Nanocomposite shelves offer superior strength, durability, and moisture resistance compared to traditional chipboard shelves. Chipboard is more affordable but is prone to swelling and damage in humid environments, making nanocomposites ideal for long-lasting, high-performance shelving.
Table of Comparison
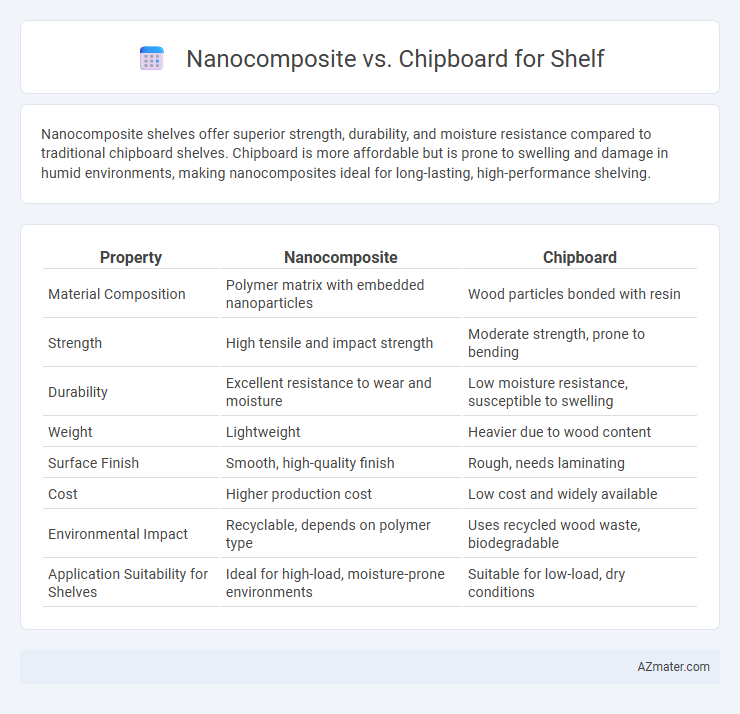
| Property | Nanocomposite | Chipboard |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Polymer matrix with embedded nanoparticles | Wood particles bonded with resin |
| Strength | High tensile and impact strength | Moderate strength, prone to bending |
| Durability | Excellent resistance to wear and moisture | Low moisture resistance, susceptible to swelling |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier due to wood content |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, high-quality finish | Rough, needs laminating |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Low cost and widely available |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable, depends on polymer type | Uses recycled wood waste, biodegradable |
| Application Suitability for Shelves | Ideal for high-load, moisture-prone environments | Suitable for low-load, dry conditions |
Introduction to Shelf Material Choices
Nanocomposite and chipboard represent two prominent shelf material choices, each offering distinct benefits for durability and aesthetics. Nanocomposite shelves exhibit enhanced strength, moisture resistance, and long-term stability due to their engineered nanomaterial composition. In contrast, chipboard shelves are valued for cost-effectiveness and ease of customization, though they may lack the same level of moisture resistance and structural integrity as nanocomposites.
What is Nanocomposite?
Nanocomposite is an advanced material composed of polymer matrices infused with nanoscale fillers, enhancing mechanical strength, durability, and resistance to moisture compared to traditional materials like chipboard. Nanocomposite shelves offer superior load-bearing capacity and improved surface finish, making them ideal for high-performance, long-lasting shelving solutions. Unlike chipboard, which is made from compressed wood particles and adhesive, nanocomposites integrate nanomaterials such as clay or carbon nanotubes to achieve enhanced structural and environmental properties.
Understanding Chipboard Shelving
Chipboard shelving, made from wood particles bonded with resin under heat and pressure, offers a cost-effective and sturdy solution for everyday storage needs. Nanocomposite shelves incorporate advanced materials that enhance strength, resistance to moisture, and durability compared to traditional chipboard. Understanding the composition and performance of chipboard shelving helps in evaluating its suitability for environments prone to humidity and heavy loads.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Nanocomposite shelves exhibit superior strength and durability compared to chipboard shelves due to the incorporation of nanoparticles that enhance structural integrity and resistance to wear. The nanocomposite materials offer higher tensile strength, improved impact resistance, and greater moisture resistance, extending the shelf's lifespan in demanding environments. In contrast, chipboard commonly suffers from swelling and weakening when exposed to humidity, limiting its durability and load-bearing capacity over time.
Weight and Load-Bearing Capacity
Nanocomposite shelves offer superior load-bearing capacity compared to chipboard due to their enhanced material strength and durability, making them ideal for heavy or industrial storage needs. Chipboard, being a composite of wood particles and resin, is significantly heavier yet less robust under stress, which limits its use to light or medium weight storage applications. Choosing nanocomposite materials results in lighter shelves with increased resistance to warping and sagging, optimizing both weight efficiency and structural integrity.
Moisture and Humidity Resistance
Nanocomposite shelves exhibit superior moisture and humidity resistance compared to chipboard, due to their enhanced polymer matrix infused with nanoscale fillers that prevent water absorption and swelling. Chipboard, made from wood particles bonded with resin, tends to absorb moisture, leading to warping and degradation in humid environments. For environments with fluctuating humidity levels, nanocomposite shelves offer greater durability and longer lifespan, reducing maintenance and replacement costs.
Aesthetic Versatility and Finishing Options
Nanocomposite shelves offer superior aesthetic versatility with their smooth surfaces that support a wide range of finishes, including high-gloss, matte, and textured coatings, enhancing modern and contemporary designs. Chipboard, while cost-effective, often requires laminates or veneers to achieve similar visual appeal but lacks the same durability against wear and moisture. The finishing options on nanocomposite materials allow for seamless integration into various interior styles, providing both functional and decorative advantages over chipboard.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nanocomposite shelves offer enhanced durability and lower environmental impact due to their use of advanced, often recycled, nanomaterials that reduce raw material consumption and extend product lifespan. Chipboard, commonly made from wood particles bonded with adhesives, often involves formaldehyde-based resins that can off-gas harmful chemicals and typically has a shorter lifespan, leading to more frequent replacement and higher waste generation. Sustainable choices favor nanocomposite shelves for their potential recyclability, reduced VOC emissions, and longer service life, contributing to lower overall ecological footprints compared to traditional chipboard options.
Cost Analysis: Nanocomposite vs Chipboard
Nanocomposite shelves generally exhibit higher upfront costs compared to chipboard due to advanced material composition and manufacturing processes, leading to greater durability and longer lifespan. Chipboard offers a budget-friendly option with lower initial expenditure but may incur higher maintenance and replacement costs over time due to susceptibility to moisture and wear. A cost analysis favors nanocomposite for long-term investment, while chipboard suits short-term budget constraints in shelving solutions.
Best Applications and Recommendations
Nanocomposite shelves offer superior strength, durability, and resistance to moisture and chemicals, making them ideal for industrial, laboratory, and high-stress environments. Chipboard shelves are best suited for low-cost, decorative, and lightweight applications such as home storage or temporary shelving, but require careful protection from moisture to prevent swelling and damage. For long-term use in humid or demanding conditions, nanocomposite is recommended, while chipboard is suitable for budget-conscious projects with minimal exposure to wear and moisture.
Infographic: Nanocomposite vs Chipboard for Shelf
 azmater.com
azmater.com