Biocomposite materials offer enhanced sustainability and biodegradability compared to traditional plastics used in furniture manufacturing. Using biocomposites reduces environmental impact by incorporating natural fibers and renewable resins, resulting in lightweight, durable, and eco-friendly furniture.
Table of Comparison
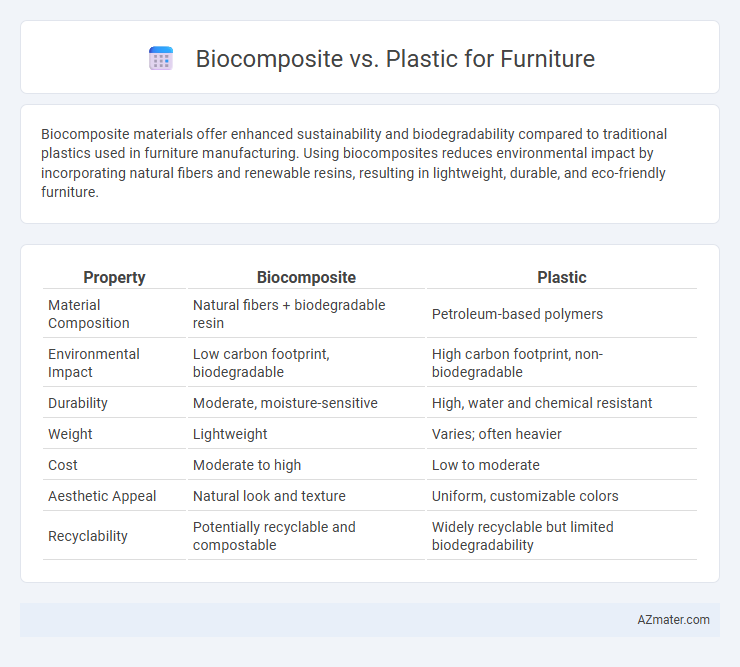
| Property | Biocomposite | Plastic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural fibers + biodegradable resin | Petroleum-based polymers |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, biodegradable | High carbon footprint, non-biodegradable |
| Durability | Moderate, moisture-sensitive | High, water and chemical resistant |
| Weight | Lightweight | Varies; often heavier |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
| Aesthetic Appeal | Natural look and texture | Uniform, customizable colors |
| Recyclability | Potentially recyclable and compostable | Widely recyclable but limited biodegradability |
Introduction to Biocomposites and Plastics in Furniture
Biocomposites in furniture combine natural fibers such as hemp, flax, or jute with bio-based resins, offering enhanced sustainability and biodegradability compared to traditional plastics. Plastics in furniture, typically derived from petrochemicals, provide durability, versatility, and cost-effectiveness but contribute significantly to environmental pollution and resource depletion. The growing demand for eco-friendly furniture fuels the shift from conventional plastic materials to innovative biocomposites that reduce carbon footprints while maintaining functional performance.
Material Composition: Biocomposite vs Plastic
Biocomposites for furniture are composed of natural fibers such as hemp, flax, or wood combined with biodegradable resins, offering enhanced sustainability and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional plastics. In contrast, plastics used in furniture manufacturing consist primarily of petrochemical-based polymers like polypropylene or polyethylene, which are non-biodegradable and rely on fossil fuel resources. The integration of natural fibers in biocomposites improves mechanical strength and thermal stability while decreasing carbon footprint, setting them apart from conventional plastic materials.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Biocomposite furniture significantly reduces environmental impact by using renewable natural fibers and biodegradable resins, resulting in lower carbon emissions and reduced landfill waste compared to conventional plastic furniture. Unlike plastics derived from petroleum, biocomposites enhance sustainability through their capacity to decompose naturally and support circular economy principles. Lifecycle analyses confirm biocomposites' superior performance in minimizing ecological footprint, making them a more eco-friendly choice for sustainable furniture manufacturing.
Durability and Longevity
Biocomposite materials exhibit superior durability and resistance to environmental factors compared to traditional plastics, making them a preferred choice for sustainable furniture manufacturing. Their composition, typically combining natural fibers like hemp or flax with bio-based resins, enhances mechanical strength and reduces wear over time. Unlike conventional plastics, biocomposites resist UV degradation and moisture buildup, extending the longevity of furniture in both indoor and outdoor settings.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetics
Biocomposites offer superior design flexibility compared to traditional plastics due to their ability to be molded into intricate shapes while incorporating natural fibers that enhance texture and visual appeal. The aesthetic qualities of biocomposite furniture emphasize organic patterns and earthy tones, creating a warm, eco-friendly look that plastic furniture often lacks. Plastic furniture generally provides a smoother, more uniform finish but falls short in delivering the unique, sustainable aesthetic that biocomposites naturally achieve.
Cost Comparison and Market Availability
Biocomposite furniture generally has higher upfront costs compared to traditional plastic furniture due to raw material sourcing and manufacturing processes, but it often offers long-term savings through durability and sustainability benefits. Plastic furniture remains more widely available in the market, with mass production enabling lower prices and extensive distribution channels. Increasing consumer demand and advances in biocomposite technology are gradually improving market availability and driving cost competitiveness.
Manufacturing Processes and Innovations
Biocomposite furniture manufacturing integrates natural fibers like hemp or flax with bio-resins, utilizing techniques such as compression molding and extrusion to enhance durability and sustainability. Plastic furniture production primarily relies on injection molding and thermoforming, offering high precision and rapid scalability but with significant environmental drawbacks. Recent innovations in biocomposites focus on improving fiber-matrix bonding and incorporating recycled agricultural waste, reducing dependency on petroleum-based plastics while maintaining competitive mechanical properties.
Health and Safety Considerations
Biocomposite furniture offers significant health and safety benefits compared to traditional plastic, as it is typically made from natural fibers and biodegradable resins that emit fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs), reducing indoor air pollution and respiratory risks. Biocomposite materials are less likely to release harmful chemicals during use or disposal, enhancing safety for both consumers and the environment. In contrast, plastic furniture often contains additives and toxins that can off-gas over time, posing potential hazards to human health and complicating safe recycling or disposal processes.
Consumer Preferences and Trends
Consumers increasingly prefer biocomposite furniture over plastic due to its sustainability, biodegradability, and eco-friendly appeal. Market trends highlight rising demand for materials that reduce carbon footprints while maintaining durability and aesthetic value. Studies reveal younger demographics prioritize ethical sourcing and recyclability, driving growth in biocomposite usage across residential and commercial furniture sectors.
Future Outlook: Biocomposite vs Plastic in Furniture Industry
Biocomposites present a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative to traditional plastics in the furniture industry, driven by growing environmental regulations and consumer demand for green products. Innovations in biocomposite materials improve durability, aesthetics, and cost-effectiveness, positioning them as viable replacements for plastic components. The future of furniture manufacturing will likely see increased adoption of biocomposites, reducing carbon footprints and reliance on fossil fuels while enhancing recyclability and end-of-life disposal options.
Infographic: Biocomposite vs Plastic for Furniture
 azmater.com
azmater.com