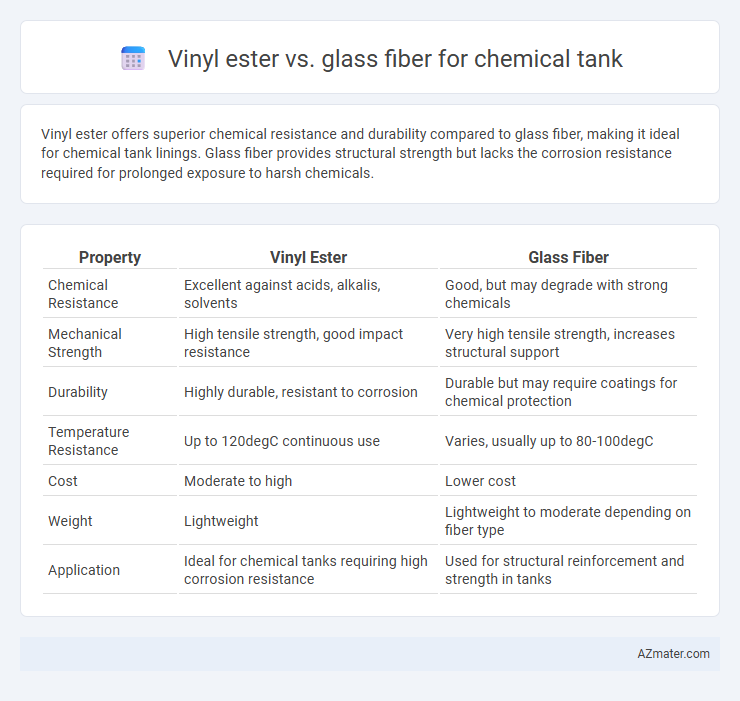
Vinyl ester offers superior chemical resistance and durability compared to glass fiber, making it ideal for chemical tank linings. Glass fiber provides structural strength but lacks the corrosion resistance required for prolonged exposure to harsh chemicals.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Vinyl Ester | Glass Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent against acids, alkalis, solvents | Good, but may degrade with strong chemicals |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength, good impact resistance | Very high tensile strength, increases structural support |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to corrosion | Durable but may require coatings for chemical protection |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 120degC continuous use | Varies, usually up to 80-100degC |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Lower cost |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight to moderate depending on fiber type |
| Application | Ideal for chemical tanks requiring high corrosion resistance | Used for structural reinforcement and strength in tanks |
Introduction: Chemical Tank Material Considerations
Vinyl ester resins represent a superior choice for chemical tanks due to their enhanced corrosion resistance and chemical stability compared to traditional polyester resins, ensuring durability in aggressive chemical environments. Glass fiber reinforcement provides exceptional mechanical strength and impact resistance, improving the tank's structural integrity under stress and pressure. Combining vinyl ester with glass fiber creates composite tanks that offer optimal resistance to chemical degradation while maintaining robust physical performance essential for industrial chemical storage.
Overview of Vinyl Ester Resins
Vinyl ester resins offer superior chemical resistance and excellent mechanical properties, making them ideal for use in chemical tanks exposed to aggressive environments. These resins provide enhanced corrosion resistance compared to standard polyester resins and exhibit strong adhesion to glass fibers, ensuring high durability and structural integrity. Vinyl ester-based tanks demonstrate excellent resistance to acids, alkalis, and solvents, extending service life and reducing maintenance in industrial applications.
Properties and Composition of Glass Fiber
Glass fiber, composed primarily of silica derived from sand, is characterized by its high tensile strength, excellent chemical resistance, and thermal stability, making it ideal for reinforcing chemical tanks. Vinyl ester resins provide superior corrosion resistance and toughness, while glass fiber offers structural integrity and durability through its fibrous network. The synergy between vinyl ester and glass fiber results in chemical tanks with enhanced mechanical strength and prolonged lifespan in aggressive chemical environments.
Chemical Resistance: Vinyl Ester vs. Glass Fiber
Vinyl ester resin offers superior chemical resistance compared to standard glass fiber composites, making it ideal for chemical tanks exposed to harsh solvents, acids, and alkalis. Glass fiber provides excellent mechanical strength and durability but requires a compatible resin like vinyl ester to ensure prolonged resistance against corrosive chemicals. Selecting vinyl ester as the matrix resin enhances the glass fiber tank's ability to withstand aggressive chemical environments, reducing maintenance and extending service life.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Vinyl ester resins exhibit superior chemical resistance and mechanical strength compared to standard glass fiber composites, making them highly suitable for chemical tank applications. The combination of vinyl ester with high-strength glass fibers enhances tensile strength and impact resistance, resulting in tanks capable of withstanding harsh chemical environments and mechanical stresses. Glass fiber composites alone may provide good structural integrity, but the integration with vinyl ester matrices significantly improves performance under corrosive conditions.
Durability and Corrosion Performance
Vinyl ester resins offer superior chemical resistance and durability compared to traditional glass fiber composites, making them ideal for chemical tank applications exposed to aggressive substances. The enhanced corrosion performance of vinyl ester reduces degradation from acids, bases, and solvents, significantly extending tank lifespan. Glass fiber reinforcement provides mechanical strength but relies heavily on the resin matrix for corrosion protection, where vinyl ester's molecular structure ensures better resilience in harsh chemical environments.
Cost Analysis and Lifecycle Value
Vinyl ester tanks offer superior chemical resistance and longer lifespan compared to glass fiber, making them cost-effective for highly corrosive environments despite higher upfront costs. Glass fiber tanks have lower initial costs and easier manufacturing processes but typically incur more frequent maintenance and replacement expenses. Evaluating lifecycle value, vinyl ester tanks present a better return on investment through reduced downtime and enhanced durability in aggressive chemical storage applications.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Vinyl ester tanks offer corrosion resistance and relatively straightforward installation due to their lighter weight and moldability, reducing labor time and costs compared to glass fiber tanks. Glass fiber tanks demand skilled labor for proper lamination and curing during installation, often requiring specialized equipment to ensure structural integrity. Maintenance for vinyl ester tanks is generally easier as their smooth surface resists chemical buildup, while glass fiber tanks might require routine inspection for fiber degradation and potential resin cracks to prevent leaks.
Industry Applications and Case Studies
Vinyl ester resins are widely used in chemical tank manufacturing due to their superior corrosion resistance and compatibility with aggressive chemicals, making them ideal for industries like wastewater treatment, chemical processing, and petrochemical storage. Glass fiber reinforcement enhances structural integrity and mechanical strength, providing excellent durability and impact resistance essential in harsh industrial environments. Case studies demonstrate that tanks constructed with vinyl ester and glass fiber composites outperform traditional materials in longevity and maintenance costs, particularly in industries handling acidic or saline substances.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Chemical Tanks
Vinyl ester resin offers superior chemical resistance and durability, making it ideal for tanks exposed to highly corrosive substances. Glass fiber reinforcement enhances structural strength and impact resistance, ensuring long-term stability and safety. Selecting the right material involves balancing chemical compatibility, mechanical performance, and cost to optimize tank longevity and reliability in specific chemical storage applications.
Infographic: Vinyl ester vs Glass fiber for Chemical tank
 azmater.com
azmater.com