Bio-based composites for decking boards offer superior environmental benefits by reducing carbon footprint and enhancing biodegradability compared to traditional plastic composites. They maintain comparable durability and weather resistance while promoting sustainable resource use and minimizing plastic pollution.
Table of Comparison
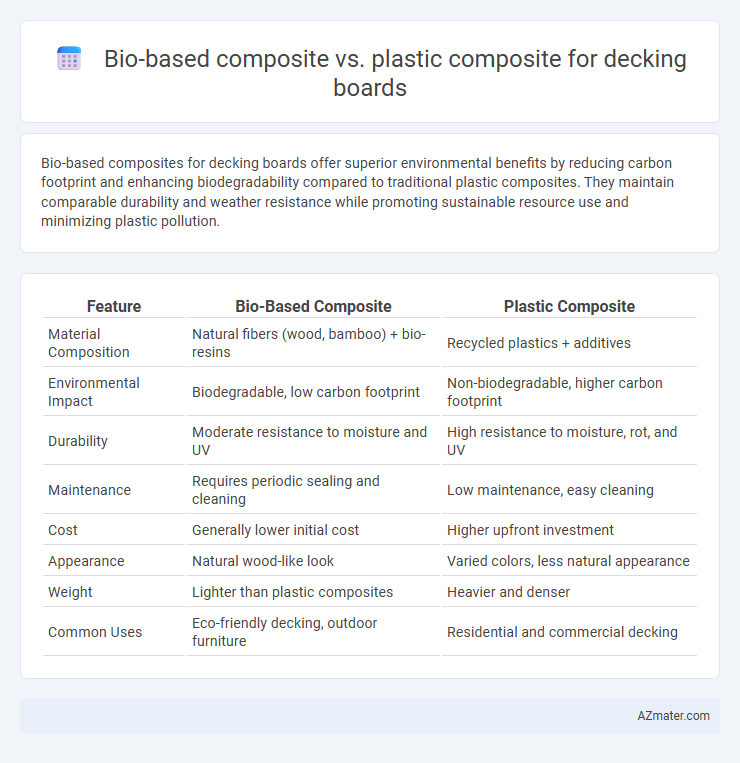
| Feature | Bio-Based Composite | Plastic Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural fibers (wood, bamboo) + bio-resins | Recycled plastics + additives |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, higher carbon footprint |
| Durability | Moderate resistance to moisture and UV | High resistance to moisture, rot, and UV |
| Maintenance | Requires periodic sealing and cleaning | Low maintenance, easy cleaning |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher upfront investment |
| Appearance | Natural wood-like look | Varied colors, less natural appearance |
| Weight | Lighter than plastic composites | Heavier and denser |
| Common Uses | Eco-friendly decking, outdoor furniture | Residential and commercial decking |
Introduction to Decking Board Materials
Decking board materials primarily consist of bio-based composites and plastic composites, each offering unique environmental and performance advantages. Bio-based composites combine natural fibers such as wood, hemp, or flax with biodegradable resins, providing enhanced sustainability and reduced carbon footprint. Plastic composites, often made from recycled polyethylene or polypropylene mixed with wood flour, deliver high durability, moisture resistance, and low maintenance requirements for long-lasting outdoor applications.
Overview of Bio-based Composites
Bio-based composites for decking boards are composed of natural fibers such as hemp, flax, or wood combined with biodegradable resins, offering enhanced sustainability compared to traditional plastic composites that rely on petroleum-based polymers. These materials provide comparable durability, resistance to moisture, and reduced environmental impact by promoting biodegradability and lower carbon footprints. Bio-based composites also improve thermal insulation and reduce the reliance on fossil fuels, making them an eco-friendly alternative in outdoor building applications.
Understanding Plastic Composites
Plastic composites used in decking boards typically combine wood fibers with thermoplastic resins like polyethylene or polypropylene, offering enhanced moisture resistance and durability compared to traditional wood. These composites exhibit excellent resistance to rot, insects, and decay but often lack the environmental benefits and biodegradability associated with bio-based composites. Understanding the chemical makeup and performance characteristics of plastic composites is essential for selecting decking materials that balance longevity with sustainability goals.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Bio-based composite decking boards significantly reduce carbon footprint by utilizing renewable natural fibers like hemp, flax, or wood fibers combined with biodegradable resins, resulting in lower greenhouse gas emissions during production compared to plastic composites made from petroleum-based polymers. The biodegradability and recyclability of bio-based composites minimize landfill waste and microplastic pollution, whereas plastic composites often persist in the environment for centuries and contribute to microplastic contamination in soil and waterways. Life-cycle assessments reveal bio-based composites offer improved sustainability metrics through reduced fossil fuel dependence and enhanced end-of-life environmental benefits.
Durability and Lifespan Analysis
Bio-based composite decking boards exhibit enhanced durability due to their natural fiber reinforcement, offering resistance to moisture, UV radiation, and fungal decay, which extends their lifespan beyond 25 years. Plastic composite decking, primarily made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or polypropylene mixed with wood fibers, provides strong resistance to rot and insect damage but tends to be more susceptible to surface scratches and fading over time. Studies highlight that bio-based composites maintain structural integrity and appearance longer under varying environmental conditions, while plastic composites may require more frequent maintenance to preserve aesthetic and functional qualities.
Maintenance Requirements and Costs
Bio-based composite decking boards require less frequent maintenance compared to plastic composites, as they resist fading, staining, and mold growth more effectively. Plastic composite boards may demand periodic cleaning and occasional sealing to prevent discoloration and surface wear, increasing long-term upkeep costs. Overall, bio-based composites offer lower maintenance expenses and extended durability, making them a cost-efficient choice for decking solutions.
Aesthetic and Design Flexibility
Bio-based composite decking boards offer a natural wood-like appearance with rich textures and authentic grain patterns, enhancing outdoor aesthetics. These materials provide superior design flexibility due to their ability to be molded into various shapes, colors, and finishes without compromising environmental sustainability. Plastic composites, while durable and low-maintenance, often lack the warmth and nuanced visual appeal found in bio-based alternatives, limiting customization options for bespoke decking designs.
Performance in Varying Climates
Bio-based composite decking boards demonstrate superior adaptability to varying climates due to their natural fibers combined with durable resins, which enhance moisture resistance and reduce thermal expansion compared to traditional plastic composites. Plastic composite decking often suffers from higher heat retention and surface temperature increases, leading to warping and faster material degradation in hot climates. In colder or fluctuating weather, bio-based composites maintain better dimensional stability and resist cracking, making them a more reliable choice for diverse environmental conditions.
Cost Comparison and Market Trends
Bio-based composite decking boards typically offer a higher initial cost compared to traditional plastic composites due to raw material sourcing and manufacturing processes involving sustainable fibers like hemp, bamboo, or wood flour combined with biopolymers. Market trends indicate a growing demand for bio-based composites driven by increasing environmental regulations and consumer preference for eco-friendly building materials, fostering innovations that gradually improve cost-efficiency. Plastic composites maintain cost competitiveness through established supply chains and lower production expenses, though their market share faces challenges as sustainability concerns reshape industry standards.
Sustainability and Future Prospects
Bio-based composites for decking boards offer enhanced sustainability by utilizing renewable materials such as plant fibers and biodegradable resins, significantly reducing carbon footprint and environmental impact compared to traditional plastic composites derived from non-renewable petroleum sources. The biodegradability and lower energy consumption in production of bio-based composites position them as a favorable choice for eco-conscious consumers and green building initiatives. Future prospects highlight increasing market adoption driven by advancements in bio-composite durability, regulatory incentives for sustainable materials, and growing demand for circular economy solutions in construction.
Infographic: Bio-based composite vs Plastic composite for Decking board
 azmater.com
azmater.com