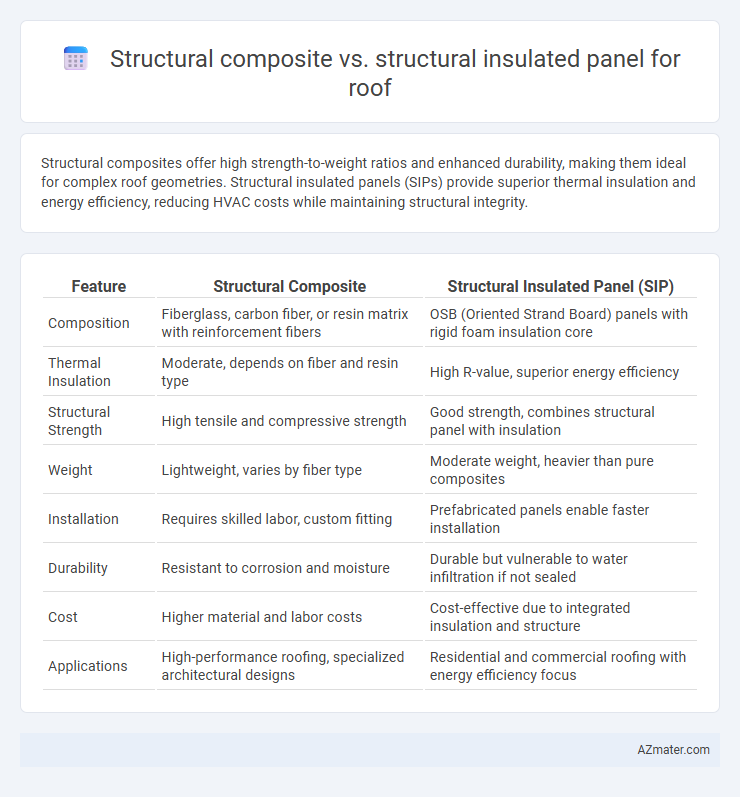
Structural composites offer high strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced durability, making them ideal for complex roof geometries. Structural insulated panels (SIPs) provide superior thermal insulation and energy efficiency, reducing HVAC costs while maintaining structural integrity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Structural Composite | Structural Insulated Panel (SIP) |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Fiberglass, carbon fiber, or resin matrix with reinforcement fibers | OSB (Oriented Strand Board) panels with rigid foam insulation core |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate, depends on fiber and resin type | High R-value, superior energy efficiency |
| Structural Strength | High tensile and compressive strength | Good strength, combines structural panel with insulation |
| Weight | Lightweight, varies by fiber type | Moderate weight, heavier than pure composites |
| Installation | Requires skilled labor, custom fitting | Prefabricated panels enable faster installation |
| Durability | Resistant to corrosion and moisture | Durable but vulnerable to water infiltration if not sealed |
| Cost | Higher material and labor costs | Cost-effective due to integrated insulation and structure |
| Applications | High-performance roofing, specialized architectural designs | Residential and commercial roofing with energy efficiency focus |
Introduction to Structural Roof Systems
Structural composite panels and structural insulated panels (SIPs) are advanced systems used in modern roofing to enhance strength and energy efficiency. Structural composite panels combine wood strands with adhesives for a durable load-bearing surface, while SIPs consist of rigid foam insulation sandwiched between engineered wood facings, offering superior thermal performance and structural integrity. These roof systems optimize building envelope performance, reduce construction time, and improve overall energy savings.
Overview of Structural Composites
Structural composites for roofing combine multiple materials such as wood fibers, resins, and adhesives to create panels with high strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced durability. These composites offer superior load-bearing capacity and resistance to environmental factors compared to traditional materials, making them ideal for various roof designs. Their adaptability supports complex architectural requirements while providing thermal insulation and improved energy efficiency.
What Are Structural Insulated Panels (SIPs)?
Structural Insulated Panels (SIPs) are high-performance building panels used for roofs, walls, and floors, consisting of an insulating foam core sandwiched between two structural facings, typically oriented strand board (OSB). SIPs provide superior thermal insulation, air tightness, and structural strength compared to traditional structural composites, resulting in enhanced energy efficiency and faster construction times. Their integrated design reduces thermal bridging, making SIPs a preferred choice for sustainable roofing solutions.
Comparative Thermal Performance
Structural insulated panels (SIPs) typically offer superior thermal performance compared to traditional structural composites due to their continuous insulation layer, which minimizes thermal bridging and air infiltration. SIPs commonly achieve R-values between 14 and 28 for roofing applications, significantly enhancing energy efficiency and reducing heating and cooling costs. Structural composites, while strong and versatile, usually provide lower insulation values unless combined with additional insulation materials, making SIPs a preferred choice for optimized thermal performance in roofs.
Load-Bearing Capabilities
Structural composites offer high load-bearing capabilities due to their layered construction of materials like plywood and fiberglass, providing excellent strength-to-weight ratios ideal for heavy roof loads. Structural insulated panels (SIPs) incorporate an insulating foam core sandwiched between oriented strand boards (OSB), delivering superior thermal performance while maintaining sufficient structural integrity for typical residential and light commercial roof loads. For roofs requiring exceptional load-bearing strength, structural composites generally outperform SIPs, although SIPs provide a balanced approach combining moderate strength with energy efficiency.
Installation Speed and Complexity
Structural insulated panels (SIPs) offer faster installation speeds compared to traditional structural composites due to their prefabricated nature, reducing on-site labor and assembly time. Structural composites require more complex handling and fastening processes because they involve multiple layers and materials assembled on-site, increasing installation complexity. SIPs simplify alignment and attachment, making them ideal for efficient roof construction with fewer installation errors.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Structural composites exhibit exceptional durability due to their high strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to warping, making them ideal for long-lasting roof applications. Structural insulated panels (SIPs) offer superior weather resistance with continuous insulation and airtight construction, effectively minimizing thermal bridging and moisture infiltration. Both materials provide robust performance, but SIPs enhance energy efficiency and weatherproofing, while structural composites excel in mechanical strength and impact resistance.
Fire and Pest Resistance
Structural composite materials used in roofing, such as laminated veneer lumber or glulam, offer enhanced fire resistance due to their dense wood fibers and fire-retardant treatments, reducing ignition risk and slowing flame spread. Structural insulated panels (SIPs), comprised of oriented strand board (OSB) facings with foam insulation cores, provide excellent pest resistance when treated for termites and rodents, but the foam core can be vulnerable without proper insect barriers and fire retardants. Fire resistance in SIPs depends significantly on the type of foam used, with materials like mineral wool cores offering superior fire performance compared to standard EPS or polyiso foams, while structural composites inherently resist pests due to dense wood construction and preservatives.
Cost Comparison and Lifecycle Analysis
Structural composites typically have a higher initial cost compared to structural insulated panels (SIPs) due to advanced materials and manufacturing processes. Over the lifecycle, SIPs offer better energy efficiency and reduced maintenance costs, resulting in lower total cost of ownership. Cost-effectiveness of each depends on project scale, insulation requirements, and long-term performance priorities.
Choosing the Right Roofing Solution
Structural composite panels provide enhanced load-bearing capacity and superior durability, making them ideal for complex roof designs requiring high strength and longevity. Structural insulated panels (SIPs) offer excellent thermal performance and airtightness, reducing energy costs and improving insulation efficiency in residential and commercial roofing applications. Selecting the right roofing solution depends on balancing structural requirements with insulation needs, where structural composites excel in strength and SIPs in energy efficiency.
Infographic: Structural composite vs Structural insulated panel for Roof
 azmater.com
azmater.com