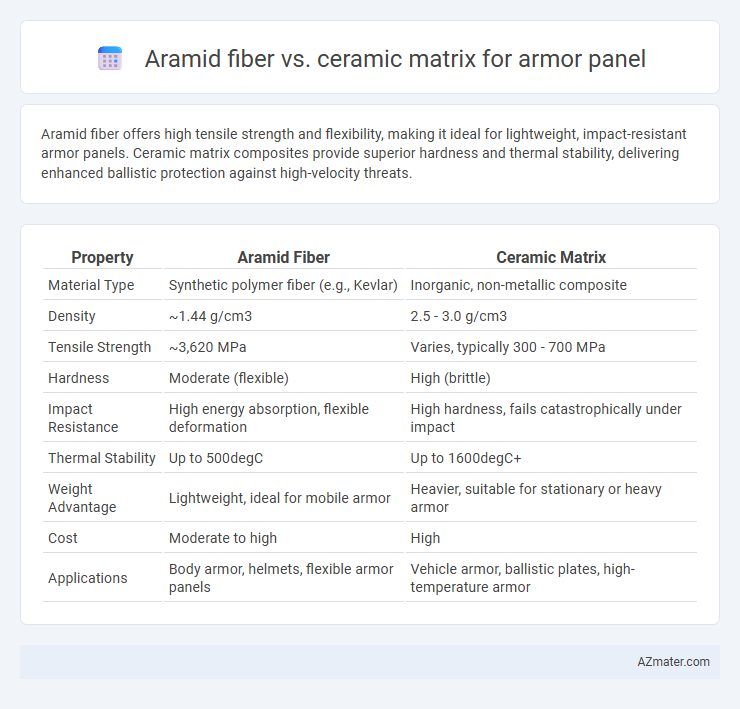
Aramid fiber offers high tensile strength and flexibility, making it ideal for lightweight, impact-resistant armor panels. Ceramic matrix composites provide superior hardness and thermal stability, delivering enhanced ballistic protection against high-velocity threats.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aramid Fiber | Ceramic Matrix |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic polymer fiber (e.g., Kevlar) | Inorganic, non-metallic composite |
| Density | ~1.44 g/cm3 | 2.5 - 3.0 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | ~3,620 MPa | Varies, typically 300 - 700 MPa |
| Hardness | Moderate (flexible) | High (brittle) |
| Impact Resistance | High energy absorption, flexible deformation | High hardness, fails catastrophically under impact |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 500degC | Up to 1600degC+ |
| Weight Advantage | Lightweight, ideal for mobile armor | Heavier, suitable for stationary or heavy armor |
| Cost | Moderate to high | High |
| Applications | Body armor, helmets, flexible armor panels | Vehicle armor, ballistic plates, high-temperature armor |
Introduction to Armor Panel Materials
Aramid fiber, known for its exceptional tensile strength and lightweight properties, is widely used in soft and flexible armor panels for ballistic protection. Ceramic matrix composites offer superior hardness and high-temperature resistance, making them ideal for hard armor plates designed to defeat high-velocity projectiles. Combining aramid fibers with ceramic matrix materials often enhances overall armor performance by balancing flexibility, impact resistance, and weight efficiency.
Overview of Aramid Fiber Armor
Aramid fiber armor, known for its high tensile strength-to-weight ratio, offers superior impact resistance and flexibility compared to ceramic matrix panels. Its woven fabric structure effectively dissipates energy from ballistic threats while maintaining lightweight properties, making it ideal for personal and vehicle armor applications. The polymer-based fibers also provide enhanced durability against multiple hits and reduce blunt force trauma on impact.
Characteristics of Ceramic Matrix Armor
Ceramic matrix armor panels exhibit exceptional hardness and high compressive strength, making them highly effective at dissipating and blunting kinetic energy from ballistic impacts. These panels offer superior thermal stability and resistance to chemical corrosion compared to aramid fiber composites, allowing for operation in extreme environments. Their brittleness requires backing materials, such as fiber composites, to absorb residual energy and prevent shattering during high-velocity impacts.
Comparative Weight and Density
Aramid fiber armor panels typically weigh less due to their lower density of approximately 1.44 g/cm3 compared to ceramic matrix composites, which have densities ranging from 2.5 to 3.0 g/cm3. This significant difference in density makes aramid fibers more suitable for lightweight ballistic protection applications, enhancing mobility without compromising strength. Ceramic matrix panels offer higher hardness and better resistance to high-velocity impacts but incur a weight penalty due to their heavier material composition.
Ballistic Protection Levels
Aramid fiber armor panels, such as those made from Kevlar, excel in reducing impact from handgun rounds and fragment threats, typically providing protection levels up to NIJ Level IIIA. Ceramic matrix armor panels offer superior ballistic protection by effectively defeating higher caliber rifle rounds and armor-piercing projectiles, often achieving NIJ Level III and IV certifications. The integration of ceramic matrix materials significantly enhances the armor's hardness and energy-dissipation capabilities, making it the preferred choice for military-grade ballistic protection.
Durability and Impact Resistance
Aramid fiber offers high tensile strength and excellent energy absorption, making it effective for impact resistance in armor panels, especially against ballistic threats. Ceramic matrix armor provides superior hardness and compressive strength, enhancing durability and protection against high-velocity projectiles by fracturing the projectile upon impact. Combining aramid fibers with ceramic matrices often results in optimal armor performance, leveraging ceramic's rigidity and aramid's toughness for enhanced overall durability and impact resistance.
Flexibility vs. Rigidity
Aramid fiber armor panels offer exceptional flexibility and impact resistance, making them ideal for applications requiring lightweight and flexible protection. Ceramic matrix armor panels provide superior rigidity and hardness, delivering enhanced ballistic resistance but with increased fragility and weight. The choice between aramid fiber and ceramic matrix hinges on the need for flexibility in movement versus maximum structural toughness.
Thermal Stability and Environmental Performance
Aramid fiber exhibits excellent impact resistance and high tensile strength but has limited thermal stability, degrading above 400degC, which restricts its use in extreme heat conditions. Ceramic matrix armor panels offer superior thermal stability, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 1000degC, making them ideal for high-temperature environments. Environmentally, aramid fibers are susceptible to moisture absorption and UV degradation, while ceramic composites resist corrosion and maintain performance under diverse environmental conditions.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Aramid fiber armor panels typically offer lower production costs and greater availability due to widespread manufacturing and established supply chains, making them suitable for budget-conscious applications. Ceramic matrix armor panels, while providing superior ballistic protection and durability, involve higher material and fabrication expenses because of complex processing and limited supplier options. Cost analysis favors aramid fibers in mass deployment scenarios, whereas ceramic matrix composites are preferred where performance justifies the premium investment.
Applications and Industry Recommendations
Aramid fiber armor panels are widely used in personal protective equipment such as bulletproof vests and helmets due to their high tensile strength and lightweight properties, making them ideal for law enforcement and military applications. Ceramic matrix armor panels are favored in vehicle armor and aerospace industries for their superior hardness and ability to dissipate high-velocity impacts, providing enhanced protection against armor-piercing threats. Industry recommendations highlight aramid fibers for situations requiring flexibility and wearability, while ceramic matrix composites are preferred for heavy-duty protection where weight is less critical.
Infographic: Aramid fiber vs Ceramic matrix for Armor panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com