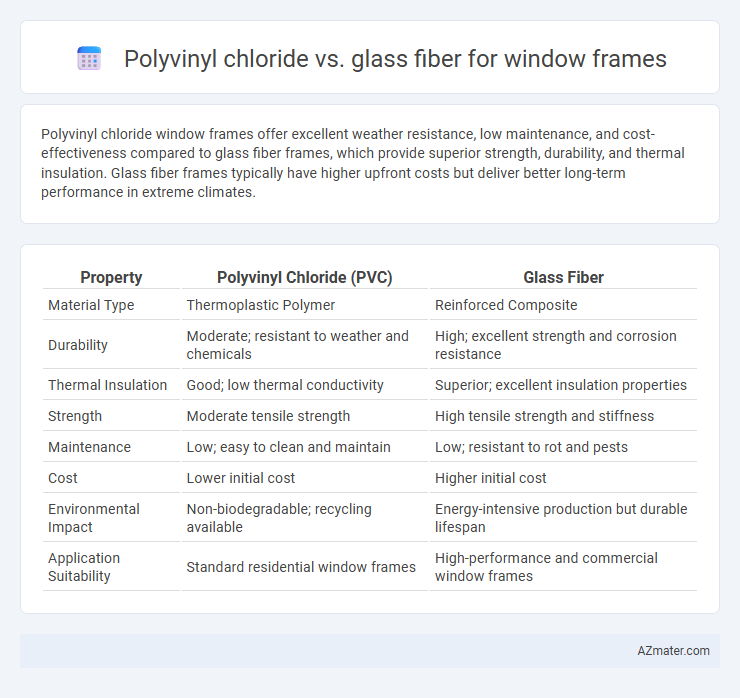
Polyvinyl chloride window frames offer excellent weather resistance, low maintenance, and cost-effectiveness compared to glass fiber frames, which provide superior strength, durability, and thermal insulation. Glass fiber frames typically have higher upfront costs but deliver better long-term performance in extreme climates.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Glass Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Polymer | Reinforced Composite |
| Durability | Moderate; resistant to weather and chemicals | High; excellent strength and corrosion resistance |
| Thermal Insulation | Good; low thermal conductivity | Superior; excellent insulation properties |
| Strength | Moderate tensile strength | High tensile strength and stiffness |
| Maintenance | Low; easy to clean and maintain | Low; resistant to rot and pests |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable; recycling available | Energy-intensive production but durable lifespan |
| Application Suitability | Standard residential window frames | High-performance and commercial window frames |
Introduction to Window Frame Materials
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and glass fiber are prominent materials used in modern window frames, offering distinct advantages in durability, insulation, and maintenance. PVC frames are renowned for their cost-effectiveness, resistance to weathering, and excellent thermal performance due to their low thermal conductivity. Glass fiber frames provide superior strength, dimensional stability, and resistance to expansion and contraction, making them ideal for high-performance and energy-efficient window applications.
Overview of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Window Frames
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) window frames are widely favored for their durability, low maintenance, and excellent insulation properties, making them energy-efficient and cost-effective. PVC frames resist moisture, rot, and corrosion, providing long-lasting performance in various climates compared to glass fiber frames that offer higher structural strength but at a greater cost. Their flexibility in design and ease of installation make PVC frames a popular choice for residential and commercial window applications.
Overview of Glass Fiber (Fiberglass) Window Frames
Glass fiber window frames, commonly known as fiberglass frames, offer exceptional durability, superior thermal performance, and resistance to warping compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) alternatives. Engineered from fine glass fibers bonded with resin, these frames provide high structural strength while maintaining lightweight properties, making them ideal for various climatic conditions. Their low thermal conductivity and minimal expansion ensure energy efficiency and long-term stability in window installations.
Durability Comparison: PVC vs Glass Fiber
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) window frames offer moderate durability, resisting moisture and rot but are prone to warping and degradation under prolonged UV exposure. Glass fiber window frames provide superior durability with high resistance to temperature fluctuations, corrosion, and UV rays, maintaining structural integrity over decades. The inherent strength and low maintenance requirements of glass fiber make it a more long-lasting option compared to PVC in demanding environmental conditions.
Energy Efficiency and Insulation Properties
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) window frames offer superior energy efficiency due to their inherent thermal insulation properties and resistance to heat transfer, significantly reducing energy loss. Glass fiber frames provide high structural strength combined with excellent thermal stability and low conductivity, ensuring effective insulation and minimizing temperature fluctuations. Both materials contribute to energy savings, but PVC typically excels in maintaining consistent indoor temperatures through better insulation performance.
Maintenance Requirements and Longevity
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) window frames offer low maintenance due to their resistance to rot, corrosion, and insect damage, requiring only occasional cleaning with mild detergents. Glass fiber frames exhibit exceptional durability and longevity, often lasting 40 years or more with minimal upkeep, as they resist warping, swelling, and fading under ultraviolet exposure. Both materials provide significant lifespan advantages over traditional wood, but glass fiber frames generally outperform PVC in long-term structural stability and resistance to environmental stressors.
Aesthetic Versatility and Design Options
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) window frames offer extensive aesthetic versatility with a wide range of colors, textures, and finishes, including wood-grain effects that suit modern and traditional architectural styles. Glass fiber frames excel in design flexibility, providing sleek, slim profiles that maximize glass area and enhance natural light without compromising strength or durability. Both materials support custom shapes and sizes, but PVC allows for more vibrant color customization, while glass fiber emphasizes minimalist, high-performance design aesthetics.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) window frames have a lower initial carbon footprint due to energy-efficient manufacturing and lightweight transport, but they release harmful chemicals during production and disposal, raising environmental concerns. Glass fiber frames offer superior durability and recyclability, reducing waste over their lifespan while requiring less frequent replacement, enhancing overall sustainability. Choosing glass fiber supports longer-term environmental benefits through reduced resource consumption and improved recyclability compared to PVC.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Long-term Investment
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) window frames typically have a lower initial cost compared to glass fiber frames, making them a budget-friendly option for residential projects. Over the long term, PVC requires less maintenance and has good durability, but may degrade under extreme weather conditions, potentially increasing replacement costs. Glass fiber frames, although more expensive upfront, offer superior strength, thermal insulation, and longevity, often resulting in lower life cycle costs and enhanced energy savings over decades.
Choosing the Right Window Frame Material for Your Needs
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers excellent insulation, low maintenance, and affordability, making it ideal for energy-efficient and budget-conscious window frames. Glass fiber frames provide superior strength, durability, and resistance to warping or thermal expansion, suitable for climates with extreme temperatures and homes requiring long-lasting, structural integrity. Choosing between PVC and glass fiber depends on prioritizing energy efficiency and cost versus durability and environmental resilience for your specific window frame needs.
Infographic: Polyvinyl chloride vs Glass fiber for Window frame
 azmater.com
azmater.com