Wood plastic composites offer enhanced durability, weather resistance, and low maintenance for roofing compared to traditional bituminous felt, which is prone to cracking and requires frequent repairs. Wood plastic materials also provide better insulation and environmental sustainability with recyclable components.
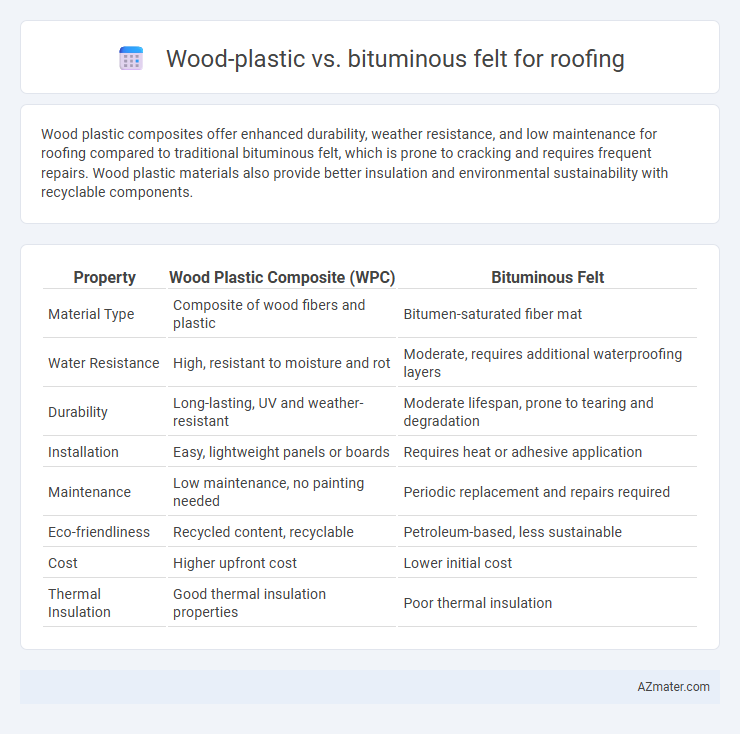
Table of Comparison
| Property | Wood Plastic Composite (WPC) | Bituminous Felt |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Composite of wood fibers and plastic | Bitumen-saturated fiber mat |
| Water Resistance | High, resistant to moisture and rot | Moderate, requires additional waterproofing layers |
| Durability | Long-lasting, UV and weather-resistant | Moderate lifespan, prone to tearing and degradation |
| Installation | Easy, lightweight panels or boards | Requires heat or adhesive application |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, no painting needed | Periodic replacement and repairs required |
| Eco-friendliness | Recycled content, recyclable | Petroleum-based, less sustainable |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost | Lower initial cost |
| Thermal Insulation | Good thermal insulation properties | Poor thermal insulation |
Introduction to Roofing Materials: Wood Plastic and Bituminous Felt
Wood plastic composites (WPC) offer durability, resistance to moisture, and low maintenance for roofing applications, making them an innovative alternative to traditional materials. Bituminous felt, composed of layers of asphalt-saturated organic or fiberglass mat, provides excellent waterproofing and weather resistance, widely used in low-slope roofing systems. Both materials serve distinct purposes in roofing: WPC for structural and aesthetic elements, and bituminous felt primarily for protective underlayment and waterproofing layers.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Wood plastic roofing combines wood fibers and thermoplastic polymers like polyethylene or polypropylene, producing a composite material through extrusion or compression molding that offers durability and resistance to moisture. Bituminous felt consists of a base layer of organic or fiberglass mat saturated with bitumen, a petroleum-derived adhesive, and is manufactured by impregnating the base with heated bitumen followed by surface treatments such as mineral granules or sand to enhance weather resistance. The manufacturing of wood plastic composites emphasizes uniform blending and curing of wood fibers and polymers, while bituminous felt production focuses on controlled bitumen saturation and coating processes to ensure waterproofing and flexibility.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Wood plastic composite roofing offers superior durability due to its resistance to rot, insects, and UV damage, extending its lifespan up to 30 years with minimal maintenance. Bituminous felt, commonly used as an underlayment, typically lasts 10 to 15 years but is susceptible to tearing, water damage, and degradation from prolonged exposure to sunlight. Choosing wood plastic roofing materials significantly enhances long-term performance and reduces replacement frequency compared to traditional bituminous felt.
Weather Resistance and Waterproofing
Wood plastic roofing offers superior weather resistance due to its composite materials that resist UV rays, moisture, and temperature fluctuations, ensuring long-term durability. Bituminous felt provides excellent waterproofing through its asphalt-based layers, effectively preventing water penetration and damage. However, wood plastic generally outperforms bituminous felt in resisting cracking, warping, and degradation caused by prolonged exposure to harsh weather conditions.
Installation Methods and Ease
Wood plastic roofing panels require precise alignment and fastening using screws or nails, often involving cutting tools for custom fits, which can prolong installation time but yield a durable and eco-friendly surface. Bituminous felt installation typically involves rolling out sheets and securing them with adhesive or heat welding, allowing for faster application on complex roof shapes but necessitating careful overlap to ensure waterproofing. Both materials demand skilled labor, but bituminous felt generally offers a quicker, more flexible installation process, while wood plastic panels emphasize structural integrity and longevity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Wood plastic composites (WPC) roofing offers improved sustainability through the use of recycled plastics and natural wood fibers, reducing landfill waste and lowering the demand for virgin materials. Bituminous felt, derived from petroleum products, presents higher environmental concerns due to its non-renewable resource base and limited recyclability. WPC's durability and potential for recycling enhance its eco-friendliness, while bituminous felt contributes to higher carbon emissions and waste challenges in roofing applications.
Cost Analysis and Budget Considerations
Wood plastic roofing generally incurs higher initial costs due to material and manufacturing complexity but offers extended durability and lower maintenance expenses over time, potentially reducing long-term budget allocations. Bituminous felt is more cost-effective upfront with simpler installation and lower material costs, making it a preferred choice for limited budgets or temporary solutions. Evaluating total cost of ownership, including lifespan and repair frequency, is crucial for an accurate budget comparison between wood plastic and bituminous felt roofing.
Maintenance Requirements and Longevity
Wood plastic composite roofing requires minimal maintenance due to its resistance to rot, insects, and weathering, significantly extending its lifespan compared to traditional materials. Bituminous felt roofing demands regular inspections and timely repairs to address issues like cracking, blistering, and water ingress, with an average lifespan of 10 to 20 years depending on installation quality and environmental exposure. Choosing wood plastic roofing reduces long-term maintenance costs and enhances durability, especially in regions prone to harsh weather conditions.
Aesthetic Appeal and Versatility
Wood plastic roofing offers a modern aesthetic with customizable textures and colors that mimic natural wood, enhancing architectural appeal in contemporary buildings. It provides versatile installation options and adaptability to various roof shapes, making it suitable for innovative designs and renovations. Bituminous felt, while traditional and less flexible in style, excels in functional applications but lacks the diverse visual appeal and customization that wood plastic materials offer.
Choosing the Right Material: Wood Plastic vs Bituminous Felt
Choosing the right roofing material depends on durability, cost, and environmental impact. Wood plastic composites offer superior resistance to moisture, rot, and insect damage compared to bituminous felt, which is more affordable but prone to cracking and wear over time. Evaluating climate conditions alongside maintenance requirements helps determine whether wood plastic's longevity or bituminous felt's cost-effectiveness best suits your roofing needs.
Infographic: Wood plastic vs Bituminous felt for Roofing
 azmater.com
azmater.com