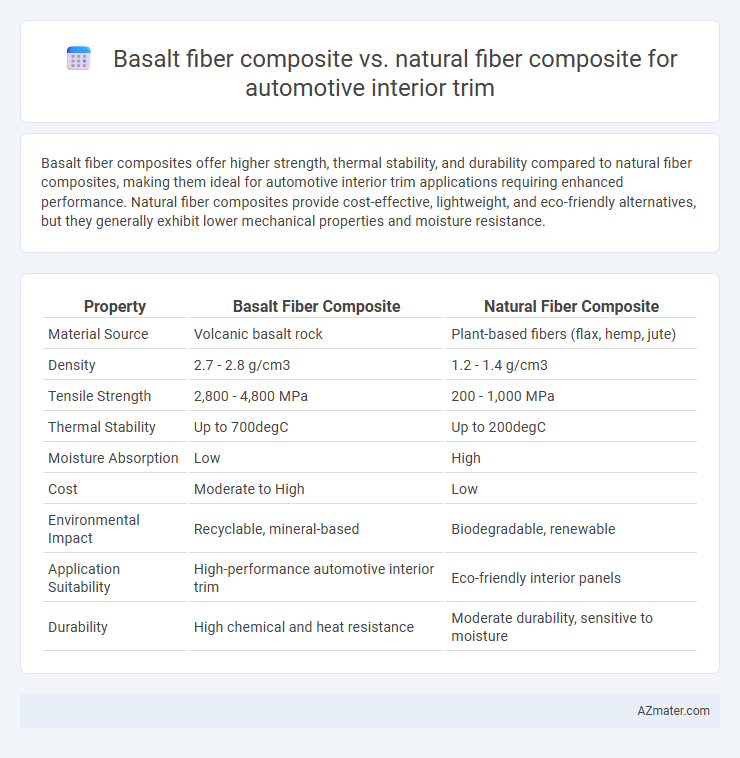
Basalt fiber composites offer higher strength, thermal stability, and durability compared to natural fiber composites, making them ideal for automotive interior trim applications requiring enhanced performance. Natural fiber composites provide cost-effective, lightweight, and eco-friendly alternatives, but they generally exhibit lower mechanical properties and moisture resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Basalt Fiber Composite | Natural Fiber Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Volcanic basalt rock | Plant-based fibers (flax, hemp, jute) |
| Density | 2.7 - 2.8 g/cm3 | 1.2 - 1.4 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 2,800 - 4,800 MPa | 200 - 1,000 MPa |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 700degC | Up to 200degC |
| Moisture Absorption | Low | High |
| Cost | Moderate to High | Low |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable, mineral-based | Biodegradable, renewable |
| Application Suitability | High-performance automotive interior trim | Eco-friendly interior panels |
| Durability | High chemical and heat resistance | Moderate durability, sensitive to moisture |
Introduction to Automotive Interior Trim Materials
Automotive interior trim materials increasingly leverage advanced composites for enhanced performance and sustainability. Basalt fiber composites offer superior mechanical strength, thermal stability, and durability compared to natural fiber composites, making them ideal for high-stress interior applications. Natural fiber composites, derived from renewable resources like hemp or flax, provide lightweight, eco-friendly alternatives with good acoustic insulation but generally lower impact resistance than basalt fiber composites.
Overview of Basalt Fiber Composites
Basalt fiber composites are gaining prominence in automotive interior trim due to their superior mechanical strength, thermal stability, and resistance to chemical corrosion compared to natural fiber composites. Derived from volcanic rock, basalt fibers offer enhanced durability and better acoustic insulation, making them ideal for high-performance automotive applications. Their sustainability and recyclability also provide an eco-friendly alternative to synthetic fibers while outperforming natural fibers in fire resistance and moisture absorption.
Overview of Natural Fiber Composites
Natural fiber composites, derived from materials such as flax, hemp, jute, and kenaf, offer lightweight, renewable, and biodegradable alternatives for automotive interior trim applications. These composites provide good thermal and acoustic insulation properties, contributing to improved vehicle comfort and sustainability standards. Their compatibility with bio-based resins enhances recyclability, making them a favorable choice for eco-friendly automotive design.
Mechanical Properties Comparison: Basalt vs Natural Fiber
Basalt fiber composites exhibit superior mechanical properties compared to natural fiber composites in automotive interior trim applications, offering higher tensile strength and improved impact resistance. Basalt fibers provide enhanced stiffness and durability, contributing to longer service life and better structural integrity under dynamic loading conditions. Natural fiber composites, while lightweight and eco-friendly, generally show lower mechanical performance and susceptibility to moisture absorption, limiting their use in high-stress, safety-critical interior components.
Thermal Stability and Fire Resistance Analysis
Basalt fiber composites exhibit superior thermal stability and fire resistance compared to natural fiber composites, making them highly suitable for automotive interior trim applications where safety is critical. Basalt fibers withstand higher temperatures without degradation, maintaining structural integrity under prolonged heat exposure, while natural fibers tend to char and lose mechanical strength. Fire resistance tests demonstrate basalt composites generate less smoke and toxic fumes, enhancing occupant safety during vehicle fires.
Weight and Density Considerations in Automotive Design
Basalt fiber composites exhibit higher density (approximately 2.7-2.8 g/cm3) compared to natural fiber composites, which typically range between 1.2-1.5 g/cm3, significantly impacting overall automotive interior trim weight. The increased density of basalt fiber composites results in heavier components, affecting fuel efficiency and vehicle dynamics, whereas natural fiber composites provide substantial weight savings critical for lightweight automotive design. Engineers prioritize natural fiber composites for interior trims to achieve lower mass and enhanced sustainability without severely compromising mechanical performance.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Basalt fiber composites offer superior sustainability compared to traditional synthetic fibers, providing high strength-to-weight ratios while being fully recyclable and non-toxic, which reduces environmental impact in automotive interior trim. Natural fiber composites, derived from renewable resources like flax and hemp, exhibit excellent biodegradability and lower carbon footprints, making them attractive for eco-friendly vehicle manufacturing. However, basalt fibers outperform natural fibers in durability and resistance to moisture and heat, leading to longer service life and reduced material waste in automotive applications.
Cost Effectiveness and Market Availability
Basalt fiber composites offer higher cost effectiveness due to their superior mechanical properties and durability, which reduce long-term replacement and maintenance expenses compared to natural fiber composites. Market availability for basalt fibers is growing steadily with increasing industrial adoption, but natural fiber composites remain more widely accessible due to established supply chains and lower raw material costs. Automotive manufacturers must balance the upfront investment in basalt fibers against their enhanced performance benefits, while natural fibers provide a more economical option with easier sourcing for interior trim applications.
Processing and Manufacturing Challenges
Basalt fiber composites offer higher temperature resistance and mechanical strength but require specialized high-temperature processing equipment, increasing manufacturing complexity and cost for automotive interior trim. Natural fiber composites are easier to process using conventional thermoplastic molding techniques, but their variability in fiber quality and moisture absorption pose challenges in achieving consistent material performance and dimensional stability. Both materials face challenges in optimizing fiber-matrix adhesion and achieving uniform dispersion to meet the stringent automotive standards for interior components.
Future Trends and Innovations in Interior Trim Materials
Basalt fiber composites are gaining traction in automotive interior trim due to their superior thermal resistance, durability, and lightweight properties, outperforming traditional natural fiber composites. Future trends indicate increased integration of hybrid composites combining basalt fibers with bio-based resins to achieve enhanced mechanical performance and sustainability. Innovations focus on developing eco-friendly processing techniques and smart materials with embedded sensors for improved safety and user experience in vehicle interiors.
Infographic: Basalt fiber composite vs Natural fiber composite for Automotive interior trim
 azmater.com
azmater.com