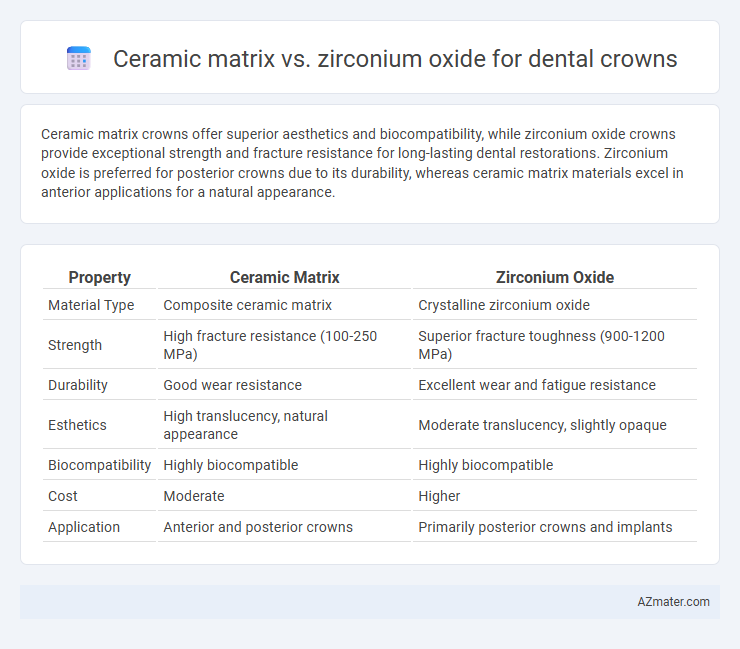
Ceramic matrix crowns offer superior aesthetics and biocompatibility, while zirconium oxide crowns provide exceptional strength and fracture resistance for long-lasting dental restorations. Zirconium oxide is preferred for posterior crowns due to its durability, whereas ceramic matrix materials excel in anterior applications for a natural appearance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ceramic Matrix | Zirconium Oxide |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Composite ceramic matrix | Crystalline zirconium oxide |
| Strength | High fracture resistance (100-250 MPa) | Superior fracture toughness (900-1200 MPa) |
| Durability | Good wear resistance | Excellent wear and fatigue resistance |
| Esthetics | High translucency, natural appearance | Moderate translucency, slightly opaque |
| Biocompatibility | Highly biocompatible | Highly biocompatible |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
| Application | Anterior and posterior crowns | Primarily posterior crowns and implants |
Introduction to Dental Crown Materials
Dental crown materials primarily include ceramic matrix composites and zirconium oxide, both valued for their strength and aesthetic qualities. Ceramic matrix crowns offer excellent translucency and mimic natural tooth enamel, making them ideal for visible front teeth restoration. Zirconium oxide crowns provide superior fracture resistance and biocompatibility, suitable for molars where durability is critical.
Overview of Ceramic Matrix Crowns
Ceramic matrix crowns consist of a composite structure where ceramic particles are embedded within a resin or glass matrix, offering excellent aesthetics and customization options for dental restorations. They provide high fracture toughness and wear resistance while maintaining a natural translucency that closely mimics the appearance of real teeth. Compared to zirconium oxide crowns, ceramic matrix crowns generally offer superior aesthetic qualities but may have slightly lower strength and durability in high-stress occlusal environments.
Overview of Zirconium Oxide Crowns
Zirconium oxide crowns, made from a high-strength ceramic known as zirconia, offer exceptional durability and biocompatibility compared to traditional ceramic matrix crowns. Their superior fracture resistance and natural tooth-like translucency make them ideal for both anterior and posterior restorations. Clinically, zirconia crowns demonstrate excellent wear resistance, minimal plaque accumulation, and high patient satisfaction due to aesthetic and functional performance.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Ceramic matrix crowns provide excellent aesthetic qualities with moderate strength, making them suitable for front teeth but less ideal for high-stress areas. Zirconium oxide crowns offer superior strength and durability due to their dense crystalline structure, resisting fracture and wear even under heavy biting forces. Zirconium oxide's performance in longevity significantly surpasses ceramic matrix, making it the preferred choice for molars and long-lasting dental restorations.
Aesthetics and Natural Appearance
Zirconium oxide crowns offer superior aesthetics with a translucency and color closely mimicking natural tooth enamel, making them highly favored for anterior restorations. Ceramic matrix crowns provide excellent aesthetic customization through shading and layering techniques, though they may lack the same level of translucency as zirconia. Both materials enable a natural appearance, but zirconium oxide's strength and lifelike translucency make it the preferred choice for achieving seamless integration with adjacent teeth.
Biocompatibility and Patient Safety
Ceramic matrix crowns demonstrate superior biocompatibility due to their inert nature, reducing the risk of allergic reactions and gum irritation. Zirconium oxide crowns are highly biocompatible as well, known for their excellent osseointegration and resistance to bacterial colonization, promoting long-term oral health. Both materials ensure patient safety, but zirconium oxide offers enhanced durability and fracture resistance, making it a preferred choice for stress-bearing applications.
Preparation and Placement Procedures
Ceramic matrix crowns require precise tooth preparation with minimal reduction to preserve enamel, enabling strong adhesive bonding during placement. Zirconium oxide crowns demand more substantial tooth reduction due to their bulk and rely on traditional cementation rather than adhesive techniques. Accurate impression and digital scanning are critical for both types to ensure optimal fit and long-term durability of the dental crown.
Cost Differences and Value
Ceramic matrix crowns typically offer a more affordable option compared to zirconium oxide crowns, with costs ranging from $800 to $1,500 per crown versus $1,000 to $2,500 for zirconium oxide crowns. Zirconium oxide crowns provide superior strength and durability, often justifying the higher price through longer lifespan and better resistance to chipping and wear. Patients seeking cost-effective solutions may prefer ceramic matrix crowns, while those prioritizing long-term value and durability tend to invest in zirconium oxide restorations.
Clinical Performance and Longevity
Ceramic matrix crowns exhibit excellent biocompatibility and esthetics but may show lower fracture resistance compared to zirconium oxide crowns, which offer superior strength and durability for long-term clinical use. Zirconium oxide crowns demonstrate higher survival rates in posterior regions due to enhanced fracture toughness and resistance to chipping over extended periods. Clinical studies indicate that the longevity of zirconium oxide crowns surpasses ceramic matrix options, particularly under high occlusal stress and in patients with parafunctional habits.
Choosing the Best Material for Your Needs
Ceramic matrix crowns offer excellent aesthetic appeal with translucency closely mimicking natural teeth, making them ideal for front teeth restorations. Zirconium oxide crowns provide superior strength and durability, suitable for patients requiring greater bite force resistance or molar crowns. Selecting the best material depends on balancing cosmetic demands and functional requirements, ensuring long-lasting performance and patient satisfaction.
Infographic: Ceramic matrix vs Zirconium oxide for Dental crown
 azmater.com
azmater.com