responsive handling but can transmit more road vibrations to the rider. Choosing bamboo fiber composites prioritizes shock absorption and comfort, making them ideal for endurance rides, whereas carbon fiber composites are favored for performance and speed-focused cycling.
Manufacturing Processes and Scalability
Bamboo fiber composites involve renewable, natural fibers embedded in resin matrices, utilizing low-energy, labor-intensive processes such as hand lay-up or compression molding, which can limit mass production scalability. Carbon fiber composites require high-temperature curing in autoclaves and precise control over fiber orientation, demanding advanced equipment and skilled labor, but allowing for highly scalable automated manufacturing lines suited for high-performance bicycle frames. The scalability of carbon fiber composites benefits from standardized industrial protocols, while bamboo composites face challenges in consistent quality control and rapid production expansion.
Future Trends in Composite Bicycle Frames
Future trends in composite bicycle frames emphasize sustainability and performance, with bamboo fiber composites emerging as eco-friendly alternatives to traditional carbon fiber composites. Bamboo fiber composites offer biodegradability and a lower carbon footprint, appealing to environmentally conscious cyclists, while advancements in hybrid composites aim to combine bamboo's natural vibration damping with carbon fiber's superior strength-to-weight ratio. Innovations in resin technology and fiber treatment are enhancing the durability and mechanical properties of bamboo composites, positioning them as a viable competitor to carbon fiber in the high-performance bicycle market.
Infographic: Bamboo fiber composite vs Carbon fiber composite for Bicycle frame
 azmater.com
azmater.com