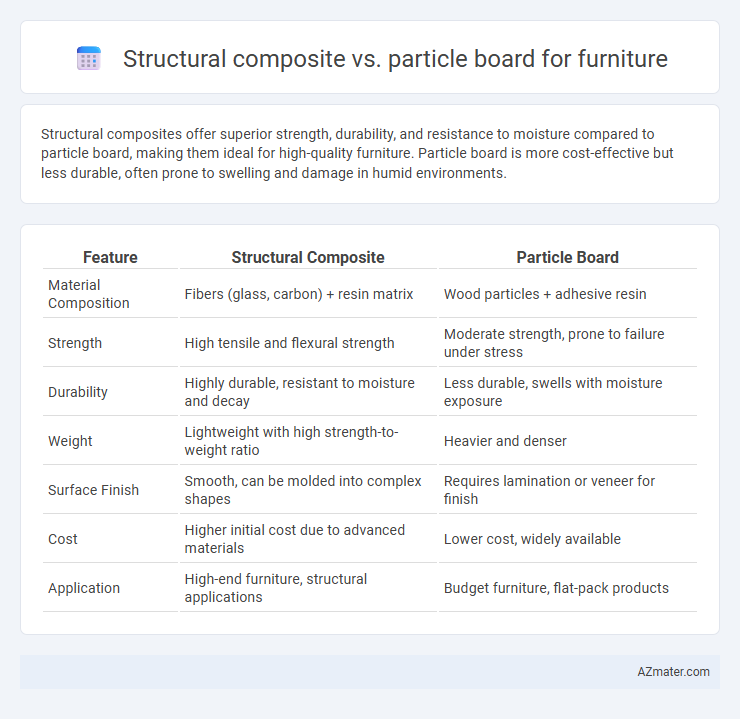
Structural composites offer superior strength, durability, and resistance to moisture compared to particle board, making them ideal for high-quality furniture. Particle board is more cost-effective but less durable, often prone to swelling and damage in humid environments.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Structural Composite | Particle Board |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Fibers (glass, carbon) + resin matrix | Wood particles + adhesive resin |
| Strength | High tensile and flexural strength | Moderate strength, prone to failure under stress |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to moisture and decay | Less durable, swells with moisture exposure |
| Weight | Lightweight with high strength-to-weight ratio | Heavier and denser |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, can be molded into complex shapes | Requires lamination or veneer for finish |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to advanced materials | Lower cost, widely available |
| Application | High-end furniture, structural applications | Budget furniture, flat-pack products |
Introduction to Furniture Material Choices
Structural composites, such as plywood and MDF, offer superior strength, durability, and moisture resistance compared to particle board, making them ideal for furniture requiring long-term stability. Particle board, composed of wood chips and resin, is cost-effective and lightweight but lacks the density and resilience of structural composites. Selecting between these materials depends on furniture application, budget constraints, and desired longevity.
What is Structural Composite?
Structural composite refers to engineered materials made from combining fibers, such as wood strands or veneers, with adhesives to create strong, durable panels designed to bear loads and resist deformation. Unlike particle board, which consists of wood chips and resin pressed together with lower density and strength, structural composites use oriented strands or laminated veneers for enhanced mechanical properties and moisture resistance. These characteristics make structural composites ideal for high-performance furniture requiring superior strength and longevity.
What is Particle Board?
Particle board is an engineered wood product made from wood chips, sawdust, and resin compacted under heat and pressure, offering a cost-effective alternative to solid wood. It is commonly used in furniture manufacturing due to its uniformity, smooth surface, and ease of finishing but is less durable and moisture-resistant compared to structural composites. Its affordability and versatility make particle board a popular choice for budget-friendly furniture, although it may be prone to swelling and damage in high-humidity environments.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Structural composite materials, such as plywood and oriented strand board (OSB), exhibit superior strength and durability compared to particle board due to their layered construction and tightly bonded wood fibers. The enhanced load-bearing capacity and resistance to warping and moisture damage make structural composites ideal for high-stress furniture applications. In contrast, particle board, composed of wood chips and resin, is less dense and more prone to sagging and deterioration over time under heavy use.
Weight and Handling in Furniture Design
Structural composite materials like plywood and MDF offer superior strength-to-weight ratios compared to particle board, making them easier to handle during furniture assembly and installation. Particle board, being denser and heavier, often results in bulkier furniture pieces that are more cumbersome to move and prone to damage under stress. Choosing structural composites enhances both the ergonomic aspects of furniture design and overall durability.
Moisture and Environmental Resistance
Structural composite materials like plywood and medium-density fiberboard (MDF) generally offer superior moisture resistance compared to particle board due to their layered construction and use of adhesives that bond wood fibers tightly. Particle board tends to absorb moisture more readily, leading to swelling, warping, and reduced durability in humid environments. Environmental resistance is also enhanced in structural composites by treatments and sealants that improve resistance to mold, decay, and insect damage, making them more suitable for long-lasting furniture applications.
Aesthetic Versatility and Finishing Options
Structural composite materials offer greater aesthetic versatility and finishing options compared to particle board, as they can be laminated, veneered, or painted to mimic natural wood grains and textures. Particle board typically has a uniform, flat surface that limits design flexibility and requires thicker veneers or laminates for an attractive finish. The enhanced surface quality of structural composites allows for smoother coatings and a wider range of color and texture customizations, making them preferable for high-end furniture design.
Cost Considerations for Manufacturers and Consumers
Structural composites typically incur higher manufacturing costs due to advanced materials and production techniques compared to particle board, which relies on cheaper wood chips and adhesives. For consumers, particle board offers lower upfront prices but may result in higher long-term expenses due to reduced durability and increased maintenance or replacement needs. Manufacturers must balance initial production expenses with consumer demands for affordability and product lifespan when selecting between structural composite and particle board options for furniture.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Factors
Structural composite materials, such as plywood and oriented strand board (OSB), offer higher durability and strength while often using fast-growing, renewable wood fibers and recycled adhesives, enhancing sustainability in furniture production. Particle board, made from wood chips, sawdust, and resin binders, generally utilizes lower-grade and recycled wood waste, reducing deforestation but may contain formaldehyde-based adhesives that pose environmental and health concerns. Choosing structural composites with low-VOC or formaldehyde-free adhesives provides a more eco-friendly option due to better recyclability and lower emissions compared to traditional particle board.
Best Applications for Structural Composite vs Particle Board
Structural composites excel in applications demanding high strength, durability, and resistance to moisture, such as load-bearing furniture frames and outdoor furniture. Particle boards are best suited for budget-friendly indoor furniture like cabinets, shelves, and flat-pack assemblies where cost-efficiency and ease of machining are prioritized. Choosing structural composites ensures longevity in demanding environments, whereas particle board offers economical options for lightweight, decorative pieces.
Infographic: Structural composite vs Particle board for Furniture
 azmater.com
azmater.com