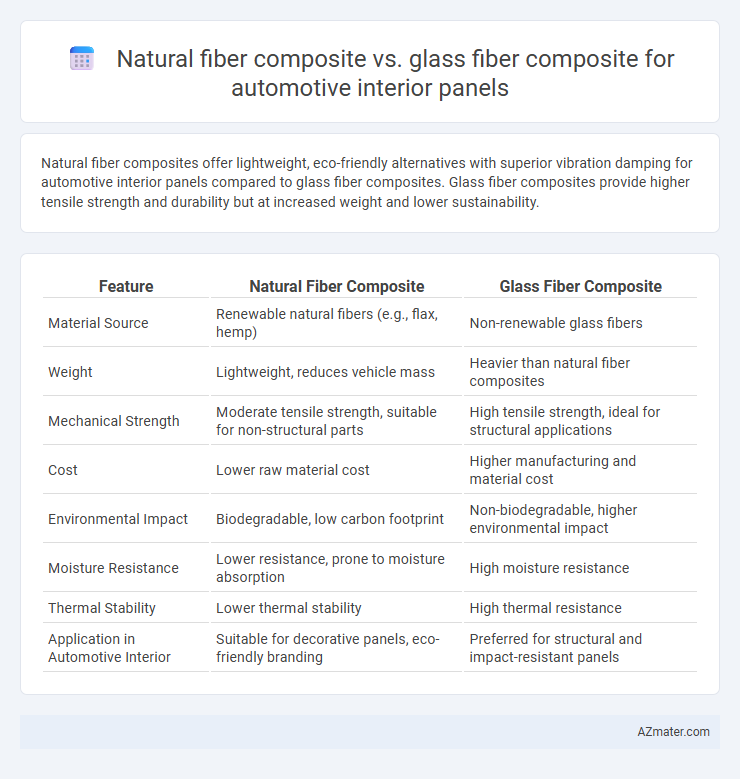
Natural fiber composites offer lightweight, eco-friendly alternatives with superior vibration damping for automotive interior panels compared to glass fiber composites. Glass fiber composites provide higher tensile strength and durability but at increased weight and lower sustainability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Natural Fiber Composite | Glass Fiber Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Renewable natural fibers (e.g., flax, hemp) | Non-renewable glass fibers |
| Weight | Lightweight, reduces vehicle mass | Heavier than natural fiber composites |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate tensile strength, suitable for non-structural parts | High tensile strength, ideal for structural applications |
| Cost | Lower raw material cost | Higher manufacturing and material cost |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, higher environmental impact |
| Moisture Resistance | Lower resistance, prone to moisture absorption | High moisture resistance |
| Thermal Stability | Lower thermal stability | High thermal resistance |
| Application in Automotive Interior | Suitable for decorative panels, eco-friendly branding | Preferred for structural and impact-resistant panels |
Introduction to Automotive Interior Panels
Automotive interior panels serve as critical components that combine aesthetics, comfort, and structural functionality within vehicle cabins. Natural fiber composites, made from materials like hemp, flax, and kenaf, offer lightweight, renewable alternatives with excellent vibration damping and improved sustainability compared to traditional glass fiber composites. Glass fiber composites retain superior strength, durability, and heat resistance, making them a standard choice for high-performance automotive interior applications despite environmental concerns.
Overview of Natural Fiber Composites
Natural fiber composites (NFCs) in automotive interior panels offer advantages like reduced weight, enhanced sustainability, and improved recyclability compared to glass fiber composites. NFCs typically use fibers such as flax, hemp, jute, or kenaf combined with polymer matrices, resulting in lower environmental impact and comparable mechanical properties for non-structural applications. Their biodegradability and reduced carbon footprint provide automotive manufacturers with eco-friendly alternatives that meet increasing regulatory and consumer demands for green materials.
Overview of Glass Fiber Composites
Glass fiber composites, composed of glass fibers embedded in a polymer matrix, are widely used in automotive interior panels due to their high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent durability. These composites offer superior resistance to heat, chemicals, and moisture, ensuring long-lasting performance in demanding automotive environments. Their ability to be molded into complex shapes allows for design flexibility while maintaining structural integrity and surface quality essential for interior applications.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Durability
Natural fiber composites offer moderate tensile strength and enhanced impact resistance, making them suitable for lightweight automotive interior panels while providing sustainable alternatives to traditional materials. Glass fiber composites exhibit superior mechanical strength and higher durability, with excellent resistance to fatigue and wear, ensuring long-term performance under mechanical stress. The choice depends on the balance between weight savings, cost-effectiveness, environmental impact, and required mechanical performance for specific automotive interior applications.
Weight and Density Comparison
Natural fiber composites offer significantly lower density, typically around 1.2 g/cm3, compared to glass fiber composites, which average about 2.5 g/cm3, resulting in lighter automotive interior panels. This reduced weight enhances fuel efficiency and reduces vehicle emissions by decreasing overall mass. The lower density of natural fibers also contributes to improved vibration damping and comfort inside the vehicle cabin.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Natural fiber composites, made from renewable resources like flax, hemp, or kenaf fibers, exhibit lower carbon footprints and enhanced biodegradability compared to glass fiber composites, which rely on energy-intensive production of glass fibers. Their reduced environmental impact includes lower emission of greenhouse gases during manufacturing and improved end-of-life disposal options, contributing to automotive industry's sustainability goals. These composites also offer weight reduction benefits, increasing fuel efficiency and further decreasing overall carbon emissions during vehicle use.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Natural fiber composites offer significant cost advantages over glass fiber composites for automotive interior panels, primarily due to lower raw material prices and reduced processing energy requirements. The biodegradability and renewable nature of natural fibers can lead to longer-term economic benefits, including lower disposal costs and potential tax incentives. However, glass fiber composites provide higher durability and performance, which might justify their higher initial costs in applications where longevity and strength are critical.
Manufacturing Processes and Compatibility
Natural fiber composites for automotive interior panels involve processes such as compression molding, resin transfer molding, and injection molding, which are compatible with biodegradable matrices like PLA or bio-epoxy, offering improved environmental sustainability. Glass fiber composites utilize traditional methods like hand lay-up, spray-up, and vacuum infusion with thermoset or thermoplastic resins, providing higher mechanical strength and thermal resistance but with less eco-friendliness. Compatibility issues arise as natural fibers require treatment to enhance adhesion with polymer matrices, while glass fibers offer superior durability but increase weight and energy consumption in manufacturing.
Aesthetic and Functional Performance
Natural fiber composites offer superior aesthetic appeal with their unique textures and matte finishes, enhancing the visual and tactile experience of automotive interior panels. Glass fiber composites provide higher functional performance in terms of strength, durability, and impact resistance, making them suitable for safety-critical components. The choice between natural and glass fiber composites balances the desire for sustainable, lightweight interiors and the need for robust, long-lasting performance.
Future Trends in Automotive Interior Materials
Natural fiber composites are gaining momentum in automotive interior panels due to their sustainability, lightweight properties, and lower environmental impact compared to traditional glass fiber composites. Advancements in bio-based resins and enhanced fiber treatments are improving the mechanical performance and durability of natural fibers, making them viable alternatives for mass production. Future trends emphasize integrating renewable materials with innovative manufacturing techniques to meet stringent emission regulations and consumer demand for eco-friendly vehicles.
Infographic: Natural fiber composite vs Glass fiber composite for Automotive interior panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com