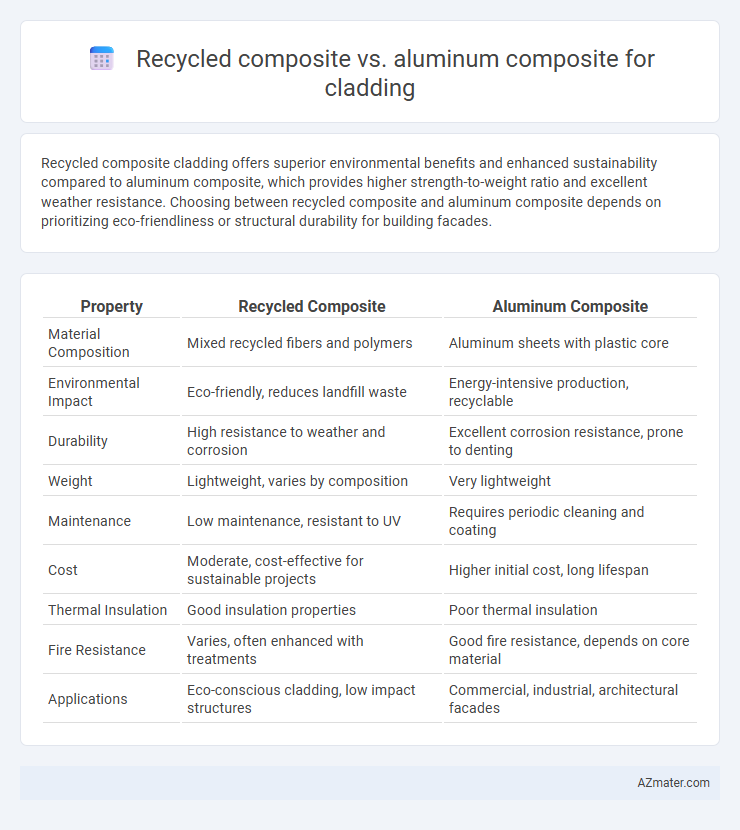
Recycled composite cladding offers superior environmental benefits and enhanced sustainability compared to aluminum composite, which provides higher strength-to-weight ratio and excellent weather resistance. Choosing between recycled composite and aluminum composite depends on prioritizing eco-friendliness or structural durability for building facades.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Recycled Composite | Aluminum Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Mixed recycled fibers and polymers | Aluminum sheets with plastic core |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, reduces landfill waste | Energy-intensive production, recyclable |
| Durability | High resistance to weather and corrosion | Excellent corrosion resistance, prone to denting |
| Weight | Lightweight, varies by composition | Very lightweight |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, resistant to UV | Requires periodic cleaning and coating |
| Cost | Moderate, cost-effective for sustainable projects | Higher initial cost, long lifespan |
| Thermal Insulation | Good insulation properties | Poor thermal insulation |
| Fire Resistance | Varies, often enhanced with treatments | Good fire resistance, depends on core material |
| Applications | Eco-conscious cladding, low impact structures | Commercial, industrial, architectural facades |
Introduction to Cladding Materials
Recycled composite cladding offers an eco-friendly alternative to traditional aluminum composite panels, utilizing sustainable materials such as reclaimed plastics and wood fibers to reduce environmental impact. Aluminum composite materials provide high durability, lightweight properties, and excellent weather resistance, making them widely preferred in modern architectural designs. Both materials require consideration of factors like thermal performance, maintenance needs, and aesthetic versatility to ensure optimal building envelope protection and energy efficiency.
Overview of Recycled Composite Cladding
Recycled composite cladding offers a sustainable alternative made from reclaimed materials such as wood fibers and plastics, reducing environmental impact compared to traditional aluminum composite panels. This eco-friendly cladding provides durability, weather resistance, and thermal insulation, often with enhanced noise reduction properties. Manufacturers emphasize its low maintenance requirements and resistance to corrosion, making it suitable for both residential and commercial facades.
Overview of Aluminum Composite Cladding
Aluminum composite cladding consists of two thin aluminum sheets bonded to a non-aluminum core, offering durability, lightweight properties, and excellent weather resistance for building facades. This material provides superior fire resistance and a sleek, modern appearance, making it a preferred choice in commercial and residential construction. Compared to recycled composite cladding, aluminum composite panels are known for their ease of installation, structural strength, and extensive color and finish options.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Recycled composite cladding significantly reduces environmental impact by utilizing post-consumer materials, lowering landfill waste and decreasing reliance on virgin resources compared to aluminum composite panels. Aluminum composites require intensive energy consumption during extraction and production processes, contributing to higher carbon emissions and resource depletion. Choosing recycled composite materials enhances sustainability through improved lifecycle performance, reduced embodied energy, and better end-of-life recyclability.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Recycled composite cladding offers enhanced resistance to moisture, corrosion, and UV damage, resulting in a lifespan of up to 30 years, making it highly durable in various climates. Aluminum composite panels (ACP) provide excellent structural strength and are resistant to fire and weathering, typically lasting 20 to 25 years with proper maintenance. Both materials offer longevity benefits, but recycled composites tend to outperform aluminum composites in terms of moisture resistance and environmental sustainability.
Aesthetic Versatility and Design Options
Recycled composite cladding offers extensive aesthetic versatility with its wide range of colors, textures, and finishes that mimic natural materials like wood, stone, and metal, enhancing design creativity and environmental appeal. Aluminum composite panels provide sleek, modern looks with smooth surfaces and vibrant color options, enabling precise architectural shapes and high durability for intricate designs. Both materials support customized profiles and facades, but recycled composites deliver eco-friendly design flexibility, while aluminum excels in lightweight strength and long-lasting color stability.
Fire Resistance and Safety Considerations
Recycled composite panels for cladding demonstrate enhanced fire resistance due to lower combustibility and reduced toxic fume emission compared to traditional aluminum composite materials (ACMs). Aluminum composite cladding, particularly those with polyethylene cores, pose higher fire risks and have been linked to severe fire incidents, prompting stricter building regulations and the adoption of fire-retardant cores. Choosing recycled composite materials improves building safety, compliance with fire codes, and reduces environmental impact without compromising structural performance.
Installation Process and Complexity
Recycled composite cladding offers simpler installation due to its lightweight nature and flexibility, reducing labor time and the need for specialized tools compared to aluminum composite panels. Aluminum composite panels require precise measurement and cutting with specialized equipment, which increases installation complexity and potential for errors. Both materials demand skilled labor, but recycled composites generally allow for faster assembly and easier handling on-site.
Maintenance Requirements and Costs
Recycled composite cladding generally requires less maintenance than aluminum composite panels due to its resistance to corrosion, fading, and denting, resulting in lower long-term upkeep expenses. Aluminum composite cladding may incur higher maintenance costs from periodic cleaning to prevent oxidation and potential repainting over time. Choosing recycled composite can reduce lifecycle costs through enhanced durability and minimal maintenance interventions.
Market Trends and Future Prospects
Recycled composite cladding is gaining traction in the construction market due to its sustainability, cost-effectiveness, and increasing regulatory support for eco-friendly materials. Aluminum composite panels remain dominant, driven by their durability, lightweight characteristics, and high aesthetic appeal, with innovations focusing on enhanced fire resistance and recyclability. Market forecasts indicate a growing preference for recycled composites as green building certifications become more stringent, alongside ongoing advancements in aluminum composites to meet evolving architectural and environmental standards.
Infographic: Recycled composite vs Aluminum composite for Cladding
 azmater.com
azmater.com