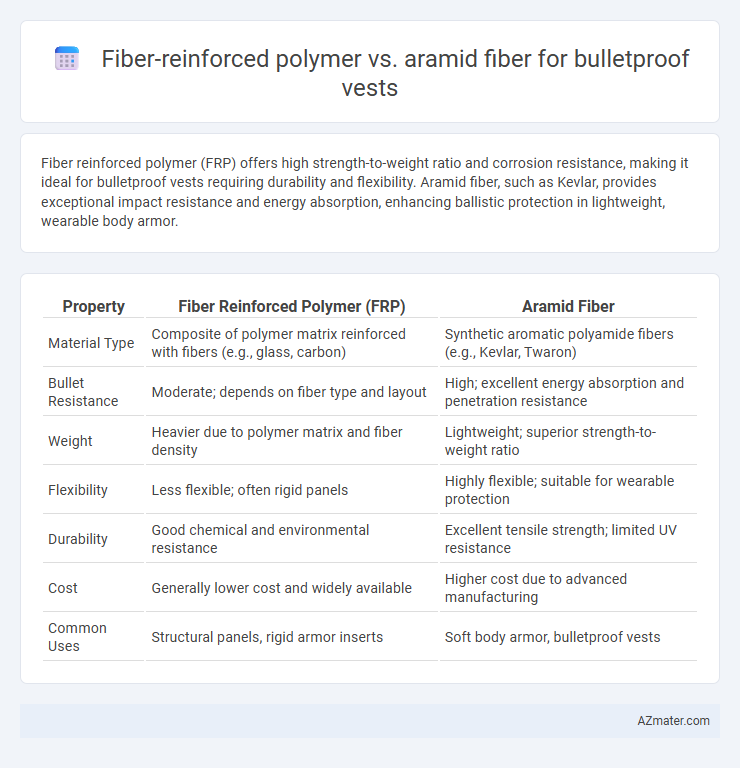
Fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) offers high strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for bulletproof vests requiring durability and flexibility. Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar, provides exceptional impact resistance and energy absorption, enhancing ballistic protection in lightweight, wearable body armor.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fiber Reinforced Polymer (FRP) | Aramid Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Composite of polymer matrix reinforced with fibers (e.g., glass, carbon) | Synthetic aromatic polyamide fibers (e.g., Kevlar, Twaron) |
| Bullet Resistance | Moderate; depends on fiber type and layout | High; excellent energy absorption and penetration resistance |
| Weight | Heavier due to polymer matrix and fiber density | Lightweight; superior strength-to-weight ratio |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; often rigid panels | Highly flexible; suitable for wearable protection |
| Durability | Good chemical and environmental resistance | Excellent tensile strength; limited UV resistance |
| Cost | Generally lower cost and widely available | Higher cost due to advanced manufacturing |
| Common Uses | Structural panels, rigid armor inserts | Soft body armor, bulletproof vests |
Introduction to Bulletproof Vests
Bulletproof vests utilize materials like fiber reinforced polymers (FRP) and aramid fibers to provide ballistic protection by absorbing and dispersing impact energy. FRPs, composed of a polymer matrix reinforced with fibers such as glass or carbon, offer high strength-to-weight ratios and corrosion resistance, making them suitable for durable vests. Aramid fibers, including Kevlar and Twaron, deliver exceptional tensile strength and thermal stability, widely recognized for their effectiveness in stopping bullets while maintaining flexibility and lightweight characteristics.
What Are Fiber Reinforced Polymers?
Fiber reinforced polymers (FRPs) are composite materials consisting of a polymer matrix reinforced with fibers such as glass, carbon, or aramid, designed to enhance mechanical properties like strength and durability. Aramid fibers, a type of synthetic fiber known for high tensile strength and heat resistance, are commonly used within FRPs for bulletproof vests to provide superior ballistic protection and lightweight performance. Compared to other FRP variants, aramid fiber-reinforced polymers offer excellent impact resistance and flexibility, making them ideal for personal armor applications.
Understanding Aramid Fibers
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, offer exceptional tensile strength and thermal resistance, making them a preferred material for bulletproof vests. These fibers provide high energy absorption and flexibility, enhancing wearer mobility while maintaining ballistic protection. Compared to fiber-reinforced polymers, aramid fibers feature superior impact resistance and lighter weight, ideal for body armor applications.
Key Material Properties Comparison
Fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) used in bulletproof vests offers high tensile strength, excellent impact resistance, and lightweight durability, making it effective in ballistic protection. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, provide superior energy absorption, high tensile strength, and thermal stability, crucial for dissipating ballistic impact and preventing penetration. Comparing both materials, aramid fibers excel in flexibility and thermal resistance, while FRPs provide enhanced stiffness and corrosion resistance, influencing the vest's overall performance and wearer comfort.
Ballistic Protection Performance
Fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) composites offer high tensile strength and excellent rigidity, making them effective for ballistic protection in bulletproof vests. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, provide superior impact resistance and energy absorption due to their high tensile strength-to-weight ratio and excellent flexibility, which enhances wearer mobility. Comparative studies show aramid fibers generally outperform FRP in stopping high-velocity projectiles, balancing weight and protection for optimal ballistic performance.
Weight and Comfort Considerations
Fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) generally offers lighter weight compared to aramid fibers, enhancing mobility and reducing fatigue for users of bulletproof vests. Aramid fibers such as Kevlar provide superior flexibility and breathability, contributing to improved comfort during extended wear. Choosing between FRP and aramid fiber depends on balancing weight reduction against the need for comfort and flexibility in protective gear.
Durability and Longevity
Fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) offers high durability with excellent resistance to environmental factors such as moisture, UV radiation, and chemical exposure, ensuring consistent performance over time in bulletproof vests. Aramid fiber, known for its exceptional tensile strength and impact resistance, maintains ballistic protection but is more susceptible to degradation from UV exposure and moisture, potentially reducing longevity without proper care. Choosing FRP enhances long-term durability in harsh conditions, while aramid fiber provides superior strength but requires maintenance to preserve vest lifespan.
Cost and Accessibility
Fiber reinforced polymers (FRPs) offer a cost-effective alternative to aramid fibers in bulletproof vest production, often resulting in lower manufacturing expenses due to cheaper raw materials and simpler processing techniques. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, tend to be more expensive because of their complex production and higher performance characteristics, which can limit accessibility for widespread use. Availability of FRPs is generally higher, with diverse supplier options that enhance scalability and reduce lead times compared to the more specialized aramid fiber market.
Environmental and Maintenance Factors
Fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) bulletproof vests offer superior resistance to environmental factors such as moisture, UV radiation, and chemical exposure, minimizing degradation over time compared to aramid fiber vests. Aramid fibers, like Kevlar, tend to absorb moisture and lose tensile strength when exposed to water or heat, requiring more frequent inspections and specialized maintenance to ensure ballistic performance. The longevity and lower maintenance demands of FRP materials make them more suitable for harsh or variable environmental conditions in ballistic protection gear.
Which Material is Best for Bulletproof Vests?
Fiber reinforced polymers (FRPs) and aramid fibers both offer high strength-to-weight ratios essential for bulletproof vests, but aramid fibers like Kevlar provide superior ballistic resistance, flexibility, and impact absorption. FRPs, including carbon or glass fiber composites, excel in structural rigidity but lack the pliability and energy dispersion critical in personal armor applications. Therefore, aramid fibers remain the preferred material for bulletproof vests due to their proven ability to effectively stop bullets while maintaining wearer mobility.
Infographic: Fiber reinforced polymer vs Aramid fiber for Bulletproof vest
 azmater.com
azmater.com