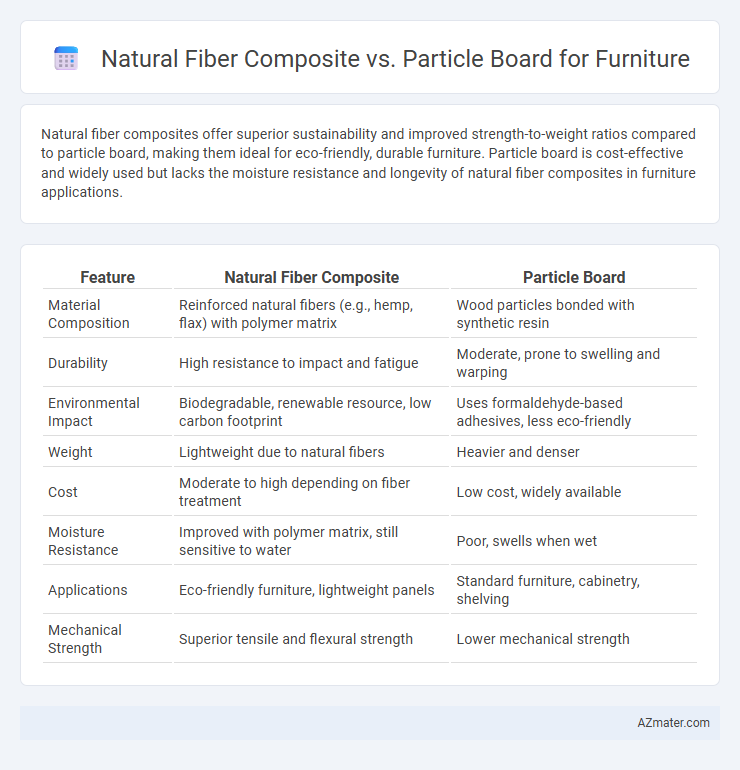
Natural fiber composites offer superior sustainability and improved strength-to-weight ratios compared to particle board, making them ideal for eco-friendly, durable furniture. Particle board is cost-effective and widely used but lacks the moisture resistance and longevity of natural fiber composites in furniture applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Natural Fiber Composite | Particle Board |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Reinforced natural fibers (e.g., hemp, flax) with polymer matrix | Wood particles bonded with synthetic resin |
| Durability | High resistance to impact and fatigue | Moderate, prone to swelling and warping |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, renewable resource, low carbon footprint | Uses formaldehyde-based adhesives, less eco-friendly |
| Weight | Lightweight due to natural fibers | Heavier and denser |
| Cost | Moderate to high depending on fiber treatment | Low cost, widely available |
| Moisture Resistance | Improved with polymer matrix, still sensitive to water | Poor, swells when wet |
| Applications | Eco-friendly furniture, lightweight panels | Standard furniture, cabinetry, shelving |
| Mechanical Strength | Superior tensile and flexural strength | Lower mechanical strength |
Introduction to Natural Fiber Composites and Particle Board
Natural fiber composites consist of renewable fibers such as jute, hemp, or flax embedded in a polymer matrix, offering a sustainable alternative for furniture manufacturing with enhanced strength-to-weight ratios and biodegradability. Particle board, made from wood chips, sawdust, and adhesives, provides an economical and uniform material widely used in affordable furniture production but lacks the natural resilience and eco-friendliness of composites. Both materials play significant roles in the furniture industry, balancing cost, environmental impact, and structural performance.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Natural fiber composites combine renewable fibers such as hemp, flax, or jute with biodegradable resins, resulting in lightweight and sustainable furniture materials. Particle board consists of wood chips, sawdust, and synthetic resin binders compressed under heat and pressure, offering a cost-effective but less eco-friendly option. Manufacturing natural fiber composites involves fiber treatment, resin impregnation, and curing, while particle board production relies on mechanical grinding, blending with adhesives, and hot pressing techniques.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Natural fiber composites exhibit superior mechanical strength and durability compared to particle board, benefiting from the high tensile strength and flexibility of fibers like hemp, flax, or jute. These composites resist moisture, impact, and wear better, resulting in longer-lasting furniture that maintains structural integrity over time. Particle board, made from wood chips and resin, tends to be prone to swelling, cracking, and reduced load-bearing capacity when exposed to humidity or mechanical stress.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Natural fiber composites outperform particle board in environmental impact by utilizing renewable resources like hemp, flax, and kenaf, which absorb CO2 during growth and reduce reliance on synthetic resins. Particle board typically incorporates wood waste bonded with formaldehyde-based adhesives, releasing harmful volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and posing indoor air quality concerns. Sustainable furniture production increasingly favors natural fiber composites for their biodegradability, lower carbon footprint, and enhanced end-of-life recyclability compared to non-biodegradable particle board materials.
Weight and Handling Differences
Natural fiber composites offer significantly lower weight compared to particle board, improving ease of handling and transportation in furniture applications. Their lightweight properties reduce strain during installation and enable more ergonomic designs without compromising strength. Particle board, while heavier, provides sturdiness but can be more cumbersome to move and manipulate during assembly.
Moisture Resistance and Dimensional Stability
Natural fiber composites exhibit superior moisture resistance compared to particle board, as the natural fibers inherently absorb less water and are often treated with hydrophobic resins to enhance durability. Particle boards tend to swell and lose dimensional stability when exposed to high humidity or water due to their wood particle core and adhesive composition. The enhanced dimensional stability of natural fiber composites makes them preferable for furniture applications in moist or variable environmental conditions.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Natural fiber composites generally offer higher initial material costs compared to particle board due to sustainable raw materials and advanced manufacturing processes. Particle board remains more cost-effective and widely available across global markets, benefiting from mass production and established supply chains. Market demand for eco-friendly furniture is increasing the availability of natural fiber composites, gradually narrowing the price gap with traditional particle board options.
Design Versatility and Aesthetic Options
Natural fiber composites offer superior design versatility for furniture due to their lightweight, flexible properties and ability to be molded into intricate shapes, enabling innovative and ergonomic designs. They provide a wide range of aesthetic options, including natural textures and customizable finishes, which appeal to eco-conscious consumers seeking sustainable yet stylish furniture. Particle board, while cost-effective and easy to cut into standard shapes, lacks the same level of aesthetic refinement and customization potential, often requiring veneers or laminates to enhance its appearance.
Applications in Modern Furniture Design
Natural fiber composites offer enhanced strength-to-weight ratios and sustainable properties, making them ideal for eco-friendly furniture frames, panels, and decorative elements. Particle boards, commonly used for flat-packed furniture, provide cost-effective, uniform surfaces but lack the durability and environmental benefits of natural fiber alternatives. Modern furniture design increasingly leverages natural fiber composites for customizable, lightweight, and resilient pieces that align with green building standards and aesthetic trends.
Choosing the Right Material for Furniture Projects
Natural fiber composites offer superior strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced environmental sustainability compared to particle board, making them ideal for eco-conscious furniture projects. Particle board provides cost-effective, uniform surface finishes but lacks durability and moisture resistance, which can compromise furniture longevity. Prioritizing natural fiber composites ensures improved mechanical performance and reduced ecological impact, essential for high-quality, sustainable furniture design.
Infographic: Natural fiber composite vs Particle board for Furniture
 azmater.com
azmater.com