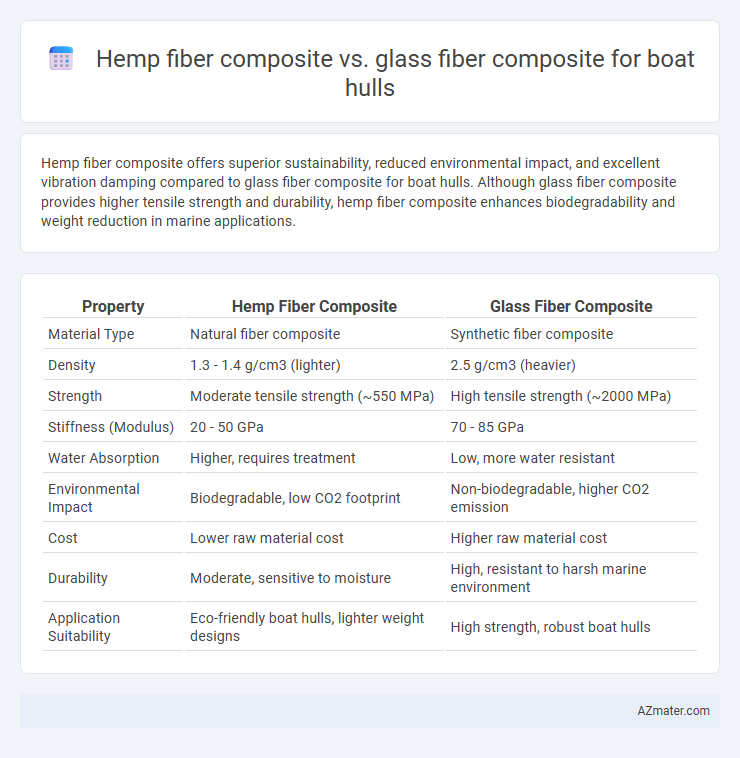
Hemp fiber composite offers superior sustainability, reduced environmental impact, and excellent vibration damping compared to glass fiber composite for boat hulls. Although glass fiber composite provides higher tensile strength and durability, hemp fiber composite enhances biodegradability and weight reduction in marine applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hemp Fiber Composite | Glass Fiber Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Natural fiber composite | Synthetic fiber composite |
| Density | 1.3 - 1.4 g/cm3 (lighter) | 2.5 g/cm3 (heavier) |
| Strength | Moderate tensile strength (~550 MPa) | High tensile strength (~2000 MPa) |
| Stiffness (Modulus) | 20 - 50 GPa | 70 - 85 GPa |
| Water Absorption | Higher, requires treatment | Low, more water resistant |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low CO2 footprint | Non-biodegradable, higher CO2 emission |
| Cost | Lower raw material cost | Higher raw material cost |
| Durability | Moderate, sensitive to moisture | High, resistant to harsh marine environment |
| Application Suitability | Eco-friendly boat hulls, lighter weight designs | High strength, robust boat hulls |
Introduction to Fiber Composites in Boat Building
Hemp fiber composites in boat hull construction offer sustainable and lightweight alternatives to traditional glass fiber composites, significantly reducing environmental impact while maintaining strength and durability. Hemp fibers provide excellent vibration damping and resistance to water absorption, enhancing hull longevity and performance in marine conditions. Glass fiber composites remain popular for their superior tensile strength and cost-effectiveness, but hemp fibers are gaining traction for eco-friendly boat building due to renewable sourcing and lower carbon footprint.
Overview of Hemp Fiber Composites
Hemp fiber composites offer a sustainable alternative to traditional glass fiber composites in boat hull construction, providing lightweight strength and improved environmental impact due to their natural origin. These composites exhibit high tensile strength, good vibration damping, and resistance to fatigue, making them suitable for marine applications. Hemp fibers also enhance biodegradability and reduce carbon footprint, aligning with eco-friendly manufacturing trends in the boating industry.
Overview of Glass Fiber Composites
Glass fiber composites, widely used in boat hull construction, consist of glass fibers embedded in a polymer matrix, providing excellent strength-to-weight ratios and corrosion resistance. Their high tensile strength and durability make them ideal for marine environments, offering significant impact resistance and dimensional stability. These composites are favored for ease of fabrication, cost-effectiveness, and proven performance in various watercraft applications.
Mechanical Properties: Hemp vs Glass Fiber
Hemp fiber composites exhibit lower tensile strength and modulus compared to glass fiber composites, typically around 300-600 MPa for hemp versus 2000-3500 MPa for glass fiber. However, hemp offers superior impact resistance and energy absorption, making it more effective in damping vibrations and reducing hull damage from impacts. The lower density of hemp fiber composites also contributes to a lighter overall boat hull, enhancing fuel efficiency and maneuverability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hemp fiber composites significantly reduce environmental impact compared to glass fiber composites due to their renewable, biodegradable nature and lower energy consumption during production. Hemp absorbs CO2 during cultivation, contributing to carbon sequestration, while glass fiber relies on energy-intensive manufacturing and non-renewable resources. The biodegradable properties of hemp fibers promote sustainability by minimizing long-term waste and pollution in marine environments.
Cost Analysis of Hemp and Glass Fiber Composites
Hemp fiber composites typically offer a lower raw material cost compared to glass fiber composites, with hemp fibers costing approximately 20-30% less per kilogram. Manufacturing costs for hemp composites can also be reduced due to lower energy consumption and simpler processing techniques, resulting in overall savings of up to 15% in production expenses for boat hulls. However, glass fiber composites, while more expensive, provide higher strength-to-weight ratios and durability, which may lead to longer-term cost benefits when considering maintenance and lifespan.
Durability and Longevity in Marine Environments
Hemp fiber composites exhibit excellent resistance to saltwater corrosion and UV degradation, enhancing durability in marine environments compared to traditional glass fiber composites. The natural fibers in hemp composites offer superior impact absorption and fatigue resistance, which contribute to prolonged structural integrity and reduced maintenance over time. While glass fiber composites provide high initial strength, their susceptibility to moisture ingress and osmotic blistering often leads to diminished longevity in harsh marine conditions.
Manufacturing and Workability
Hemp fiber composites offer significant advantages in manufacturing for boat hulls due to their natural fiber structure, which allows for easier cutting, shaping, and reduced tool wear compared to glass fiber composites. The workability of hemp fibers results in lower resin absorption and improved bonding, enhancing processing efficiency and reducing production times. Glass fiber composites, while providing high strength and durability, typically require more complex handling and specialized equipment to manage dust and brittleness during fabrication.
Performance in Real-World Applications
Hemp fiber composites exhibit superior vibration damping and improved impact resistance compared to glass fiber composites, enhancing comfort and safety in boat hull applications. Their lower density results in lighter hulls that contribute to increased fuel efficiency and better handling in rough waters. While glass fiber composites offer higher tensile strength, hemp composites provide sufficient structural integrity with added environmental benefits such as biodegradability and reduced carbon footprint.
Future Trends and Innovations in Boat Hull Materials
Hemp fiber composites are gaining traction in boat hull manufacturing due to their sustainability, lightweight properties, and superior vibration dampening compared to traditional glass fiber composites. Innovations in bio-based resins combined with hemp fibers enhance durability and water resistance, positioning hemp composites as a more eco-friendly alternative for future marine applications. Ongoing research focuses on improving the mechanical performance and long-term UV stability of hemp fiber composites to meet or exceed the standards set by glass fiber composites in high-performance boat hulls.
Infographic: Hemp fiber composite vs Glass fiber composite for Boat hull
 azmater.com
azmater.com