Glass fiber offers excellent strength-to-weight ratio and cost-effectiveness for boat hulls, while basalt fiber provides superior thermal stability, higher impact resistance, and enhanced corrosion resistance, making it a durable alternative. Basalt fiber's eco-friendly properties and better mechanical performance often justify its higher price in marine applications.
Table of Comparison
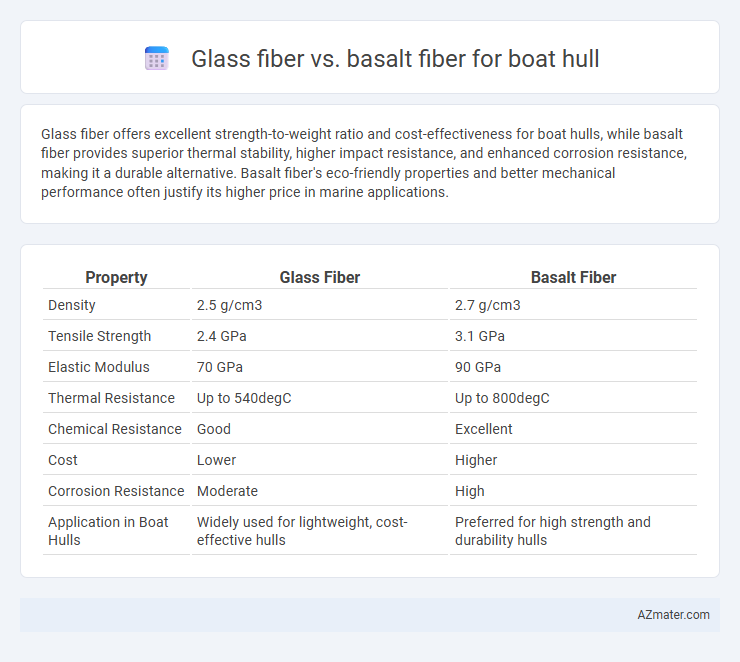
| Property | Glass Fiber | Basalt Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 2.5 g/cm3 | 2.7 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 2.4 GPa | 3.1 GPa |
| Elastic Modulus | 70 GPa | 90 GPa |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 540degC | Up to 800degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Application in Boat Hulls | Widely used for lightweight, cost-effective hulls | Preferred for high strength and durability hulls |
Introduction to Composite Fibers in Boat Building
Glass fiber and basalt fiber are prominent composite materials widely used in boat hull construction due to their high strength-to-weight ratios and corrosion resistance. Glass fiber offers excellent tensile strength and affordability, making it a standard choice in marine applications, while basalt fiber provides superior thermal stability, enhanced impact resistance, and better environmental sustainability. Both fibers contribute to lightweight, durable, and structurally sound boat hulls, with basalt fiber emerging as a promising alternative for performance-oriented and eco-friendly boat building.
What is Glass Fiber?
Glass fiber, also known as fiberglass, is a composite material made from fine strands of glass woven into a fabric and combined with a resin matrix, widely used for boat hulls due to its lightweight and high strength-to-weight ratio. It offers excellent resistance to corrosion, flexibility, and impact, making it a popular choice for marine applications. Compared to basalt fiber, glass fiber is more cost-effective and has a well-established supply chain, though basalt fiber provides higher thermal resistance and strength in certain conditions.
What is Basalt Fiber?
Basalt fiber is a natural volcanic rock-based material known for its superior thermal resistance, high tensile strength, and excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for boat hull construction. Compared to glass fiber, basalt fiber offers enhanced durability, better impact resistance, and improved environmental sustainability due to its natural origins and lower energy production processes. Its inherent chemical stability and resistance to seawater degradation provide longer-lasting performance in marine environments.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Glass fiber exhibits high tensile strength ranging from 2.4 to 3.5 GPa and a moderate modulus of elasticity around 70 GPa, making it a cost-effective choice for boat hull construction with good impact resistance. Basalt fiber offers superior mechanical properties, including tensile strength between 2.8 to 4.8 GPa and a higher modulus of elasticity approximately 89 GPa, providing enhanced stiffness and improved resistance to fatigue and environmental degradation. The increased durability and stiffness of basalt fiber contribute to better performance under stress and longer service life in marine environments compared to traditional glass fiber composites.
Corrosion and Chemical Resistance
Basalt fiber exhibits superior corrosion and chemical resistance compared to glass fiber, making it highly suitable for boat hull applications exposed to harsh marine environments. Its natural composition allows it to withstand acidic and alkaline conditions without degradation, unlike glass fiber which can suffer from alkali attack over time. This enhanced durability of basalt fiber ensures longer service life and reduced maintenance for boat hulls in corrosive water conditions.
Weight and Density Differences
Glass fiber typically has a density of around 2.5 g/cm3, whereas basalt fiber ranges from 2.6 to 2.7 g/cm3, making basalt fiber slightly heavier. In boat hull construction, the higher density of basalt fiber results in increased weight but offers superior strength and durability compared to glass fiber. Choosing between the two depends on the desired balance between weight savings and enhanced mechanical properties for optimal hull performance.
Cost Analysis: Glass Fiber vs Basalt Fiber
Glass fiber remains the more cost-effective option for boat hull construction, with its lower raw material and manufacturing expenses compared to basalt fiber. Basalt fiber, though pricier due to its natural volcanic rock source and energy-intensive production, offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. The initial higher investment in basalt fiber may be offset by reduced maintenance and longer lifespan, but glass fiber dominates in upfront cost efficiency.
Durability and Longevity in Marine Environments
Basalt fiber exhibits superior durability and longevity compared to glass fiber when used in boat hulls due to its higher resistance to chemical corrosion, UV exposure, and saltwater degradation in marine environments. Glass fiber is prone to water absorption and eventual weakening, whereas basalt fiber maintains structural integrity and mechanical strength over extended periods. This enhanced resistance makes basalt fiber a more sustainable choice for marine applications, offering prolonged service life and reduced maintenance costs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Basalt fiber exhibits superior environmental benefits over glass fiber, as it is derived from natural volcanic rock without requiring energy-intensive melting processes uncommon in glass fiber production. The sustainability of basalt fiber is enhanced by its recyclability and non-toxic nature, reducing hazardous waste disposal compared to glass fiber composites. Moreover, basalt fiber's lower carbon footprint and biodegradability potential make it a more eco-friendly option for boat hull construction, aligning with sustainable marine industry goals.
Final Recommendations for Boat Hull Material
Basalt fiber offers superior strength, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability compared to glass fiber, making it a more durable choice for boat hulls exposed to harsh marine environments. Glass fiber remains cost-effective and widely available, suitable for standard recreational boats where budget constraints exist. For high-performance or commercial vessels requiring enhanced longevity and resilience, basalt fiber is recommended due to its improved mechanical properties and environmental resistance.
Infographic: Glass fiber vs Basalt fiber for Boat hull
 azmater.com
azmater.com