Aramid fiber provides superior impact resistance and heat durability for helmets compared to synthetic fibers. Its high tensile strength and lightweight properties enhance helmet safety and comfort during extreme conditions.
Table of Comparison
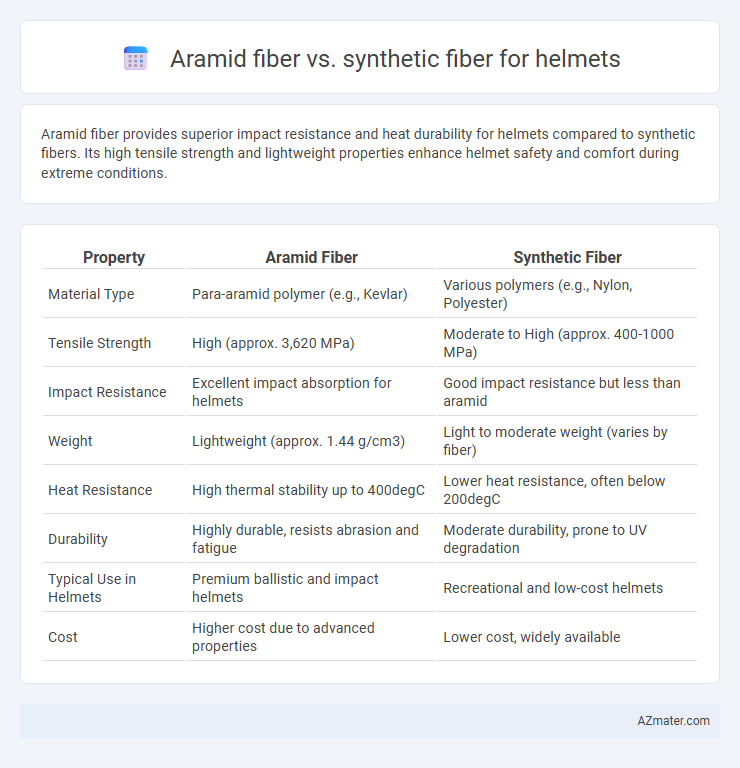
| Property | Aramid Fiber | Synthetic Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Para-aramid polymer (e.g., Kevlar) | Various polymers (e.g., Nylon, Polyester) |
| Tensile Strength | High (approx. 3,620 MPa) | Moderate to High (approx. 400-1000 MPa) |
| Impact Resistance | Excellent impact absorption for helmets | Good impact resistance but less than aramid |
| Weight | Lightweight (approx. 1.44 g/cm3) | Light to moderate weight (varies by fiber) |
| Heat Resistance | High thermal stability up to 400degC | Lower heat resistance, often below 200degC |
| Durability | Highly durable, resists abrasion and fatigue | Moderate durability, prone to UV degradation |
| Typical Use in Helmets | Premium ballistic and impact helmets | Recreational and low-cost helmets |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced properties | Lower cost, widely available |
Introduction to Aramid and Synthetic Fibers
Aramid fibers, known for exceptional strength and heat resistance, are widely used in helmet manufacturing due to their superior impact absorption and durability. Synthetic fibers, including polyester and nylon, offer flexibility and lightweight properties but generally provide less protection compared to aramid fibers. The choice between aramid and synthetic fibers directly influences helmet performance, safety standards, and longevity.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Aramid fibers used in helmets consist of rigid, rod-like polymer chains with aromatic polyamide structures that provide high tensile strength and heat resistance. Synthetic fibers such as nylon or polyester are composed of flexible, aliphatic or semi-aromatic polymers with less molecular orientation, resulting in lower thermal stability and impact resistance compared to aramid. The tightly bonded, crystalline regions in aramid fibers contribute to their superior durability and structural integrity, making them ideal for protective helmet applications.
Weight and Strength Comparison
Aramid fiber helmets offer superior strength-to-weight ratios, providing lightweight protection without compromising impact resistance. Synthetic fibers, such as nylon or polyester blends, generally have higher weight and lower tensile strength compared to aramid fibers like Kevlar. This makes aramid fiber the preferred choice for helmets requiring maximum durability and minimal weight.
Impact Resistance Analysis
Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar, offers superior impact resistance in helmets due to its high tensile strength and energy-absorbing molecular structure, effectively dispersing shock forces upon impact. Synthetic fibers like polyester or nylon provide some durability but generally lack the exceptional toughness and heat resistance found in aramid fibers, resulting in lower performance under extreme impact conditions. Extensive impact resistance testing confirms that helmets reinforced with aramid fibers exhibit significantly higher protection levels, making them a preferred choice for advanced safety equipment.
Thermal and Flame Resistance
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, exhibit exceptional thermal and flame resistance, withstanding temperatures up to 370degC without degrading, making them ideal for protective helmets in high-heat environments. Synthetic fibers like nylon and polyester have significantly lower melting points, typically around 220degC and 260degC respectively, which limits their effectiveness against extreme heat and flame exposure. The superior thermal stability and flame-resistant properties of aramid fibers enhance helmet durability and provide critical protection for users in fire-prone or high-temperature conditions.
Durability and Longevity
Aramid fiber, known for its exceptional tensile strength and heat resistance, offers superior durability and longevity in helmet construction compared to synthetic fibers like nylon or polyester. Helmets made from aramid fiber provide enhanced impact resistance and maintain structural integrity over time, ensuring prolonged protection. Synthetic fibers tend to degrade faster under UV exposure and wear, leading to reduced helmet lifespan.
Comfort and Wearability in Helmets
Aramid fiber offers superior impact resistance and heat durability, making helmets lightweight yet strong, which enhances wearer comfort during prolonged use. Synthetic fibers like nylon and polyester provide flexibility and moisture-wicking properties, improving breathability and reducing perspiration inside the helmet. Combining aramid fiber with synthetic liners often results in helmets with optimal wearability, balancing protection and comfort for diverse conditions.
Cost and Market Availability
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, offer superior strength and impact resistance for helmet manufacturing but come with higher production costs, limiting their use to premium or military-grade helmets. Synthetic fibers like nylon and polyester are more cost-effective and widely available, making them common in commercial and recreational helmets. Market availability favors synthetic fibers due to easier sourcing and lower prices, while aramid fibers remain niche due to their specialized applications and expense.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Aramid fibers, made from synthetic polymers like Kevlar, offer high durability and strength while being less recyclable, leading to more environmental waste in helmet manufacturing. Synthetic fibers such as polyester and nylon are derived from petrochemicals, contributing significantly to carbon emissions and non-biodegradability, which poses sustainability challenges in helmet production. Choosing aramid fibers over other synthetic fibers can reduce helmet weight and improve impact resistance, but neither option currently offers a fully sustainable lifecycle, highlighting the need for innovation in eco-friendly materials.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Helmet Applications
Aramid fiber offers exceptional tensile strength, heat resistance, and impact absorption, making it ideal for high-performance helmet applications requiring superior protection and durability. Synthetic fibers such as polyethylene (UHMWPE) provide lightweight, flexible, and cost-effective solutions with good impact resistance but generally lower thermal stability compared to aramid. Selecting the right fiber depends on balancing factors like weight, protective capabilities, environmental exposure, and budget constraints to optimize helmet safety and performance.
Infographic: Aramid fiber vs Synthetic fiber for Helmet
 azmater.com
azmater.com