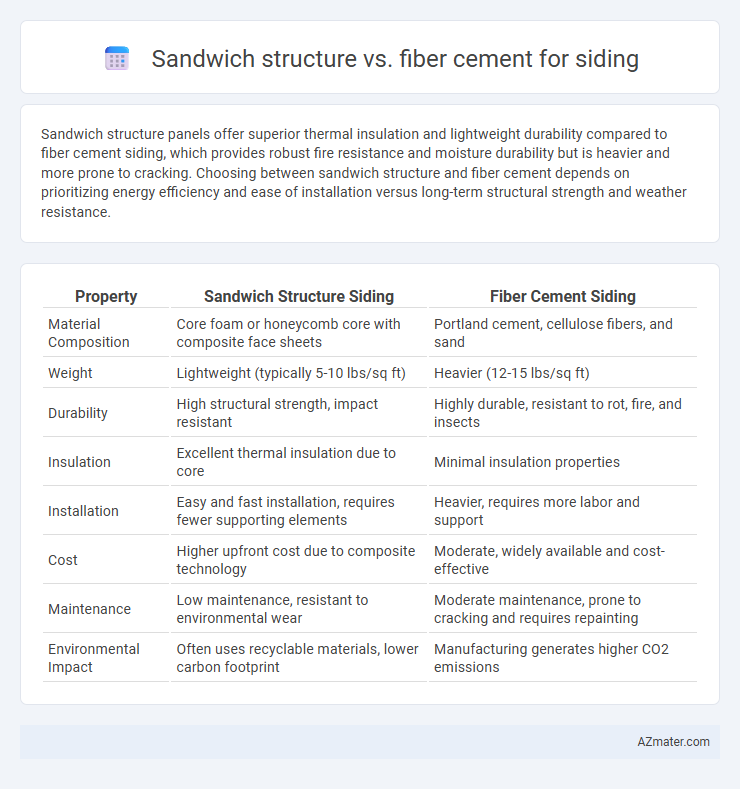
Sandwich structure panels offer superior thermal insulation and lightweight durability compared to fiber cement siding, which provides robust fire resistance and moisture durability but is heavier and more prone to cracking. Choosing between sandwich structure and fiber cement depends on prioritizing energy efficiency and ease of installation versus long-term structural strength and weather resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Sandwich Structure Siding | Fiber Cement Siding |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Core foam or honeycomb core with composite face sheets | Portland cement, cellulose fibers, and sand |
| Weight | Lightweight (typically 5-10 lbs/sq ft) | Heavier (12-15 lbs/sq ft) |
| Durability | High structural strength, impact resistant | Highly durable, resistant to rot, fire, and insects |
| Insulation | Excellent thermal insulation due to core | Minimal insulation properties |
| Installation | Easy and fast installation, requires fewer supporting elements | Heavier, requires more labor and support |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost due to composite technology | Moderate, widely available and cost-effective |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, resistant to environmental wear | Moderate maintenance, prone to cracking and requires repainting |
| Environmental Impact | Often uses recyclable materials, lower carbon footprint | Manufacturing generates higher CO2 emissions |
Introduction to Modern Siding Materials
Sandwich structure siding combines layers of materials such as insulation foam and metal or composite panels to provide enhanced thermal performance and durability for modern buildings. Fiber cement siding, made from a mix of cement, cellulose fibers, and sand, offers superior resistance to fire, moisture, and pests while mimicking the appearance of wood or masonry. Both materials represent advancements in exterior cladding technology, balancing aesthetic appeal with energy efficiency and long-lasting protection.
What is Sandwich Structure Siding?
Sandwich structure siding consists of multiple layers, typically involving a core insulation material such as polyurethane or polystyrene, bonded between two outer panels made of metal, wood, or composite materials, providing enhanced thermal insulation and structural strength. Fiber cement siding, composed of cement, sand, and cellulose fibers, offers durability, fire resistance, and low maintenance but lacks the integrated insulation properties of sandwich panels. Sandwich structure siding is ideal for energy-efficient buildings requiring lightweight, strong, and insulating exterior cladding solutions.
What is Fiber Cement Siding?
Fiber cement siding is a durable, composite material made from cement, sand, and cellulose fibers designed to mimic the appearance of wood, stucco, or masonry. It offers excellent resistance to fire, termites, and moisture, making it a low-maintenance option for exterior cladding. Compared to sandwich structure panels, fiber cement siding provides superior weather resistance and longevity, ideal for harsh climates and long-term performance.
Key Material Composition Differences
Sandwich structure siding consists of multiple layers, typically combining a core material like foam or wood with outer protective facings made of metal or fiber-reinforced composites, offering high insulation and structural strength. Fiber cement siding is primarily composed of a mixture of cement, sand, and cellulose fibers, creating a dense, durable, and fire-resistant cladding that mimics the appearance of wood or masonry. The key material composition difference lies in the sandwich structure's layered composite design focused on multi-functional performance versus fiber cement's homogenous, mineral-based formulation emphasizing durability and weather resistance.
Thermal Insulation and Energy Efficiency
Sandwich structure siding typically offers superior thermal insulation due to its multi-layer composition that includes insulating foam cores, which reduce heat transfer and improve overall energy efficiency in buildings. Fiber cement siding, while durable and moisture-resistant, lacks inherent insulating properties and often requires additional insulation for comparable thermal performance. Choosing sandwich structure siding can significantly lower heating and cooling costs by enhancing a building's thermal envelope and reducing energy consumption.
Durability and Weather Resistance Comparison
Sandwich structure siding typically features a composite core laminated between protective outer layers, offering superior impact resistance and thermal insulation compared to fiber cement, which is known for its density and fire-resistant properties. Fiber cement siding excels in resisting moisture, rot, and insect damage but can be prone to cracking under extreme temperature fluctuations, whereas sandwich structures maintain structural integrity due to their multi-layered design. Both materials provide excellent weather resistance, but sandwich structures often deliver enhanced durability in climates with frequent temperature changes, while fiber cement performs reliably in humid or fire-prone environments.
Installation Process and Complexity
Sandwich structures for siding typically feature prefabricated layers that simplify installation by reducing on-site assembly, allowing faster panel placement with fewer specialized tools. Fiber cement siding demands more precise cutting, handling, and fastening due to its heavier weight and brittle nature, often requiring professional expertise to prevent cracking and ensure durable attachment. The installation complexity of fiber cement increases labor time and costs compared to the quicker, more modular sandwich panel systems.
Maintenance and Longevity
Sandwich structure siding typically offers enhanced durability and thermal insulation, reducing maintenance frequency due to its composite design that resists warping and moisture intrusion. Fiber cement siding is highly resistant to fire, insects, and rot, requiring periodic repainting and sealing to maintain its longevity, which can extend up to 50 years with proper care. Both materials provide long-lasting performance, but sandwich structures generally demand less upkeep due to their engineered layers and protective coatings.
Cost Analysis and Value
Sandwich structure siding generally offers a higher upfront cost than fiber cement due to its multi-layer construction and superior insulation properties, which can reduce long-term energy expenses. Fiber cement provides a more affordable initial investment with durability against weather and fire but may incur higher maintenance costs over time. Evaluating overall value, sandwich structures deliver better thermal efficiency and longevity, whereas fiber cement appeals to budget-conscious projects with moderate performance needs.
Choosing the Right Siding: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right siding involves evaluating durability, maintenance, insulation, and aesthetic appeal between sandwich structure panels and fiber cement boards. Sandwich structures offer superior thermal insulation and lightweight properties, making them ideal for energy-efficient buildings, while fiber cement excels in fire resistance and weather durability, requiring less frequent upkeep. Cost, climate conditions, and installation complexity also play crucial roles in determining the most suitable siding material for specific construction needs.
Infographic: Sandwich structure vs Fiber cement for Siding
 azmater.com
azmater.com