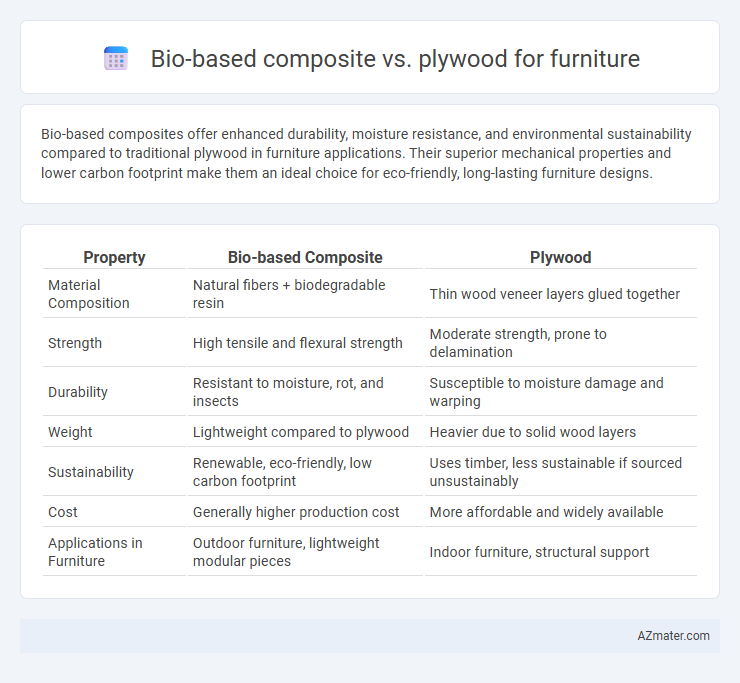
Bio-based composites offer enhanced durability, moisture resistance, and environmental sustainability compared to traditional plywood in furniture applications. Their superior mechanical properties and lower carbon footprint make them an ideal choice for eco-friendly, long-lasting furniture designs.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bio-based Composite | Plywood |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural fibers + biodegradable resin | Thin wood veneer layers glued together |
| Strength | High tensile and flexural strength | Moderate strength, prone to delamination |
| Durability | Resistant to moisture, rot, and insects | Susceptible to moisture damage and warping |
| Weight | Lightweight compared to plywood | Heavier due to solid wood layers |
| Sustainability | Renewable, eco-friendly, low carbon footprint | Uses timber, less sustainable if sourced unsustainably |
| Cost | Generally higher production cost | More affordable and widely available |
| Applications in Furniture | Outdoor furniture, lightweight modular pieces | Indoor furniture, structural support |
Introduction to Bio-based Composites and Plywood
Bio-based composites are materials composed of natural fibers such as hemp, flax, or wood combined with bio-resins, offering enhanced sustainability and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional options. Plywood, a widely used engineered wood product, consists of thin layers of wood veneer glued together to create strong, versatile panels commonly applied in furniture production. The choice between bio-based composites and plywood depends on factors like durability, environmental footprint, and aesthetic preferences in furniture manufacturing.
Material Composition and Sustainability
Bio-based composites consist primarily of natural fibers such as hemp, flax, or kenaf combined with biodegradable or bio-derived resins, offering a renewable alternative to traditional wood veneers and adhesives used in plywood. Plywood is composed of thin layers of wood veneer glued together with synthetic adhesives, which can release formaldehyde and other volatile organic compounds, impacting indoor air quality. Bio-based composites generally demonstrate superior sustainability due to lower carbon footprints, reduced reliance on fossil fuels, and enhanced biodegradability compared to conventional plywood products.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Bio-based composites reduce environmental impact through the use of renewable materials like natural fibers and biodegradable resins, significantly lowering carbon emissions compared to traditional plywood, which relies on hardwood logging and resin-based adhesives that release formaldehyde. The production of bio-based composites generates less waste and energy consumption, contributing to reduced ecological footprints and improved sustainability in furniture manufacturing. In contrast, plywood often involves deforestation and chemical treatments that can harm ecosystems and reduce biodiversity.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Bio-based composites offer superior mechanical strength compared to traditional plywood, exhibiting higher tensile and flexural strength due to their reinforced natural fibers. These composites also demonstrate enhanced durability, resisting moisture, impact, and warping better than plywood, which tends to degrade in humid environments. The improved mechanical properties and longevity of bio-based composites make them a more sustainable and robust choice for furniture manufacturing.
Aesthetic Qualities and Design Flexibility
Bio-based composites offer superior design flexibility compared to plywood due to their moldability and ability to incorporate diverse textures and colors, enabling more innovative and customized furniture aesthetics. Plywood, while strong and cost-effective, tends to have a more traditional wood grain look that limits creative surface finishes and complex shapes. The inherent versatility of bio-based composites allows designers to achieve both modern appeal and sustainable aesthetics that cater to evolving consumer preferences in furniture design.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Bio-based composites generally present higher initial costs compared to traditional plywood due to raw material sourcing and specialized manufacturing processes, but offer long-term savings through durability and eco-friendly benefits. Plywood remains widely available in global markets with established supply chains, driving its affordability and accessibility for mass furniture production. Increasing demand for sustainable materials is expanding the market availability of bio-based composites, potentially reducing costs as production scales up and technology advances.
Workability and Manufacturing Processes
Bio-based composites offer superior workability compared to plywood, as their materials can be molded into complex shapes and allow for easier customization during manufacturing. The manufacturing process of bio-based composites involves layering natural fibers with bio-resins, which requires less energy and produces less waste than traditional plywood production that involves cutting and assembling wood veneers. These features make bio-based composites more adaptable for innovative furniture designs and environmentally sustainable practices in manufacturing.
Health and Safety Considerations
Bio-based composites for furniture offer significant health advantages over traditional plywood by minimizing formaldehyde emissions, a common concern due to the urea-formaldehyde resins used in plywood manufacturing. These composites are typically made from natural fibers and bio-resins that reduce exposure to volatile organic compounds (VOCs), enhancing indoor air quality and reducing respiratory risks. Their non-toxic, sustainable materials also contribute to safer handling and reduced allergen potential during production and use.
Applications in Modern Furniture Design
Bio-based composites offer superior sustainability and lightweight properties compared to traditional plywood, making them ideal for eco-friendly and innovative furniture designs. Their enhanced durability and resistance to moisture enable versatile applications in both indoor and outdoor modern furniture, including chairs, tables, and cabinetry. Plywood remains favored for its cost-effectiveness and structural stability in classic furniture pieces but is increasingly supplemented or replaced by bio-based composites in high-end, environmentally conscious projects.
Future Trends in Sustainable Furniture Materials
Bio-based composites are emerging as a cutting-edge alternative to traditional plywood, offering enhanced sustainability, reduced carbon footprint, and superior resistance to moisture and pests. Innovations in natural fiber reinforcements and bio-resins are driving the evolution of furniture materials toward greater environmental compatibility and circular economy integration. Future trends emphasize scalable production, biodegradability, and improved mechanical properties, positioning bio-based composites as the forefront choice in sustainable furniture manufacturing.
Infographic: Bio-based composite vs Plywood for Furniture
 azmater.com
azmater.com