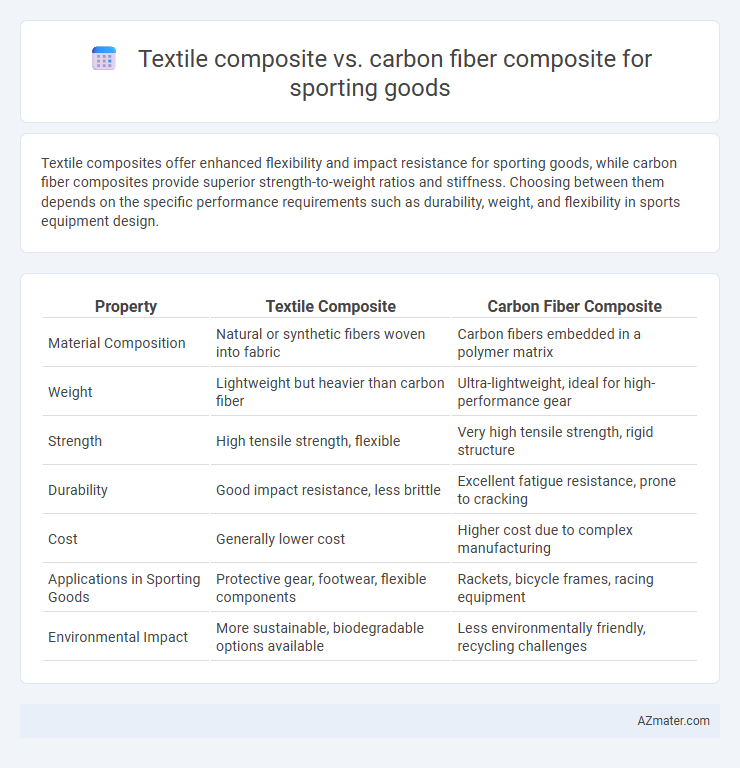
Textile composites offer enhanced flexibility and impact resistance for sporting goods, while carbon fiber composites provide superior strength-to-weight ratios and stiffness. Choosing between them depends on the specific performance requirements such as durability, weight, and flexibility in sports equipment design.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Textile Composite | Carbon Fiber Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural or synthetic fibers woven into fabric | Carbon fibers embedded in a polymer matrix |
| Weight | Lightweight but heavier than carbon fiber | Ultra-lightweight, ideal for high-performance gear |
| Strength | High tensile strength, flexible | Very high tensile strength, rigid structure |
| Durability | Good impact resistance, less brittle | Excellent fatigue resistance, prone to cracking |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to complex manufacturing |
| Applications in Sporting Goods | Protective gear, footwear, flexible components | Rackets, bicycle frames, racing equipment |
| Environmental Impact | More sustainable, biodegradable options available | Less environmentally friendly, recycling challenges |
Introduction to Composite Materials in Sporting Goods
Textile composites and carbon fiber composites are essential materials in sporting goods, offering advanced performance and durability. Textile composites provide flexibility and impact resistance through woven fibers, ideal for equipment like protective gear and apparel. Carbon fiber composites deliver exceptional strength-to-weight ratios, making them preferred for high-performance items such as racing bicycles, tennis rackets, and golf clubs.
Overview of Textile Composites
Textile composites used in sporting goods consist of woven or knitted fibers, such as glass, aramid, or carbon, embedded in a polymer matrix, offering flexibility and impact resistance. These composites provide enhanced durability, lightweight performance, and customizable mechanical properties, making them ideal for applications like protective gear, footwear, and apparel. Compared to carbon fiber composites, textile composites offer better formability and cost-effectiveness, though they generally have lower stiffness and strength.
Overview of Carbon Fiber Composites
Carbon fiber composites in sporting goods offer superior strength-to-weight ratios compared to traditional textile composites, making them ideal for high-performance applications such as bike frames, tennis rackets, and golf clubs. These composites consist of carbon fibers embedded in a polymer matrix, providing exceptional stiffness, durability, and resistance to fatigue. The enhanced mechanical properties result in improved athletic performance and reduced equipment weight, critical factors in competitive sports.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Textile composites offer superior flexibility and abrasion resistance, making them ideal for sports equipment requiring comfort and durability, while carbon fiber composites exhibit higher tensile strength and stiffness, providing enhanced performance in applications demanding lightweight rigidity. Carbon fiber composites typically have a tensile strength of 3500 MPa and a modulus of 230 GPa, greatly surpassing textile composites, which generally range around 600 MPa tensile strength and 30 GPa modulus. The choice between these composites depends on the specific mechanical property requirements for sporting goods, balancing strength-to-weight ratio and impact absorption capabilities.
Weight and Performance Differences
Textile composites, typically made from woven fibers such as fiberglass or aramid, offer a lighter weight option with excellent flexibility, making them suitable for sports equipment requiring moderate strength and shock absorption. Carbon fiber composites provide superior strength-to-weight ratios, delivering enhanced stiffness and durability which leads to improved performance in high-demand sports applications like racing bicycles and tennis rackets. The choice between textile and carbon fiber composites affects the balance of weight reduction and structural performance, with carbon fiber favored for its ability to maximize power transfer while minimizing overall weight.
Durability and Longevity in Sports Applications
Textile composites offer enhanced flexibility and impact resistance, making them durable for sports equipment subjected to frequent bending and stretching, such as protective gear and apparel. Carbon fiber composites provide exceptional strength-to-weight ratios and superior fatigue resistance, ensuring long-lasting performance in high-stress applications like racing bikes and tennis rackets. Both materials extend the lifespan of sporting goods, but carbon fiber composites generally deliver greater structural integrity and longevity under extreme conditions.
Cost Analysis: Textile vs Carbon Fiber Composites
Textile composites generally offer a lower-cost alternative to carbon fiber composites in sporting goods due to their less expensive raw materials and simpler manufacturing processes. Carbon fiber composites provide superior strength-to-weight ratios and durability but incur higher costs from complex production techniques and raw material expenses. The choice between textile and carbon fiber composites hinges on budget constraints and performance requirements specific to sports equipment applications.
Manufacturing Techniques and Scalability
Textile composites for sporting goods are typically manufactured using traditional weaving and braiding techniques that allow for flexibility in design and cost-effective scalability, making them suitable for mass production. Carbon fiber composites require precise layup and curing processes such as resin transfer molding or autoclave curing, which provide superior strength and stiffness but involve higher manufacturing complexity and costs that may limit large-scale scalability. The choice between textile and carbon fiber composites depends heavily on the balance between desired mechanical performance and production volume requirements.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Textile composites, often made from natural fibers like flax or hemp combined with bio-based resins, exhibit a lower environmental footprint due to renewable sourcing and biodegradability, contrasting sharply with carbon fiber composites derived from energy-intensive, non-renewable petroleum-based processes. The energy consumption in producing carbon fibers is significantly higher, contributing to increased carbon emissions and environmental degradation, which challenges the sustainability claims in sporting goods manufacturing. Textile composites promote circular economy principles through easier recyclability and reduced end-of-life waste, making them a more sustainable alternative for eco-conscious sporting goods innovation.
Choosing the Right Composite for Sporting Equipment
Textile composites offer enhanced flexibility, impact resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making them suitable for sports equipment requiring durability and comfort, such as protective gear and apparel. Carbon fiber composites provide superior strength-to-weight ratio and stiffness, ideal for high-performance sporting goods like bicycle frames, tennis rackets, and hockey sticks where lightweight and rigidity are critical. Selecting the right composite depends on balancing factors like weight, flexibility, cost, and performance to optimize athletic efficiency and durability.
Infographic: Textile composite vs Carbon fiber composite for Sporting goods
 azmater.com
azmater.com