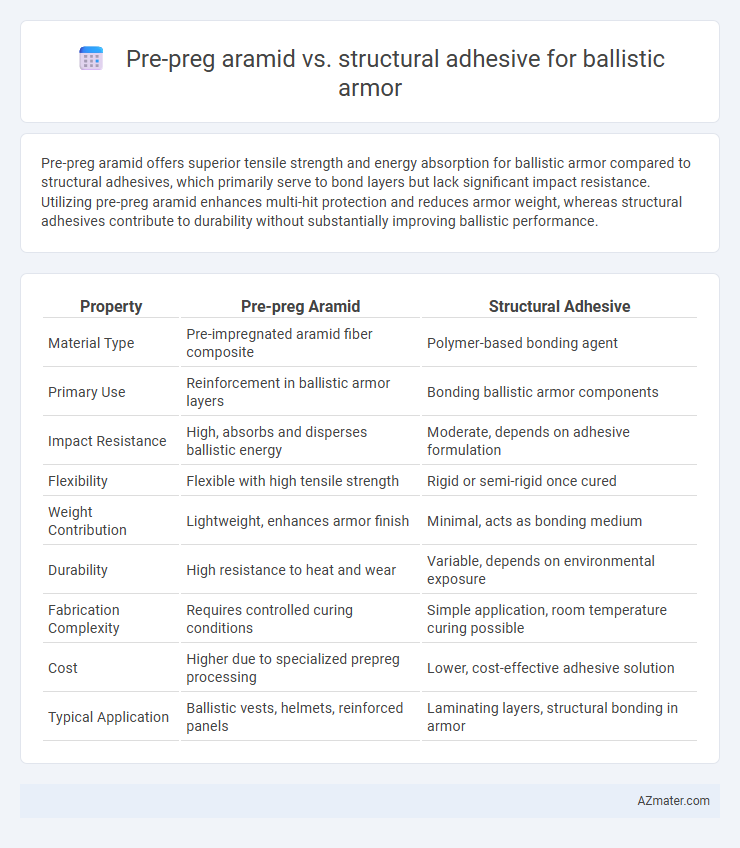
Pre-preg aramid offers superior tensile strength and energy absorption for ballistic armor compared to structural adhesives, which primarily serve to bond layers but lack significant impact resistance. Utilizing pre-preg aramid enhances multi-hit protection and reduces armor weight, whereas structural adhesives contribute to durability without substantially improving ballistic performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Pre-preg Aramid | Structural Adhesive |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Pre-impregnated aramid fiber composite | Polymer-based bonding agent |
| Primary Use | Reinforcement in ballistic armor layers | Bonding ballistic armor components |
| Impact Resistance | High, absorbs and disperses ballistic energy | Moderate, depends on adhesive formulation |
| Flexibility | Flexible with high tensile strength | Rigid or semi-rigid once cured |
| Weight Contribution | Lightweight, enhances armor finish | Minimal, acts as bonding medium |
| Durability | High resistance to heat and wear | Variable, depends on environmental exposure |
| Fabrication Complexity | Requires controlled curing conditions | Simple application, room temperature curing possible |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized prepreg processing | Lower, cost-effective adhesive solution |
| Typical Application | Ballistic vests, helmets, reinforced panels | Laminating layers, structural bonding in armor |
Introduction to Ballistic Armor Materials
Pre-preg aramid fibers, known for their high tensile strength and lightweight properties, are widely used in ballistic armor to provide superior energy absorption and impact resistance. Structural adhesives enhance ballistic armor performance by securely bonding composite layers, ensuring durability and maintaining integrity under high-velocity impacts. Combining pre-preg aramids with advanced structural adhesives creates a robust, multi-layered protection system optimized for both flexibility and ballistic resistance.
Overview of Pre-preg Aramid in Ballistic Applications
Pre-preg aramid fibers, impregnated with resin matrices, offer superior tensile strength and energy absorption ideal for ballistic armor, providing lightweight and high-performance protection against ballistic threats. The uniform resin distribution in pre-preg materials ensures consistent mechanical properties and enhances delamination resistance under high-impact conditions. Advanced pre-preg aramid composites deliver improved multi-hit capability and flexibility compared to conventional structural adhesives, making them essential in modern armor designs.
Structural Adhesives: Definition and Role in Armor Systems
Structural adhesives are advanced bonding agents designed to join composite materials in ballistic armor, ensuring high strength and durability under impact. These adhesives enhance the integrity and energy dispersion of armor systems by securely bonding layers of fabrics like pre-preg aramid, metals, or ceramics. Their role is critical in maintaining the armor's structural performance while reducing weight and improving flexibility compared to traditional mechanical fasteners.
Mechanical Properties: Pre-preg Aramid vs. Structural Adhesives
Pre-preg aramid fibers exhibit superior tensile strength and impact resistance, making them ideal for ballistic armor applications where energy absorption and durability are critical. Structural adhesives provide essential bonding strength and flexibility but generally possess lower mechanical properties compared to pre-preg composites, impacting overall armor rigidity and ballistic performance. Combining pre-preg aramid with high-performance structural adhesives optimizes mechanical integrity, enhancing multi-hit resistance and structural cohesion under ballistic impact.
Impact Resistance and Ballistic Performance Comparison
Pre-preg aramid composites exhibit superior impact resistance due to their high tensile strength and energy absorption capacity, making them ideal for ballistic armor applications requiring lightweight and flexible protection. Structural adhesives contribute to ballistic performance by securely bonding layers, enhancing the overall integrity and distributing impact forces across the armor system. Comparative studies reveal that while pre-preg aramid provides excellent multi-hit resistance and deformation control, the integration of high-performance structural adhesives improves delamination resistance and structural durability under ballistic impacts.
Weight and Thickness Considerations
Pre-preg aramid offers superior lightweight properties and thinner laminate construction, crucial for enhancing ballistic armor mobility without compromising protection. Structural adhesives add minimal thickness but can increase overall weight when multiple adhesive layers are required to bond aramid fibers effectively. Optimizing the balance between pre-preg aramid's inherent low density and the adhesive's bonding efficiency significantly influences the final armor's weight and thickness performance metrics.
Durability and Environmental Stability
Pre-preg aramid fibers exhibit superior durability in ballistic armor applications due to their inherent high tensile strength and resistance to impact fatigue, ensuring long-term performance under repeated ballistic stress. Structural adhesives provide critical environmental stability by maintaining strong bonds under varying temperature, humidity, and chemical exposures, preventing delamination and degradation of multi-material armor assemblies. Combining pre-preg aramid with high-performance structural adhesives enhances overall armor resilience by balancing mechanical durability with robust environmental resistance.
Manufacturing Processes: Laminating vs. Bonding
Pre-preg aramid composites undergo precise laminating processes involving heat and pressure to cure fibers and resin into strong, lightweight ballistic armor panels, enabling controlled fiber alignment and resin distribution for optimal impact resistance. Structural adhesives facilitate bonding pre-formed components by chemically joining aramid layers, providing flexibility in assembly but potentially introducing variability in adhesive thickness and bond integrity under ballistic stress. Laminating ensures uniform composite consolidation crucial for multi-hit ballistic performance, while bonding allows modular armor construction but requires rigorous quality control to maintain armor reliability.
Cost-Effectiveness and Scalability
Pre-preg aramid offers superior ballistic performance with consistent fiber alignment but involves higher material and processing costs, limiting cost-effectiveness for large-scale production. Structural adhesives provide a more scalable solution by enabling faster assembly and lower labor expenses, though they may compromise peak ballistic resistance due to variable layer bonding. Balancing cost-effectiveness and scalability depends on specific armor requirements, with pre-pregs preferred for high-performance applications and adhesives favored in mass-produced, cost-sensitive contexts.
Future Trends in Ballistic Armor Material Integration
Future trends in ballistic armor material integration emphasize optimizing the synergy between pre-preg aramid composites and advanced structural adhesives to enhance impact resistance and weight efficiency. Innovations in nano-engineered adhesives improve interlaminar bonding strength, increasing the durability and performance of multilayered aramid armor systems. Research into hybrid integration techniques aims to achieve scalable manufacturing processes that maintain ballistic protection while reducing material costs and improving flexibility for next-generation personal and vehicle armor.
Infographic: Pre-preg aramid vs Structural adhesive for Ballistic armor
 azmater.com
azmater.com